Abstract
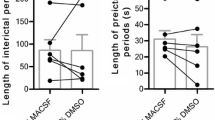
Methysticin is one of the constituents of Piper methysticum which possesses anticonvulsant and neuroprotective properties. Its effects on different in vitro seizure models were tested using extracellular recordings in rat temporal cortex slices containing the hippocampus and the entorhinal cortex. Elevating [K+]o0 induced seizure-like events with tonic and clonic electrographic phases in area CA1. Lowering [Ca2+]0 caused recurrent seizure like episodes with large negative field potential shifts. Lowering Mg2+ induced short recurrent discharges in area CA3 and CA1 while ictaform events lasting for many seconds were induced in the subiculum, entorhinal and temporal neocortex. In the hippocampus the activity stayed stable over a number of hours. In contrast, the ictaform events in the subiculum, entorhinal and temporal cortex changed their characteristics after one to two hours to late recurrent discharges. In a concentration-range from 10 to 100 μM methysticin reversibly blocked all these types of epileptiform activity. Decreases in [Ca2+]0 and associated slow field potentials evoked by repetitive stimulation of the stratum radiatum or the alveus remained almost unaffected by methysticin. A paired pulse stimulus paradigm used to test for effects of methysticin on synaptically evoked transient field potentials in normal medium revealed interference with mechanisms involved in frequency potentiation. While responses to alvear stimulation were largely unaffected, the responses to a paired pulse stimulus to stratum radiatum were depressed over the whole range of tested stimulus intervals. The findings suggest that methysticin has effects on different patterns of epileptiform activity possibly by interfering with processes responsible for frequency potentiation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Backhauß C, Krieglstein J (1992) Extract of kava (Piper methysticum) and its methysticin constiuents protect brain tissue against ischemic damage in rodents. Eur J Pharmacol 215:265–269
Cawte J (1988) Macabre effects of a cult of Kava. Med J Austr 148:545–546
Cuzent M (1861) Composition chimique de la kavahine. Comptes Rendus Hebdomadaires des Seances de L'Academie des Sciences 52:205–206
Dreier JP, Heinemann U (1990) Late low magnesium-induced epileptiform activity in rat entorhinal cortex slices becomes insensitive to the anticonvulsant valproic acid. Neurosci Lett 119: 68–70
Dreier JP, Heinemann U (1991) Regional and time dependent variations of low Magnesium induced epileptiform activity in rat temporal cortex. Exp Brain Res 87:581–596
Editorial (1988) Kava. The Lancet 30:258–259
Efron DH, Holmstedt B, Kline NS (1979) Ethnopharmacoligic search for psychoactive drugs. Raven Press, New York, pp 105–181
Franceschetti S, Hamon B, Heinemann U (1986) The action of valproate on spontaneous epileptiform activity in absence of synaptic transmission and on evoked changes in [Ca2+]o in the hippocampal slice. Brain Res 386:1–11
Goubley M (1860) Recherches Chimiques sur la racine de kava. Journal de Pharmacie et de Chimie 37:19–23
Haas HL, Jefferys JGR (1984) Low-calcium field burst discharges of CA1 pyramidal neurones in rat hippocampal slices. J Physiol (Long) 353:185–201
Heinemann U, Jones RSG (1990) Neurophysiology, In: Dam M, Gram L (eds) Comprehensive epiletology, Raven Press, New York, pp 17–42
Heinemann U, Lux HD, Gutnick MJ (1977) Extracellular free calcium and potassium during paroxysmal activity in the cerebral cortex of the cat. Exp Brain Res 27:237–243
Heinemann U, Franceschetti S, Hamon B, Konnerth A, Yaari Y (1985) Effects of anticonvulsants on spontaneous epileptiform activity which devevops in the absence of chemical synaptic transmission in hippocampal slices. Brain Res 325:349–352
Heinemann U, Konnerth A, Pumain R, Wadman WJ (1986) Extracellular calcium and potassium concentration changes in chronic epileptic brain tissue. In: Delgado-Escueta AV, Ward AA, Woodbury DM, Porter RJ (eds) Advances in neurology, vol 44. Basic mechanism of the epilepsis: Molecular and cellular approaches. Raven Press, New York, pp 641–661
Heinemann U, Arens J, Dreier JP, Stabel J, Zhang CL (1991) In vitro epileptiform activity: Role of excitatory amino acids. Epilepsy Res 10:18–23
Herberg KW (1991) Fahrtüchtigkeit nach Einnahme von Kava-Spezial-Extrakt WS 1490:Doppleblinde placebokontrollierte Probandenstudie. Z Allgemeinmed 67:842–846
Hood TW, Siegfried J, Haas HL (1983) Analysis of carbamazepine actions in hippocampal slices of the rat. Cell Mol Neurobiol 3:213–222
Johnson D, Frauedorf A, Strecker K, Stein U (1991) Neurophysiologisches Wirkprofil und Verträglichkeit von Kava-Extrackt WS 1490. TW Neurologie Psychiatrie 5:349–354
Keller F, Klohs MW (1963) A review of chemistry and pharmacology of the constituents of Piper methysticum. Llyoda 26:1–15
