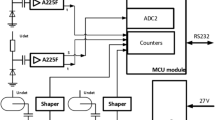
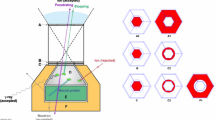
Summary
The results of dosimetric measurements are presented which were performed as part of a German experiment package flown onboard the Russian space station MIR. These results are compared to those of previous missions: the first United States Spacelab mission and the first German Spacelab mission. Detector packages consisting of plastic nuclear track detectors, nuclear emulsions, and thermoluminescence dosimeters were exposed in different sections of the Russian space station. The equivalent dose for the astronauts was calculated from the measurements to be 3.9 mSv. Before and after the flight venous blood was taken from the astronauts. Chromosomal aberrations in peripheral lymphocytes were analyzed. It was found that the radiation exposure during the spaceflight leads to an elevation of dicentric chromosomes, indicating a radiation burden of the astronauts.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- D1:
-
first German Spacelab mission
- LET:
-
linear energy transfer
- SL1:
-
first US Spacelab mission
- TLD:
-
thermoluminescence dosimeter
References
Armstrong TW, Chandler KC, Barish J (1973) Calculations of neutron flux spectra induced in the earth's atmosphere by galactic cosmic rays. J Geophys Res 78:2715–2726
Bailey JV, Hoffman RA, English RA (1977) Radiobiological protection and medical dosimetry for the Skylab crewmen. In: RS Johnston, LF Dietlein (eds) Biomedical results from Skylab. NASA SP-377, pp 64–69
Benton EV, Henke RP (eds) (1972) Heavy cosmic-ray exposure of Apollo 16 astronauts. Technical report no. 20. Department of Physics, University of San Francisco, San Francisco, CA
Benton EV, Henke RP (eds) (1972) High Z particle cosmic-ray exposure of Apollo 8–14 astronauts. Technical report no. AFWL-TR-72–5. Air Force Weapons Laboratory, Albuquerque
Benton EV, Henke RP (eds) (1972) The HZE particle exposure of the Microbial Ecology Evaluation Device (MEED) aboard Apollo 16. Technical report no. 24. Department of Physics, University of San Francisco, San Francisco
Benton EV, Henke RP (eds) (1973) Heavy cosmic-ray exposure of Apollo 17 astronauts. Technical report no. 26. Department of Physics, University of San Francisco, San Francisco
Benton EV, Henke RP (1983) Radiation exposures during space flight and their measurements. Adv Space Res 3:171–185
Benton EV, Parnell TA (1988) Space radiation dosimetry on U.S. and Soviet manned missions. NATO ASI Series A. Life Sciences, vol 154, pp 729–794
Benton EV, Henke RP, Peterson DD, Bailey JV, Tobias CA (1975) Flux of high-LET cosmic-ray particles in manned space flight. Life Sci Space Res XIII:121–128
Benton EV, Henke RP, Bailey JV (1975) Heavy cosmic-ray exposure of Apollo astronauts. Science 187:263–265
Benton EV, Peterson DD, Henke RP (1977) Summary of measurements of high-LET particle radiation in U.S. manned space missions. Life Sci Space Res XV:119–127
Benton EV, Peterson DD, Marenny AM, Popov VI (1978) HZE particle radiation studies aboard Kosmos 782. Health Physics 35:643–648
Benton EV, Henke RP, Frank AL, Johnson CS, Cassou RM, Tran M, Etter E (1981) Space radiation dosimetry aboard Cosmos 1129: U.S. portion of experiment K-309. In: Final reports of U.S. plant and radiation dosimetry experiments flown on the Soviet satellite Cosmos 1129. NASA TM-81288, pp 123–188
Fleischer RL, Hart HR jr, Comstock GM, Carter M, Renshaw A, Hardy A (1973) Apollo 14 and Apollo 16 heavy-particle dosimetry experiments. Science 181:436–438
Grahn D (ed) (1973) HZE-Particle effects in manned spaceflight. National Academy of Sciences, Washington
Haffner JW (1964) RBE for protons and alpha particles. NASA SP-71, pp 513–525
Heinrich W, Wiegel B, Ohrndorf T, Bücker H, Reitz G, Schott JU (1989) LET spectra of cosmic-ray nuclei for near earth orbits. Radiat Res 118:63–82
Horrowitz YS (1984) Thermoluminescence and thermoluminescent dosimetry, vol II. CRC, Boca Raton
International Atomic Energy Agency (1986) Biological dosimetry: chromosomal aberration analysis for dose assessment. Technical report series no. 260, IAEA, Vienna
International Commission on Radiation Protection (1991) ICRP report no. 60. Pergamon Press, Oxford New York
Madey R (1978) A preliminary evaluation of the ionizing-radiation environment of the Satellite Power System. Report Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory-8581, pp 216–261
National Commission on Radiation Protection (1989) Guidance on radiation received in space activities. NCRP report no. 98. NCRP, Bethesda
Reitz G, Bücker H, Facius R, Beaujean R, Enge W (1991) Dosimetry results of Cosmos 1887. Nucl Tracks Radiat Meas 17:99–104
Reitz G, Bücker H, Facius R, Schäfer M, Beaujean R (1992) Dosimetry results of Cosmos 2044. Nucl Tracks Radiat Meas 20:161–165
Schaefer HJ (ed) (1977) Nuclear emulsion measurements of the dose contribution from tissue disintegration stars on the Apollo-Soyuz mission. Report no. 105–860/2. Faculty of Physics, University of West Florida, Pensacola
Schaefer HJ, Sullivan JJ (eds) (1975) Nuclear emulsion measurements of the astronauts' radiation exposures on Skylab missions 2, 3, and 4. Report Naval Aerospace Medical Research Laboratory-1220
Schaefer HJ, Sullivan JJ (eds) (1976) Atlas of nuclear emulsion micrographs from personnel dosimeters of manned space missions. Naval Aerospace Medical Research Laboratory, monograph 22, NASA order no. T-3057C
Schaefer JH, Sullivan JJ (eds) (1976) Nuclear emulsion measurements of the astronauts' radiation exposure on the Apollo-Soyuz mission. Report Naval Aerospace Medical Research Laboratory-1228
Schaefer HJ, Benton EV, Henke RP, Sullivan JJ (1972) Nuclear track recordings of the astronauts' radiation exposure on the first lunar landing mission Apollo XI. Radiat Res 49:245–271
Todd P (1983) Unique biological aspects of radiation hazards —an overview. Adv Space Res 3:187–194
Wailly LF, Watters JW, Carter PB (1974) Foil activation analysis and thermoluminescent dosimetry on Skylab II. USAFA-TRR-74-11
Wailly LF, Schneider MF, Janni JF, Grimm AD, Ainsworth GC (1974) Passive dosimetry measurements on board the Skylab II mission. Aerospace Med 45:1237–1243
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reitz, G., Beaujean, R., Heckeley, N. et al. Dosimetry in the space radiation field. Clin Investig 71, 710–717 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00209725
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00209725