Summary
The first part of this review describes the chemistry, the occurrence and the metabolism of extracellular connective tissue components in the liver. The normal liver contains typical connective tissue proteins (collagens, structural glycoproteins and proteoglycans) not only in vessel walls, perivascular areas and in the capsule, but they occur also in small amounts in the parenchyma, mainly in the space of Disse along the sinusoidal walls.
The “interstitial” collagens type I and III represent the major amount of collagen in the normal as well as in the fibrotic liver, showing a relative increase of type III in fibrosis. Basement membrane collagens type IV and V as well as the cysteine-rich collagenous components “7 S collagen” and “short chain collagen” have been shown to occur in extracts prepared after limited pepsin digestion. In the normal liver, basement membrane collagen can hardly be detected within the parenchyma by immunofluorescence microscopy; increased occurrence, however, can be shown along the sinusoids even in early stages of chronic liver diseases.
The glycoprotein fibronectin was shown to be distributed very similarly to collagens type I and III, whereas the basement membrane specific glycoprotein laminin is restricted to vessel walls and the epithelial layer of bile ductuli in the normal liver but is also found in the parenchyma in fibrosis.
Occurrence of proteoglycans is increased in fibrosis: a change in the composition of glycosaminoglycans from mainly heparan sulfate in the normal to dermatan- and chondroitin sulfate in the fibrotic liver was observed.
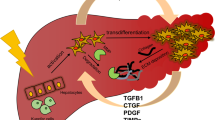
It is not yet clear which cell type is mainly responsible for increased connective tissue synthesis in fibrosis. The occurrence of cells resembling smooth muscle cells (“myofibroblasts”) in connective tissue septa of fibrotic livers and the fact that similar cells which actively synthesize collagen grow from explants of fibrotic livers may indicate the significance of this cell type in the process of liver fibrosis.
Zusammenfassung
Im ersten Teil dieser Übersicht werden die Chemie, das Vorkommen im Gewebe und der Stoffwechsel bindegewebstypischer extrazellulärer Komponenten in der Leber beschrieben. Die normale Leber enthält Proteine des Bindegewebes (Kollagene, Struktur-Glykoproteine, Proteoglykane) nicht nur in den Gefäßwänden, den perivasculären Bereichen und in der Kapsel, sondern sie sind auch im Parenchym in geringer Menge, vor allem im Disse'schen Raum entlang den Sinusoiden nachweisbar.
Die „interstitiellen“ Kollagentypen I und III bilden die Hauptmenge des Kollagens sowohl in der normalen als auch in der fibrotischen Leber; dabei ist der relative Anteil an Typ III in der fibrotischen gegenüber der normalen Leber erhöht. Die „Basalmembrankollagene“ Type IV und V sowie die cysteinreichen kollagenen Komponenten 7 S und das Kurzkettenkollagen (Intimenkollagen) konnten aus nach limitiertem Pepsinabbau gewonnenen Extrakten isoliert werden. In der normalen Leber sind die Basalmembrankollagene im Parenchym immunhistologisch kaum nachzuweisen; ein verstärktes Auftreten entlang der Sinusoide ist jedoch schon in frühen Stadien chronischer Lebererkrankungen sichtbar.
Das extrazelluläre Glykoprotein Fibronectin tritt in der Leber in einer dem Typ I und III Kollagen sehr ähnlichen Verteilung auf, während das basalmembranspezifische Glykoprotein Laminin in der nicht-fibrotischen Leber auf Gefäßwände und Gallengangepithelien beschränkt ist und erst bei Fibrose auch in parenchymalen Bereichen nachgewiesen werden kann.
Proteoglykane treten in der fibrotischen Leber ebenfalls vermehrt auf, eine Veränderung der Zusammensetzung der Glykosaminoglykane von überwiegend Heparansulfat in der normalen zu Dermatan-und Chondroitinsulfat in der fibrotischen Leber wurde beobachtet.