Kinzler E, Krömer J, Lehmann E (1991) Wirksamkeit eines Kava-Spezial-Extraktes bei Patienten mit Angst-, Spannungs- und Erregungszuständen nicht-physchotischer Genese, Arzneim Forsch 41:584–588
Konnerth A, Heinemann U, Yaari Y (1984) Slow transmission of neural activity in hippocampal area CA1 in absence of active chemical synapses. Nature 307:69–71
Kretzschmar R, Meyer HJ, Teschendorf JH (1970) Strychnine antagonistic potency of pyrone compounds of the Kava root (Piper methysticum, Forst). Experientia 26:283–284
Leschinger A, Stabel J, Igelmund P, Heinemann U (1993) Pharmacological and electrographic properties of epileptiform activity induced by elevated K+ and lowered Ca2+ and Mg2+ concentration in rat hippocampal slices. Exp Brain Res 96:230–240
Lux HD, Neher E (1973) The equilibration time course of [K+]0 in cat cortex. Exp Brain Res 17:190–205
Lux, HD, Heinemann U, Dietzel I (1986) Ionic changes and alterations in the size of the extracellular space during epileptic activity. In: Delgado-Escueta AV, Ward AA, Woodbury DM, Porter RJ (eds) Advances in neurology, vol 44. Basic mechanisms of the epilepsics: molecular and cellular approaches. Raven Press, New York, pp 619–639
Mathews JD, Riley MD, Fejo L, Munoz E, Milns R, Gardner ID, Power JR, Ganygulpa E, Gununuwawuy BJ (1989) Effects of the heavy usage of Kava on physical health: Summary of a pilot survey in an aboriginal community. Med J Austr 148:548–555
Meyer HJ (1964) Untersuchungen über den antikonvulsiven Wirkungstyp der Kawa-Pyrone Dihydromethysticin und Dihydrokawain mit Hilfe chemisch induzierter Krämpfe. Arch int Pharmacodyn 150:118–131
Meyer HJ, Kretzschmar R (1969) Untersuchungen über Beziehungen zwischen Molekularstruktur und pharmakologischer Wirkung C6-arylsubstituierter 4-Mehyoxy-a-pyrone vom Typ der Kawa-Pyrone. Arzneim Forsch 19:617–623
Mody I, Lambert JDC, Heinemann U (1987) Low extracellular magnesium induces eplileptiform activity and spreading depression in rat hippocampal slices. J Neurophysiol 57:869–888
Münte TF, Heinze HJ, Matzke M, Steitz J (1993) Effects of oxazepam and an extract of Kava roots (Piper methysticum) on event-related potential in a word recognition task. Neuropsychobiology 27:46–53
Paxinos G, Watson C (1986) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. 2nd edn. Academic Press, London
Pfeiffer CC, Murphree HB, Goldstein L (1979) EFfects of kawa on normal subjects and patients. In: Efron et al (eds) Ethnopharmacologic search for psyschoactive drugs. Raven Press, New York, pp 155–161
Pumain R, Menini C, Heinemann U, Silvat-Barrat C, Louvel J (1985) Chemical synaptic transmission is not necessary for epileptic activity to persist in the neocortex of the photosensitive baboon. Neurol 89:250–258
Pumain R, Kurcewicz I, Louvel J (1987) Ionic changes induced by excitatory amino acids in the rat cerebral cortex. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 65:1067–1077
Shulgin At (1973) The narcotic pepper - The chemistry and pharmacology of Piper methysticum and related species. Bull Narcotics 25:59–74
Siesjö BK (1981) Cell damage in the brain: A speculative synthesis. J Cerebr Blood Flow Metab 1:155–185
Singh YN (1992) Kava: an overview. J Ethnopharmacol 37:13–45
Steinegger E, Hänsel R (1988) Lehrbuch der Pharmakognosie und Phytopharmazie, 4th edn. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, p 663
Traynelis SF, Dingledine R (1988) Potassium-induced spontaneous electrographic seizures in the rate hippocampal slice. J Neurophysiol 59:259–276
Walther H, Lambert JDC, Jones RSG, Heinemann U, Hamon B (1986) Epileptiform activity in combined slices of the hippocampus, subiculum and entorhinal cortex during perusion with low magnesium medium. Neurosci Lett 69:156–161
Warnecke G (1991) Psychosomatische Dysfunktion im weiblichen Klimakterium. Klinische Wirksamkeit und Verträglichkeit von Kava-Extrakt WS 1490. Fortschr Med 109:119–122
Yaari Y, Konnerth A, Heinemann U (1983) Spontaneous epileptiform activity of CA1 hippocampal neurons in low extracellular calcium solutions. Exp Brain Res 51:153–156
Yaari Y, Konnerth A, Heinemann U (1986) Nonsynaptic epileptogenesis in the mammalian hippocampus in vitro. II. Role of extracellular potassium. J Neurophysiol 56:424–438
Zhang CL, Glovelli T, Heinemann U (1994) Effects of NMDA- and AMPA-receptor antagonists on different forms of epileptiform activity in rat temporal cortex slices. Epilepsia 35 [Suppl 5]: 68–73
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmitz, D., Zhang, C.L., Chatterjee, S.S. et al. Effects of methysticin on three different models of seizure like events studied in rat hippocampal and entorhinal cortex slices. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 351, 348–355 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00169074
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00169074