Summary
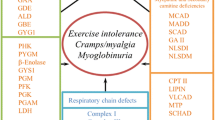
A muscular syndrome has been described in patients on clofibrate and fenofibrate therapy. The present paper describes four patients with impaired renal function in whom symptoms and signs of skeletal muscle damage developed during treatment with another clofibrinic acid derivative, bezafibrate. The syndrome was characterized by variable degrees of muscular cramps and paresis, excessive elevation of muscle enzymes in serum, myoglobinemia and myoglobinuria. Transient deterioration of renal function was also common. All patients had been overdosed with bezafibrate with regard to their renal function. It is concluded that bezafibrate like other lipid lowering agents of the clofibrate type may induce muscle damage, at least if doses are not adjusted to renal function. Extreme caution is warranted when treating patients with renal impairment with bezafibrate and strict dose adjustment to kidney function is necessary to avoid muscle damage.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Abshagen U, Kösters W, Kaufmann B, Lang PD (1980) Pharmacokinetics of bezafibrate after single and multiple doses in the presence of renal failure. Klin Wochenschr 58:889–896
Bridgman JF, Rosen SM, Thorp JM (1972) Complications during clofibrate treatment of nephrotic syndrome hyperlipoproteinaemia. Lancet: 2:506–509
Denizot M, Fabre J, Pometta J, Wildi E (1973) Clofibrate, nephrotic syndrome, and histological changes in muscle. Lancet 1:1326
Dosa S, Mallick NP, Slotki IN (1976) Acute — on — chronic renal failure precipitated by clofibrate. Lancet 1:250
Giraud P, Cassou M, Paul R, Guidet M (1982) Toxicité musculaire due au fénofibrate. A propos d'un cas. Rev Rhumat Malad Ostéo-Artic 49:162
Heidemann H, Bock KD, Kreuzfelder E (1981) Rhabdomyolysis with acute renal failure due to bezafibrate. Klin Wochenschr 59:413–414
Kaiser H, Spaar U, Sold G, Wolfrum DI, Kreuzer H (1979) Radioimmunologische Bestimmung von Humanmyoglobin in der Diagnostik des akuten Myokardinfarktes. Klin Wochenschr 57:225–235
Langer T, Levy RI (1968) Acute muscular syndrome associated with administration of clofibrate. New Engl J Med 279:856–858
Munk ZM, Nantel A (1977) Acute lindane poisoning with development of muscle necrosis. Canad Med Assoc J 117:1050–1054
Pierides AM, Alvarez-Ude F, Kerr DNS (1975) Clofibrate-induced muscle damage in patients with chronic renal failure. Lancet 2:1279–1282
Rumpf KW, Albers R, Scheler F (1976) Clofibrate-induced myopathy syndrome. Lancet 1:249–250
Rumpf KW, Quellhorst E, Scheler F (1976) Diabetisches Spätsyndrom, Hypothyreose und clofibratinduziertes Muskelsyndrom. Med Klin 71:2023–2027
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rumpf, K.W., Barth, M., Blech, M. et al. Bezafibrat-induzierte Myolyse und Myoglobinurie bei Patienten mit eingeschränkter Nierenfunktion. Klin Wochenschr 62, 346–348 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01716252
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01716252