Unklarheit besteht noch über den Zelltyp, der hauptsächlich zur vermehrten Bindegewebsbildung in der Leber beiträgt. Vermehrtes Auftreten von Zellen, die glatten Muskelzellen ähneln (Myofibroblasten) in den Septen fibrotischer Lebern und der Befund, daß aus Explantaten fibrotischer Lebern hauptsächlich ähnliche Zellen auswachsen, die eine aktive Kollagensynthese zeigen, können auf die Bedeutung dieses Zelltyps für die Fibrose hindeuten.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson JC (1976) Glycoproteins of the connective tissue matrix. In: Hall DA, Jackson DS (ed) International review of connective tissue research. Academic Press, New York (vol 7, pp 251–330)
Alitalo K, Hovi T, Vaheri A (1980) Fibronectin is produced by human macrophages. J Exp Med 151:602–613
Becker K (1969) Untersuchungen zur chemischen Beschaffenheit des Bindegewebes der Leberzirrhose. Z Ges Exp Med Exp Chir 151:1–9
Bentz H, Bächinger H-P, Glanville R, Kühn K (1978) Physical evidence for the assembly of A and B chains of human placental collagen in a single triplehelix. Eur J Biochem 92:563–567
Biempica L, Morecki R, Wu CH, Giambrone MA, Rojkind M (1980) Immuno cytochemical localization of type B Collagen. A component of Am J Pathol 98:591–597
Bornstein P (1974) The biosynthesis of collagen. Ann Rev Biochem 43:567–603
Bornstein P, Traub W (1979) The chemistry and biology of collagen. In: Neurath H, Hill RL (ed) The proteins. Academic Press, New York, pp 412–605
Boxer PA, Leibovich SJ (1976) Production of collagenase by mouse peritoneal macrophages in vitro. Characterization of sites of cleavage of tropocollagen. Biochem Biophys Acta 444:626–632
Chung E, Rhodes RK, Miller EJ (1976) Isolation of three collagenous components of probable basement membrane origin from several tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 71:1167–1174
Church RL, Tanzer ML, Pfeiffer SE (1973) Collagen and procollagen production by a clonal line of Schwann cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 70:1943–1946
Dessau W, Adelmann BC, Timpl R, Martin GR (1978) Identification of the sites in collagen α-chains that bind serum antigelatin factor (cold-insoluble globulin). Biochem J 169:55–59
Dixit SN (1979) Isolation and characterization of two α-chain size collagenous polypeptide chains C and D from glomerular basement membrane. FEBS 106:379–384
Eisen AZ, Bauer EA, Jeffrey JJ (1970) Animal and human collagenases. J Invest Dermatol 55:359–373
Epstein DH, Munderloh NH (1975) Isolation and characterization of CNBr peptides of human [α1 (III)]3 collagen and tissue distribution of [α1 (I)]2 α2 and (α1 (III))3 collagens. J Biol Chem 250:9304–9312
Fessler JH, Fessler LI (1978) Biosynthesis of procollagen. Ann Rev Biochem 47:129–162
Fietzek PP, Kühn K (1976) The primary structure of collagen. Int Rev Connect Tiss Res 7:1–39
Furuto DK, Miller EJ (1980) Isolation of a unique collagenous fraction from limited pepsin digest of human placental tissue. J Biol Chem 255:290–295
Galambos JT, Hollingsworth MA, Falek A (1977) Rate of synthesis of glycosaminoglycans and collagen by fibroblasts cultured from adult human liver biopsies. J Clin Invest 60:107–114
Galambos JT, Shapira R (1973) Natural history of alcoholic hepatitis IV: Glycosaminoglycans and collagen in hepatic connective tissue. J Clin Invest 60:107–111
Gay S, Fietzek PP, Remberger K, Eder M, Kühn K (1975) Liver cirrhosis: Immunfluorscence and biochemical studies demonstrate two types of collagen. Klin Wochenschr 53:205–208
