Abstract
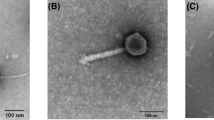
The biosynthesis of a phage tail-like Bacteriocin by cells of the group A-bacteriocinogenic (bA+ Serratia marcescens strain no. 16 after induction with mitomycin C (MC) was examined electronmicroscopically. This bacteriocin (total length 117 nm) consists of a hollow core and a contractile sheath. At 60 min following induction, rod-like bacteriocin-partieles were identifiable in ultrathin sections. The particles were found to comprise three morphologically different forms of aggregation: 1. hexagonal inclusions, 2. contiguous, bank-like particles, and 3. staples of superimposed layers of bacteriocin particles. At 120 min after induction bA+ cells revealed maximally 450 bacteriocin particles.
Similarly, the phage tail particles could be demonstrated with the “in situ lysis technique” at 60 min following induction. Occasionally, phage heads were demonstrable, but in no instance were complete phage particles discernible.
Dividing cells of the bA+ strain of S. marcescens maintained their rod-form following induction with MC until intracellular phage tail bacteriocin particles were seen. However, at 120 min after induction, the swollen, sphaeroplast-like cells lysed, an event that could be correlated with fine structural alterations of the cell wall.
Zusammenfassung
Die Genese eines phagenschwanzähnlichen Bacteriocins in Zellen des Gruppe A-bacteriocinogenen (bA+) Serratia marcescens-Stammer Nr. 16 wurde nach Mitomycin C (MC) Induktion elektronenoptisch untersucht. Dieses Bacteriocin (Gesamtlänge 117 nm) besteht aus einem hohlen Stift mit kontraktiler Scheide. Nach 60 min Induktion wurden in Dünnschnitten stäbchenförmige Bacteriocine identifiziert. Sie erscheinen in drei Aggregationsformen: 1. als hexagonale Einschlüsse, 2. als Bänder dicht nebeneinanderliegender Bacteriocine und 3. als Stapel von übereinanderliegenden Bacteriocinschichten, wenn nach 120 min Induktion ein Maximum von ca. 450 Bacteriocinen pro Zelle erreicht wird.
Bacteriocine konnten nach der gleichen Induktionszeit von 60 min auch mit der “in situ lysis technique” nachgewiesen werden. Neben Bacteriocinen traten relativ selten und unregelmäßig auch Phagenköpfe auf.
Die Stäbchenform teilungsfähiger Zellen blieb bis zum Auftreten von intracellulären Bacteriocinen erhalten. Ihre Umwandlung in geblähte, sphäroplastenähnliche Zellformen, die nach 120 min Induktion lysierten, war zeitlich korreliert mit Feinstrukturveränderungen der Zellwand.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- B:
-
Bacteriocine in Bandform
- C:
-
“core”
- CM:
-
Cytoplasmamembran
- F:
-
Schwanzfasern
- H:
-
hexagonale Aggregationsform
- M:
-
Mesosom
- MC:
-
Mitomycin C
- OM:
-
“outer membrane”
- ZW:
-
Zellwand
Literatur
Ackermann, H. W., Brochu, G.: Particulate bacteriocins. In: Handbook of microbiology, Vol 1 (A J. Laskin, H. A. Lechevalier, eds.), pp. 629–632. Cleveland: CRC Press 1973
Bijlenga, R. K., Scraba, D., Kellenberger, E.: Studies on the morphopoiesis of the T-even phage. IX. τ-Particles: Their morphology, kinetics of appearance and possible precursor function. Virology 56, 250–267 (1973)
Bradley, D. E.: The morphology of some bacteriophages specific to Serratia marcescens. J. appl. Bact. 28, 271–277 (1965)
Bradley, D. E.: Ultrastructure of bacteriophages and bacteriocins. Bact. Rev. 31, 230–314 (1967)
Bradley, D. E., Dewar, C. A.: The structure of phage-like objects associated with non-induced bacteriocinogenic bacteria. J. gen. Microbiol. 45, 399–408 (1966)
Braun, V., Hantke, K.: Biochemistry of bacterial cell envelopes. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 43, 89–121 (1974)
