Abstract
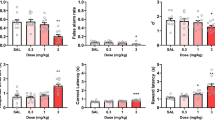
The effects of the competitive NMDA antagonist CPP and the non-competitive NMDA antagonist MK 801 (dizolcipine) on short term working memory in the rat were investigated. The behavioural paradigm used was discrete trial, operant delayed matching to position, as originally described by Dunnett (1985), with delays of 0, 5, 15 and 30 s. These delays generated an orderly “forgetting” curve in control rats, with matching accuracy decreasing from approximately 100% at 0-s delay to approximately 75% at 30-s delay. Intraperitoneal (IP) administration of CPP (10 mg/kg) produced a markeddelay dependent impairment in performance, suggesting a specific effect on short term working memory. This effect was accompanied by a minor decrease in the speed of responding, and a slight increase in the number of missed trials. Lower doses of CPP had no significant effects on either matching accuracy or sedation. In contrast, IP administration of MK 801 (0.1 and 0.2 mg/kg) caused a markeddelay independent impairment in the accuracy of delayed matching performance, suggesting a non-specific disruption of performance. A lower dose (0.05 mg/kg) of MK 801 had no significant effect on matching accuracy. The two lower doses of MK 801 increased the number of nose pokes made during the delays and tended to increase the speed of responding, suggesting a stimulant-like action. The highest dose of MK 801 had the opposite effects and also decreased the number of trials completed. The results with CPP therefore support the hypothesized role of NMDA receptors in learning and memory, and the contrasting effects of these two NMDA antagonists support previous suggestions of different behavioural effects resulting from administration of competitive and non-competitive NMDA antagonists.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham WC, Mason SE (1988) Effects of the NMDA receptor/channel antagonists CPP and MK801 on hippocampal field potentials and long-term potentiation in anesthetized rats. Brain Res 462:40–46
Aggleton JP, Keith AB, Sahgal A (1991) Both fornix and anterior thalamic, but not mammillary, lesions disrupt delayed non-matching-to-position memory in rats. Behav Brain Res 44:151–161
Anis NA, Berry SC, Burton NR, Lodge D (1983) The dissociative anaesthetics, ketamine and phencyclidine, selectively reduce excitation of central mammalian neurones by N-methyl-aspartate. Br J Pharmacol 79:565–575
Beardsley PM, Hayes BA, Balster RL (1990) The self-administration of MK-801 can depend upon drug-reinforcement history, and its discriminative stimulus properties are phencyclidine-like in rhesus monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 252:953–959
Butelman ER (1989) A novel NMDA antagonist, MK-801, impairs performance in a hippocampal-dependent spatial learning task. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 34:13–16
Butelman ER (1990) The effect of NMDA antagonists in the radial arm maze task with an interposed delay. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 35:533–536
Clissold DB, Ferkany JW, Pontecorvo MJ (1991) Competitive and non-competitive N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) antagonists, haloperidol, and scopolamine impair performance in a nonspatial operant discrimination task. Psychobiology 19:332–338
Collingridge GL, Singer W (1990) Excitatory amino acid receptors and synaptic plasticity. TIPS 11:290–296
Collingridge GL, Kehl SJ, McLennan H (1983) Excitatory amino acids in synaptic transmission in the Schaffer collatoral-commissural pathway of the rat hippocampus. J Physiol (Lond) 334:33–46
Cotman CW, Monaghan DT, Ottersen OP, Storm-Mathisen J (1987) Anatomical organization of excitatory amino acid receptors and their pathways. TINS 10:273–280
Curtis DR, Phillis JW, Watkins JC (1959) Chemical excitation of spinal neurones. Nature 183:611–612
Davies J, Francis AA, Jones AW, Watkins JC (1981) 2-Amino-5-phosphonovalerate (2APV), a potent and selective antagonist of amino acid-induced and synaptic excitation. Neurosci Lett 21:77–81
Dunnett SB (1985) Comparative effects of cholinergic drugs and lesions of nucleus basalis or fimbria-fornix on delayed matching in rats. Psychopharmacology 87:357–363
Dunnett SB, Evenden JL, Iversen SD (1988) Delay-dependent short-term memory impairments of aged rats. Psychopharmacology 96:174–180
Dunnett SB, Martel FL, Iversen SD (1990a) Proactive interference effects on short-term memory in rats: II. Effects in young and aged rats. Behav Neurosci 104:666–670
Dunnett SB, Wareham AT, Torres EM (1990b) Cholinergic blockade in prefrontal cortex and hippocampus disrupts short-term memory in rats. Neuroreport 1:61–64
Ferkany JW, Kyle DJ, Willets J, Rzeszotarski WJ, Guzewska ME, Ellenberger SR, Jones SM, Sacaan AI, Snell LD, Borosky S, Jones BE, Jonson KM, Balster RL, Burchett K, Kawasaki K, Hoch DB, Dingledine R (1989) Pharmacological profile of NPC 12626, a novel, competitive N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 250:100–109
Gilbert ME, Mack CM (1990) The NMDA antagonist, MK 801, suppresses long-term potentiation, kindling, and kindling-induced potentiation in the perforant path of the unanesthetized rat. Brain Res 519:89–96
Halliwell RF, Morris RGM (1987) Anticonvulsant doses of MK-801 fail to block long-term potentiation in vivo, or impair spatial memory in the rat. Neurosci Lett Supp 29:S99
