Summary
Previous in vitro studies have suggested that GBR 13098 (1-(2-(bis(4-fluophenyl methoxy) ethyl)-4-(3-(4-fluorophenyl)-propyl)piperazine) dimethane sulfonate) acts as a selective dopamine uptake inhibitor. In the present study, behavioural, biochemical and electrophysiological effects of GBR 13098 in rats were analyzed.
GBR 13098 (10–40 mg/kg, i.p.) increased locomotor activity of habituated rats. The effect was almost totally prevented by pretreatment with the monoamine-depleting drug reserpine (5 mg/kg, 6 h) or the dopamine receptor antagonist haloperidol (0.3 mg/kg, 30 min).
GBR 13098 (20 mg/kg, i.p.) reduced DOPA formation in the striatum and in the limbic region, whereas the dopamine poor hemispheres were unaffected in this regard.
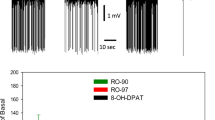
GBR 13098 (0.1–20 mg/kg, i.v.; or 20 mg/kg, i.p.) did not alter the spontaneous firing rate of dopamine neurons in the substantia nigra zona compacta. However, pretreatment with the drug (20 mg/kg, i.p., 10–30 min) enhanced the inhibitory response of microiontophoretically applied dopamine onto the dopamine neurons of substantia nigra.
Taken together, the present series of experiments show that GBR 13098 acts as a specific and potent inhibitor of dopamine uptake in brain. Present electrophysiological data are in line with the existence of a somatic or dendritic uptake system of dopamine within the substantia nigra but do not support the notion that the impulse activity of nigral dopamine neurons is regulated via a striatonigral feedback pathway.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bunney BS, Walters JR, Roth RH, Aghajanian GK (1973) Dopaminergic neurons: Effect of antipsychotic drugs and amphetamine on single cell activity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 185:560–571
Bunney BS, Aghajanian GK (1976) d-Amphetamine-induced inhibition of central dopaminergic neurons: Mediation by a striatonigral feed-back pathway. Science 192:391–393
Bunney BS, Aghajanian GK (1978) d-Amphetamine-induced depression of central dopamine neurons: Evidence for mediation by both autoreceptors and a striato-nigral feed-back pathway. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 304:255–261
Björklund A, Lindvall O (1975) Dopamine in dendrites of substantia nigra neurons: Suggestion for a role in dendritic terminals. Brain Res 83:531–537
Carlsson A, Lindqvist M (1978) Effects of antidepressant agents on the synthesis of brain monoamines. J Neur Transm 43:73–91
Carlsson A, Davis DN, Kehr W, Lindqvist M, Atack CV (1972) Simultaneous measurement of tyrosine and tryptophan hydroxylase activities in brain in vivo using an inhibitor of the aromatic amino acid decarboxylase. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 275:153–168
Carlsson A, Lindqvist M (1973) Effects of ethanol on the hydroxylation of tyrosine and tryptophan in rat brain in vivo. J Pharm Pharmacol 25:437–440
Clark D, Engberg G, Pileblad E, Svensson TH, Carlsson A, Freeman AS, Bunney BS (1985) An electrophysiological analysis of the actions of 3-PPP enantiomers on the nigrostriatal system. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 329:344–354
Cuello AC, Iversen LL (1978) Interactions of dopamine with other neurotransmitters in the rat substantia nigra: A possible functional role of dentritic dopamine. In: Garattini S, Pujol JF, Samanin R (eds) Interactions between putative neurotransmitters in brain. Raven Press, New York
Grace AA, Bunney BS (1983) Intracellular and extracellular electrophysiology of nigral dopaminergic neurons. 1. Identification and characterization. Neuroscience 10:301–315
Greenfield SA (1985) The significance of dendritic release of transmitter and protein in the substantia nigra. Neurochem Int 7:887–901
Heikkula RE, Manzino L (1984) Behavioural properties of GBR 12909, GBR 13069 and GBR 13098: Specific inhibitors of dopamine uptake. Eur J Pharmacol 103:241–248
Kelly E, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1985) Evidence that [3H]-dopamine is taken up and released from nondopaminergic nerve terminals in the rat substantia nigra in vitro. J Neurochem 45:137–144
Koe BK (1976) Molecular geometry of inhibitors of the uptake of catecholamines and serotonin in synaptosomal preparations of rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 199:649–661
König JFR, Klippel RA (1970) The rat brain. A stereotaxic atlas of the forebrain and the lower parts of the brain stem. Krieger, New York
Nissbrandt H, Pileblad E, Carlsson A (1985) Evidence for dopaminergic release and metabolism beyond the control of nerve impulses and dopamine receptors in rat substantia nigra. J Pharm Pharmacol 37:884–889
Nybäck HV, Walters JR, Aghajanian GK, Roth RH (1975) Tricyclic antidepressants: Effects on the firing rate of brain noradrenergic neurons. Eur J Pharmacol 32:302–312
Scheel-Krüger J (1971) Comparative studies of various amphetamine analogues demonstrating different interactions with the metabolism of the catecholamines in the brain. Eur J Pharmacol 14:47–59
Shum A, Sole MJ, van Loon GR (1982) Simultaneous measurement of 5-hydroxytryptophan andL-dihydroxyphenylalanine by high-performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection — measurement of serotonin and catecholamine turnover in discrete brain regions. J Chromatography 228:123–130
Svensson TH, Usdin T (1978) Feed-back inhibition of brain noradrenaline neurons by tricyclic antidepressants; alpha-receptor mediation. Science 202:1089–1091
Tasaki K, Tsukahara U, Ito S, Wayner MJ, Yu WY (1968) A simple, direct and rapid method for filling microelectrodes. Physiol Behav 3:1009–1010
van der Zee P, Koger HS, Gootjes J, Hespe W (1980) Aryl 1,4-dialk(en)ylpiperazines as selective and very potent inhibitors of dopamine uptake. Eur J Med Chem 15:363–370
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pileblad, E., Engberg, G. GBR 13098, a selective dopamine uptake inhibitor; behavioural, biochemical and electrophysiological studies. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 334, 383–387 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00569374
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00569374