Abstract
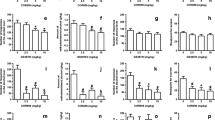
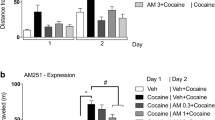
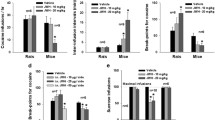
SR 141716, a selective central CB1 cannabinoid receptor antagonist, markedly and selectively reduces sucrose feeding and drinking as well as neuropeptide Y-induced sucrose drinking in rats. SR 141716 also decreases ethanol consumption in C57BL/6 mice. In contrast, blockade of CB1 receptors only marginally affects regular chow intake or water drinking. The active doses of SR 141716 (0.3–3 mg/kg) are in the range known to antagonize the characteristic effects induced by cannabinoid receptor agonists. These results suggest for the first time that endogenous cannabinoid systems may modulate the appetitive value of sucrose and ethanol, perhaps by affecting the activity of brain reward systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 31 January 1997/Final version: 16 March 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arnone, M., Maruani, J., Chaperon, F. et al. Selective inhibition of sucrose and ethanol intake by SR 141716, an antagonist of central cannabinoid (CB1) receptors. Psychopharmacology 132, 104–106 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130050326
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130050326