Gay S, Miller EJ (1978) Collagen in the physiology and pathology of connective tissue. G Fischer, Stuttgart
Glanville RW, Rauter A, Fietzek PP (1979) Isolation and characterization of a native placental basement-membrane collagen and its component α-chains. Eur J Biochem 95:383–389
Gnädiger MC, Schwager-Hübner ME (1976) Kollagen und Mucopolysaccharidsynthese durch Hornhautzellen des Kaninchens in vitro. Opthalmologie 172:84–89
Grant ME, Jackson DS (1976) The biosynthesis of procollagen. Essays Biochem 12:77–113
Grant ME, Prockop DJ (1972) Biosynthesis of collagen. N Engl J Med 286:194–199; 242–249; 291–300
Gressner AM (1980) Zur Pathobiochemie und klinisch-chemischen Diagnostik der Leberfibrose. Med Welt 31:11–16
Grimaud JA, Druguet M, Peyrol S, Chevalier O, Herbage D, El Bradawy N (1980) Collagen immunotyping in human liver. Light and electron microscope study. J Histochem Cytochem 28:1145–1156
Grinell F, Minter D (1978) Attachment and spreading of baby hamster kidney cells to collagen substrate effects of cold-insoluble globulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 75:4408–4412
Gross J (1976) Aspects of animal collagenases. In: Ramachandran GN, Reddi AH (eds) Biochemistry of collagen. Plenum Press, New York, pp 275–317
Hahn E, Wick G, Pencev D, Timpl R (1980) Distribution of basement membrane proteins in normal and fibrotic human liver: collagen type IV, laminin and fibronectin. Gut 21:63–71
Hascall VC (1977) Interaction of cartilage proteoglycans with hyaluronic acid. J Supramol Struct 7:101–120
Harper E (1980) Collagenases. Ann Rev Biochem 49:1063–1078
Harris ED, Krane SM (1974) Collagenases. N Engl J Med 291:557–563; 605–612; 652–659
Hata RJ, Ninomiya Y, Tsaukada Y, Nagai Y (1980) Biosynthesis of interstitial types of collagen by albumin producing rat liver parenchymal cell (hepatocytes) clones in culture. Biochemistry 19:169–176
Jander R, Rauterberg J, Voss B, Bassewitz DB von (1981) A cysteine-rich collagenous component from bovine placenta. Isolation of its constituent polypeptide chains and some properties of the non-denatured protein. Eur J Biochem 114:17–25
Johansson S, Rubin K, Höök M, Ahlgren T, Seljelid R (1979) In vitro biosynthesis of cold insoluble globulin (fibronectin) by mouse peritoneal macrophages. FEBS Lett 105:313–316
Kefalides NA (1973) Structure and biosynthesis of basement membranes. Int Rev Connect Tiss Res 6:63–104
Kent G, Gay S, Inouye T, Bahne R, Minick OT, Popper H (1976) Vitamin-A-containing lipocytes and formation of type III collagen in liver injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 73:3719–3722
Kivirikko KJ, Risteli L (1976) Biosynthesis of collagen and its alterations in pathological states. Med Biol 54:159–186
Koizuma T, Nakamura N, Abe H (1967) Changes in acid mucopolysacharide in the liver in hepatic fibrosis. Biochim Biophys Acta 148:749–756
Kresina TF, Miller EJ (1979) Isolation and characterization of basement membrane collagen from human placental tissue. Evidence for the presence of two genetically distinct collagen chains. Biochemistry 18:3089–3097
Lazarus GS, Hatcher VB, Levine N (1975) Lysosomes and the skin. Invest Dermatol 265:259–271
Linder E, Stenman S, Lehto VP, Vaheri A (1978) Distribution of fibronectin in human tissues and relationship to other connective tissue components. Ann NY Acad Sci 312:151–159
Mathews MB (1975) Connective tissue. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