Costerton, J. W., Ingram, J. M., Cheng, K.-J.: Structure and function of the cell envelope of Gram-negative bacteria. Bact. Rev. 38:87–110 (1974)
De Klerk, H. C., Coetzee, J. N., Lecatsas, G.: Intracellular organisation of bacteriocin particles in Proteus vulgaris. Arch. Microbiol. 98, 271–274 (1974)
Farkas-Himsley, H., Kormendy, A., Jayawardene, A.: Electron microscopy of Vibrio comma during vibriocin production. Cytobios. 3, 97–116 (1971)
Garro, A. J., Marmur, J.: Defective bacteriophages. J. Cell Physiol. 76, 253–263 (1970)
Glauert A. M., Thornley, M. J.: The topography of the bacterial cell wall. Ann. Rev. Microbiol. 23, 159–198 (1969)
Greenawah, J. W., Whiteside, T. J.: Mesosomes: Membranous bacterial organelles. Bact. Rev. 39, 405–463 (1976)
Hainon, Y., Peron, Y.: Étude de la propriété bacteriocinogène dans la genre Serratia. Ann. Inst. Pasteur 100, 818–821 (1961)
Kellenberger, E., Huber, L.: Contribution á l'étude des equivalentes des mitochondries dans les bactéries. Experientia (Basel) 9, 289–291 (1953)
Kellenberger, E., Eiserling, F. A., Boy de la Tour, E.: Study on the morphopoiesis of the haed of phage T-even. III. The cores of head-related structures. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 21, 335–360 (1968)
Lewin, R. A., Kiethe, J.: Formation of rhapidosomes in Saprospira. Canad. J. Microbiol. 11, 935–937 (1965)
Lotz, W.: Defective bacteriophages: The phage tail-like particles. Progr. Molec. and Subcell. Biol., Vol. 4 (F. E. Hahn, ed.), pp. 53–102. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1976
Lotz, W., Mayer, F.: Isolation and characterisation of a bacteriophage tail-like bacteriocin from a strain of Rhizobium. Virology 9, 160–173 (1972)
Prinsloo, H. E.: Bacteriocins and phages produced by Serratia marcescens. J. gen. Microbiol. 45, 205–212 (1966)
Reusch, V. M., Burger, M. M.: The bacterial mesosome. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 300, 79–104 (1973)
Reynolds, D. S.: The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron opaque stain in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 17, 208–212 (1963)
Rucinsky, T. E., Cota-Robles, E. H.: The intracellular organisation of bacteriophage tail-like particles in cells of Chromobacterium violaceum following mitomycin C treatment. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 43, 260–269 (1973)
Rucinsky, T. E., Gregory, J. P., Cota-Robles, E. H.: Organisation of bacteriophage tail-like particles in cells of Chromobacterium violaceum. J. Bact. 110, 754–757 (1972)
Traub, W. H.: Studies on group A bacteriocins of Serratia marcescens: Preliminary characterisation of two subgroups of bacteriocins. Zbl. Bakt. I. Abt. Orig. A 222, 232–244 (1972a)
Traub, W. H.: Continued surveillance of Serratia marcescens infections by bacteriocin typing: Investigation of two outbreaks of cross-infection in an intensive care unit. Appl. Microbiol. 23, 982–985 (1972b)
Traub, W. H., Acker, G., Kleber, I.: Studies on group A (phage tail) bacteriocins of subgroup I and II bacteriocins. Zbl. Bakt., I. Abt. Orig. A 229, 383–390 (1974)
Traub, W. H., Acker, G., Kleber, I.: Ultrastructural surface alterations of Serratia marcescens after exposure to polymycin B and/or fresh human serum. Chemotherapie 22, 104–113 (1976)
Valentine, R. C., Shapiro, B. M., Stadtman, E. R.: Regulation of glutamine synthetase. XII. Electron microscopy of the enzyme from E. coli. Biochemistry 7, 2143–2152 (1968)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Acker, G. Intracelluläre Organisation phagenschwanz-ähnlicher Bacteriocine der Gruppe A in Serratia marcescens . Arch. Microbiol. 111, 175–183 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00446566
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00446566