Summary
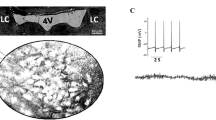
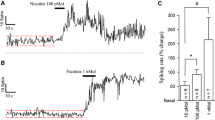
The goal of this study was to investigate whether locus coeruleus neurons of the rat are sensitive to agonists of the different excitatory amino acid receptors. All experiments were performed on a midpontine rat slice preparation. Bath-applied l-glutamate, kainate, N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) and quisqualate induced concentration-dependent activations of all neurons which were reflected in an increase of the neurons' mean discharge rate. The rank order of cell activation was kainate ∼ quisqualate > NMDA > l-glutamate. None of the agonists induced a bursting-type of discharge. The NMDA-receptor blocker dl-2-amino-5-phosphonovaleric acid (APV, 30 μM) selectively antagonized the NMDA-induced increase in cell firing. Kynurenic acid (100 μM) non-selectively attenuated the response to NMDA, kainate and quisqualate. Neither APV nor kynurenic acid per se had any effect on the spontaneous firing rate. If the Mg2+ concentration in the superfusion medium was lowered from 2 mM to nominally zero the response to NMDA was selectively increased. In conclusion, locus coeruleus neurons share with other neurons their sensitivity to agonists of all three types of excitatory amino acid receptors. However, in contrast to other neurons, they do not respond with a bursting type of discharge.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ascher P, Nowak L (1988) The role of divalent cations in the N-methyl-d-aspartate responses of mouse central neurons in culture. J Physiol (Lond) 399:247–266
Aston-Jones G, Bloom FE (1981) Norepinephrine-containing locus coeruleus neurons in behaving rats exhibit pronounced responses to non-noxious environmental stimuli. J Neurosci 1:887–900
Aston-Jones G, Matthews E, Pieribone VA, Nickell WT, Shipley MT (1986) The brain nucleus locus coeruleus: restricted afferent control of a broad efferent network. Science 234:734–737
Ault B, Evans RH, Francis AS, Oakes DJ, Watkins JC (1980) Selective depression of excitatory amino acid induced depolarizations by magnesium ions in isolated spinal cord preparations. J Physiol 307:413–428
Barry DI, Kikvadze I, Brundin P, Bolwig TG, Bjölund A, Lindvall O (1987) Grafted noradrenergic neurons suppress development in kindling-induced epilepsy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:8712–8715
Ennis M, Aston-Jones G (1986) A potent excitatory input to the nucleus locus coeruleus from the ventrolateral medulla. Neurosci Lett 71:299–305
Foote SL, Aston-Jones G, Bloom FE (1980) Impulse activity of locus coeruleus neurons in awake rats and monkeys is a function of sensory stimulation and arousal. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:3033–3037
Ganong AH, Cotman CW (1986) Kynurenic acid and quinolinic acid act at N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors in the rat hippocampus. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 236:293–299
Herrling PL, Morris R, Salt TE (1983) Effects of excitatory amino acids and their antagonists on membrane and action potentials of cat candate neurones. J Physiol (Lond) 339:207–222
Johnson JW, Ascher P (1987) Glycine potentiates the NMDA response in cultured mouse brain neurons. Nature 325:529–531
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Send offprint requests to H.-R. Olpe at the above address
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Olpe, HR., Steinmann, M.W., Brugger, F. et al. Excitatory amino acid receptors in rat locus coeruleus. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 339, 312–314 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00173584
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00173584