McMurtrey J, Radhakrishnamurthi B, Dalferes ER, Berenson GS, Gregora JD (1979) Isolation of proteoglycan-hyaluronate complexes from bovinc aorta. J Biol Chem 254:1621–1626
Meier S, Hay ED (1973) Synthesis of sulfated glycosaminoglycans by embryonic corneal epithelium. Develop Biol 35:318–331
Miller EJ (1976) Biochemical characteristics and biological significance of the genetic distinct collagens. Mol Cell Biochem 13:165–192
Mosesson MW (1977) Cold-insoluble globulin (CIG), a circulating cell surface protein. Thromb Haemost 38:742–750
Munthe-Kaas AC, Berg T, Seljelid R (1975) Mass isolation and culture of rat kupffer cells. J Exp Med 141:1–10
Oegema TR, Hascall VC, Eisenstein R (1979) Characterization of bovine aorta proteoglycan extracted with guanidine hydrochloride in the presence of protease inhibitors. J Biol Chem 254:1312–1318
Ott U, Hahn E, Moshudis E, Bode JC, Martini GA (1977) Immunhistologischer Nachweis von Type I- und Typ III-Kollagen in Leberbiopsien: Frühe und späte Veränderungen bei alkoholischer Lebererkrankung. Verhandl Dtsch Ges Inn Med 83:537–540
Popper H (1978) Die Leberfibrose. — Entstehung, Dynamik und klinische Bedeutung. Leber Magen Darm 8:65–72
Popper H, Becker K (eds) (1975) Collagen metabolism in the liver. Grune and Stratton, New York
Popper H, Piez K (1978) Collagen metabolism in the liver. Digest Dis 23:641–659
Pott G, Rauterberg J, Voss B, Allam S, Brehmer U, Liehr H, Gerlach U (1980) Connective tissue metabolism and lysosomal glycosidases in nonparenchymal cells from normal and fibrotic human livers and from livers of galactosamine-treated rats. In: Liehr H, Grün M (eds) The reticuloendothelial system and the pathogenesis of liver disease. Elsevier/North-Holland, Biochemical Press, Amsterdam, pp 205–210
Prockop DJ, Kivirikko KI, Tuderman L, Geezman NA (1979) The biosynthesis of collagen and its disorders. N Engl J Med 301:13–23 and 77–85
Quaroni A, Isselbacher KJ, Ruoslahti E (1978) Fibronectin synthesis by epithelial crypt cells of rat small intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 75:5548–5552
Ramachandran GN, Reddi AH (eds) (1976) Biochemistry of collagen. Plenum Press, New York
Rauterberg J, Allam SS (1977) Occurrence of type I and III collagen in normal and atherosclerotic human aortas. In: Schettler G, Goto Y, Hata Y, Klose G (eds) Atherosclerosis IV. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 368
Rhodes RK, Miller EJ (1978) Physicochemical characterization and molecular organization of the collagen A and B chains. Biochemistry 17:3442–3448
Roden L (1980) Structure and metabolism of connective tissue proteoglycans. In: Lennarz, WJ (ed) The biochemistry of glacoproteins and proteoglycans. Plenum Press, New York London, pp 267–371
Rojkind M, Martinez-Palomo A (1976) Increase in type I and type III collagens in human alcoholic liver cirrhosis. Proc Natl AcaD Sci USA 73:539–543
Rojkind M, Dunn MA (1979) Hepatic fibrosis. Gastroenterology 76:849–863
Rojkind M, Giambrone M-A, Biempica L (1979) Collagen types in normal and cirrhotic liver. Gastroenterology 76:710–719
Ross R, Bornstein P (1969) The elastic fiber I. The separation and partial characterization of its macromolecular components. J Cell Biol 40:366–381
Rubin K, Oldberg A, Höök M, Öbrink B (1978) Adhesion of rat hepatocytes to collagen. Exp Cell Res 117:165–177
Rudolph R, McClure WJ, Woodward M (1979) Contractile fibroblasts in chronic alcoholic cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 76:704–709
