Summary
-
1.
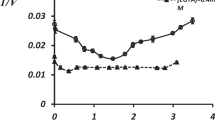
Injections of cobaltous chloride (5 mg/rat) on ten consecutive days, producing heart insufficiency, increase the specific activity of the sodium-potassiumactivated ATPase of the vesicle-fraction by about 100%.
-
2.
After only one injection of 5 or 7.5 mg cobaltous chloride the activity of the Na+ + K+-ATPase is not increased. The activity of the enzyme from kidneys is not increased before the fourth injection, whereas in the heart an increase is found after the second injection. Even after ten injections the increase of activity of the enzyme from heart muscle is more than that of the enzyme from kidneys.
-
3.
In adrenalectomized as well as in metyrapone-pretreated rats cobaltous chloride increases the enzyme activity. Therefore this increase cannot be caused by a stimulation of the adrenal cortex. We propose that repeated administrations of cobaltous chloride cause a cardiac insufficiency combined with structural alterations of the membranes of the sarcoplasmatic reticulum which change the activity of membrane-bound enzymes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Auger, C., Chenard, J.: Quebec beer-drinkers' oardiomyopathy: Ultrastructural changes in one case. Canad. med. Ass. J.97, 916–921 (1967).
Bomskov, Cb.: Methodik der Hormonforschung, S. 480. Leipzig: G. Thieme 1937.
Bonenfant, J. L., Miller, G., Roy, P. E.: Quebec beer-drinkers' cardiomypathy: Pathological studies. Canad. med. Ass. J.97, 910–915 (1967).
Chignell, C. F., Roddy, P. M., Titus, B. O.: Effect of adrenal steroids on a Na++K+ dependent adenosinetriphosphatase. Life Sci.4, 559–566 (1965).
—, Titus, E. O.: Effect of adrenal steroids on a Na++K+-requiring adenosinetriphosphatase from rat kidney. J. biol. Chem.241, 5083–5089 (1966).
Dixon, M., Webb, E. C.: Enzymes, pp. 498–510. London: Longmans, Green and Co. Ltd. 1966.
Dransfeld, H., Greeff, K.: Der Einflu\ des Prednison- und Prednisolonbisguanylhydrazons auf die Na++K+-stimulierte Membran-ATPase des Meerschweinchenherzens. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. exp. Path.Pharmak.249, 425–431 (1964).
——, Berger, H., Cautius, V.: Die verschiedene Empfindlichkeit der Na++K+-aktivierten ATPase des Herz- und Skeletmuskels gegen k-Strophanthin. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmak. exp. Path.254, 225–234 (1966).
——, Meng, K., Schwarzmann, D.: Zum Wirkungsmechanismus der neuen herzwirksamen Sterinderivate Prednison- und Prednisolonbisguanylhydrazon. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. exp. Path. Pharmak.247, 341 (1964).
Fleckenstein, A.: Stoffwechselprobleme bei der Myokardinsuffizienz. Verh. dtsch. Ges. Path.51, 15–29 (1967).
—: Experimentelle Pathologie der akuten und chronischen Herzinsuffizienz. Verh. Dtsch. Ges. Kreisl.-Forsch.34, 15–31 (1968).
—, Döring, J., Kammermeier, H.: Myokardstoffwechsel und Insuffizienz. Ärztl. Forsch.21, 1–14(1967).
Glynn, I. M.: The action of cardiac glycosides on ion movements. Pharmacol.Rev.16, 381–407(1964).
Herrell, W. E.: Beer au cobalt and cardiohepatic failure. Clin. Med.74, 15–16 (1967).
J.A.M.A.: Quebec beer-drinkers' cardiomyopathy. J. Amer. med. Ass.202, 1145 (1967).
Joergensen, P. L.: Regulation of the Na++K+-activated ATP hydrolizing enzyme system in rat kidney. 1. The effect of adrenalectomy and the supply of sodium on the enzyme system. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.)151, 212–224 (1968).
Kasperek, K., Siller, V., Knieriem, H. J.: Neutronen-aktivierungsanalytische Bestimmung von Kobalt und Calcium bei der experimentellen Herzinsuffizienz durch Kobaltchlorid. Z. ges. exp. Med.150, 316–324 (1969).
Knieriem, H. J., Herbertz, G.: Elektronenmikroskopische Befunde sowie photometrische und aktivierungsanalytische Ergebnisse bei experimenteller Herzinsufffizienz durch Kobaltchlorid. Virchows Arch., Abt. B Zellpath.2, 32–46 (1969).
Manitius, A., Bensch, K., Epstein, F. H.: Na++K+-activated ATPase in kidney cell membranes of normal and Methylprednisolone-treated rats. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.)150, 563–571 (1968).
McDermott, P. H., Delaney, R. L., Egan, J. B., Sullivan, I. F.: Myocardosis and cardiac failure in men. J. Amer. med. Ass.198, 253 (1966).
Morin, G., Daniel, P.: Quebec beer-drinkers' cardiomyopathy: Etiological Considerations. Canad. med. Ass. J.97, 926–928 (1967).
Sargent, A. U., Rose, B.: Quebec beer-drinkers' cardiomyopathy: Immunochemical studies. Canad. med. Ass. J.97, 922–923 (1967).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Die Ergebnisse wurden auf der 11. Frühjahrstagung der Deutschen Pharmakologischen Gesellschaft am 18. MÄrz 1970 in Mainz vorgetragen.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dransfeld, H., Lipinski, J. & Borsch-Galetke, E. Die Na+ + K+- aktivierte Transport-ATPase bei experimenteller Herzinsuffizienz durch Kobaltchlorid. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmak. 270, 335–342 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01002345
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01002345