Heise GA, Milar KS (1984) Drugs and stimulus control. In: Iversen LL, Iversen SD, Snyder SH (eds) Handbook of psychopharmacology, vol 18. Plenum, New York, pp 129–190
Jackson A, Sanger DJ (1988) Is the discriminative stimulus produced by phencyclidine due to an interaction with N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors? Psychopharmacology 96:87–92
Keith JR, Rudy JW (1990) Why NMDA-receptor-dependent long-term potentiation may not be a mechanism of learning and memory: reappraisal of the NMDA-receptor blockade strategy. Psychobiology 18:251–257
Kemp JA, Foster AC, Wong EHF (1987) Non-competitive antagonists of excitatory amino acid receptors. TINS 7:294–298
Koek W, Colpaert FC (1990) Selective blockade of N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA)-induced convulsions by NMDA antagonists and putative glycine antagonists: Relationship with phencyclidine-like behavioral effects. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 252:349–357
Koek W, Woods JH, Winger GD (1988) MK-801, a proposed non-competitive antagonist of excitatory amino acid neurotransmission, produces phencyclidine-like behavioral effects in pigeons, rats and rhesus monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 245:969–974
Koek W, Woods JH, Colpaert FC (1990) N-methyl-d-aspartate antagonism and phencyclidine-like activity: A drug discrimination analysis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 253:1017–1025
Ksir C, Slifer B (1982) Drug effects on discrimination performance at two levels of stimulus control. Psychopharmacology 76:286–290
Lehmann J, Schneider J, McPherson S, Murphy DE, Bernard P, Tsai C, Bennett DA, Pastor G, Steel DJ, Boehm C, Cheney DL, Liebman JM, Williams M, Wood PL (1987) CPP, a selective N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA)-type receptor antagonist: Characterization in vitro and in vivo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 240:737–746
Lyford GL, Jarrard LE (1991) Effects of the competitive NMDA antagonist CPP on performance of a place and cue radial maze task. Psychobiology 19:157–160
Morris RGM (1989) Synaptic plasticity and learning: selective impairment of learning in rats and blockade of long-term potentiation in vivo by the N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonist AP5. J Neurosci 9:3040–3057
Morris RGM, Anderson E, Lynch GS, Baudry M (1986) Selective impairment of learning and blockade of long-term potentiation by an N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonist, AP5. Nature 319:774–776
Perkins MN, Stone TW, Collins JF, Curry K (1981) Phosphonate analogues of carboxylic acids as excitatory amino acid antagonists on rat cortical neurones. Neurosci Lett 23:333–336
Pontecorvo MJ, Clissold DB, White MF, Ferkany JW (1991) N-methyl-d-aspartate antagonists and working memory performance: comparison with the effects of scopolamine, propanolol, diazepam, and phenylisopropyladenosine. Behav Neurosci 105:521–535
Robinson GS Jr, Crooks GB Jr, Shinkman PG, Gallagher M (1989) Behavioral effects of MK-801 mimic deficits associated with hippocampal damage. Psychobiology 17:156–164
Spencer DG, Emmett-Oglesby MW (1985) Parallel processing strategies in the application of microcomputers to the behavioral laboratory. Behav Res Methods Instrum Comput 17:294–300
Staubli U, Thibault O, DiLorenzo M, Lynch G (1989) Antagonism of NMDA receptors impairs acquisition but not retention of olfactory memory. Behav Neurosci 103:54–60
Tan S, Kirk RC, Abraham WC, McNaughton N (1989) Effects of the NMDA antagonists CPP and MK-801 on delayed conditional discrimination. Psychopharmacology 98:556–560
Tang AH, Ho PM (1988) Both competitive and non-competitive antagonists of N-methyl-d-aspartic acid disrupt brightness discrimination in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 151:143–146
Tonkiss J, Rawlins JNP (1991) The competitive NMDA antagonist AP5, but not the non-competitive antagonist MK801, induces a delay-related impairment in spatial working memory in rats. Exp Brain Res 85:349–358
Tricklebank MD, Singh L, Oles RJ, Wong EHF, Iversen SD (1987) A role for receptors of N-methyl-d-aspartic acid in the discriminative stimulus properties of phencyclidine. Eur J Pharmacol 141:497–501
Tricklebank MD, Singh L, Oles RJ, Preston C, Iversen SD (1989) The behavioural effects of MK-801: a comparison with antagonists acting non-competitively and competitively at the NMDA receptor. Eur J Pharmacol 167:127–135
Venable N, Kelly PH (1990) Effects of NMDA receptor antagonists on passive avoidance learning and retrieval in rats and mice. Psychopharmacology 100:215–221
Ward L, Mason SE, Abraham WC (1990) Effects of the NMDA antagonists CPP and MK-801 on radial arm maze performance in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 35:785–790
Watkins JC, Krogsgaard-Larsen P, Honore T (1990) Structure-activity relationships in the development of excitatory amino acid receptor agonists and competitive antagonists. TIPS 11:25–33
Willets J, Balster RL, Leander JD (1990) The behavioral pharmacology of NMDA receptor antagonists. TIPS 11:423–428
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cole, B.J., Klewer, M., Jones, G.H. et al. Contrasting effects of the competitive NMDA antagonist CPP and the non-competitive NMDA antagonist MK 801 on performance of an operant delayed matching to position task in rats. Psychopharmacology 111, 465–471 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02253537
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02253537