Sage H, Bornstein P (1979) Characterization of a novel collagen chain in human placenta and its relation to AB-collagen. Biochemistry 18:3815–3822
Sakakibara K, Saito M, Umeda M, Enaka K, Tsukada Y (1976) Native collagen formation by liver parenchymal cells in culture. Nature 262:316–318
Schaffner F, Popper H (1963) Capillarization of hepatic sinosoids in man. Gastroenterology 44:239–242
Scott PG, Pearson CH (1978) Cathepsin-D-cleavage of soluble collagen and crosslinked peptides. FEBS Lett 88:41–45
Seglen PO (1976) Preparation of isolated rat liver cells. In: Prescott D (ed) Methods in cell biology. Academic Press, New York London (vol XIII, pp 29–83)
Seyer JM, Hutcheson ET, Kang AH (1977) Collager polymorphism in normal and cirrhotic human liver. J Clin Invest 59:241–248
Steven FS (1972) Current concepts of collagen structure. Clin Orthop Rel Res 85:257–274
Takeichi M (1977) Functional correlation between cell adhesive properties and some cell surface proteins. J Cell Biol 75:464–474
Timpl R (1977) Struktur, Biosynthese und Immunologie des Kollagens. Med Zeit 1:119–126
Timpl R, Rohde H, Robey PG, Rennard SI, Foidart I-M, Martin GR (1979) Laminin — a glycoprotein from basement membrane. J Biol Chem 254:9933–9937
Traub W, Piez KA (1971) The chemistry and structure of collagen. Adv Prot Chem 25:243–352
Trelstad RL, Coulombre AJ (1971) Morphogenesis of the collagenous stroma in the chick cornea. J Cell Biol 50:840–858
Trelstad RL, Lawley KR (1977) Isolation and initial characterization of human basement membrane collagens. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 76:376–384
Vaheri A, Ruoslahti E (1975) Fibroblast surface antigen produced but not retained by virus-transformed human cells. J Exp Med 142:530–535
Vaheri A, Mosher DF (1978) High-molecular weight, cell surface-associated glycoprotein (fibronectin) lost in malignant transformation. Biochem Biophys Acta 516:1–25
Voss B, Allam S, Rauterberg J, Ullrich K, Gieselmann V, Figura K von (1979) Primary cultures of rat hepatocytes synthesize fibronectin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 90:1348–1354
Voss B, Rauterberg J, Allam S, Pott G, (1980) Distribution of collagen type I and type III and of two collagenous components of basement membranes in the human liver. Pathol Res Pract 170:50–60
Wahl LM, Wahl SM, Mergenhagen E, Martin GR (1974) Collagenase production by endotoxin-activated macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 71:3598–3601
Wahl LM, Wahl SM, Mergenhagen SE, Martin GR (1975) Collagenase production by lymphokine-activated macrophages. Science 187:261–262
Weber L, Meigel WN, Rauterberg J (1977) SDS-Polyacrylamide gel electrophoretic determination of type I and type III collagen in small skin samples. Arch Dermatol Res 258:251–257
Weiss JB (1976) Enzymic degradation of collagen. Int Rev Connect Tiss Res 7:101–157
Woolley DE, Evanson JM (eds) (1980) Collagenase in normal and pathological connective tissues. Wiley and Sons
Zimmermann BK, Pikkarainen J, Fietzek PP, Kühn K (1970) Cross-linkages in collagen. Demonstration of three different intermolecular bonds. Eur. J Biochem 16:217–225
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (Grants Ra 255/4 and SFB 104/A4
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rauterberg, J., Voss, B., Pott, G. et al. Connective tissue components of the normal and fibrotic liver. Klin Wochenschr 59, 767–779 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01724682
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01724682