Abstract
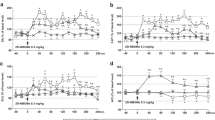
Three experiments were carried out to test the long-term behavioral effects of 12 days administration of CDP (5 mg/kg/day) in rats. In the first two experiments, 4 weeks after the end of drug administration (CDP or placebo), and after 2 weeks of training to run a straight alley for food reward, animals were tested in extinction, i.e., following omission of reward (Expt. 1) or with punishment, i.e., 0.3 mA electric shock in addition to the food reward (Expt. 2). Drug-treated animals showed significantly increased resistance to extinction and to punishment compared with controls. In the third experiment, 10 weeks after drug administration, animals were exposed to 60 s of intense noise to induce audiogenic seizures. The convulsant metrazol was injected 5 min prior to successive sessions (10 min apart) with doses starting at 10 mg/kg and increased by 10 mg/kg each session up to 40 mg/kg. Drug-treated animals were significantly less susceptible to seizures than their placebo controls. These results suggest that chronic benzodiazepine treatment causes long-term neurochemical changes which are responsible for the observed behavioral effects.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Browne TR, Penry JR (1973) Benzodiazepines in the treatment of epilepsy: a review. Epilepsia 14:277–310
Cassone MC, Molinego L (1981) Drug action of memory decay. Life Sci 29:1983–1988
Cook L, Davidson AB (1973) Effects of behaviorally active drugs in a conflict punishment procedure in rats. In: Garattini S, Mussini E, Randall LD (eds) The benzodiazepines. Raven Press, New York, pp 327–345
Cook L, Sepinwall J (1975) Behavioral analysis of the effects and mechanism of aotion of benzodiazepines. In: Costa E, Greengard P (eds) Mechanism of action of benzodiazepines. Raven Press, New York, pp 1–28
Costa E, Guidotti A, Mao CC (1975) Evidence for the involvement of GABA in the action of benzodiazepines: Studies on rat cerebellum. In: Costa E, Greengard P (eds) Mechanism of action of benzodiazepines. Raven Press, New York, pp 113–130
Davis N, Brookes S, Gray JA, Rawlins J (1981) Chlordiazepoxide and resistance to punishment. Q J Exp Psychol 33B:227–239
Feldon J, Gray JA (1981) The partial reinforcement extinction effect after treatment with chlordiazepoxide. Psychopharmacology 73:269–275
Feldon J, Guillamon A, Gray JA, deWit H, McNaughton N (1979) Sodium amylobarbitone and responses to non-reward. Q J Exp Psychol 31:19–50
File SE, Hyde JRG (1978) Social interaction as a measure of anxiety. Br J Pharmacol 62:19–24
Geller I, Seifter J (1960) The effects of meprobamate, barbiturates, d-amphetamine and promazine on experimentally induced conflict in the rat. Psychopharmacologia 1:482–492
Goldberg ME, Manian AA, Efron DH (1967) A comparative study of certain pharmacological responses following acute and chronic administration of chlordiazepoxide. Life Sci 6:481–491
Gray JA (1977) Drug effects on fear and frustration: possible limbic site of minor tranquilizers. In: Iversen LL, Iversen SD, Snyder SH (eds) Handbook of psychopharmacology, vol 8. Plenum Press, New York, pp 433–529
Gray JA, McNaughton N, Holt L, Tsaltas E, Feldon J, Shemer A (1982) The effects of anti-anxiety drugs on tolerance for stress. In: Spiegelstein MY, Levy A (eds) Behavioral models and the analysis of drug action. Elsevier, Amsterdam pp 175–194
Grimm VE, Hershkowitz M (1981) The effect of chronic diazepam treatment on discrimination performance and 3H-flunitrazepam binding in the brains of shocked and non shocked rats. Psychopharmacology 74:132–136
Lader M (1978) Benzodiazepines: the opium of the masses? Neuroscience 3:159–165
Margules DL, Stein L (1967) Neuroleptics vs transquilizers: Evidence from animal studies of mode and site of action. In: Brill H, Cole O, Deniker P, Hippius H, Bradley PB (eds) Neuropsychopharmacology, Excerpts. Medica Foundation, Amsterdam, pp 108–120
Margules DL, Stein L (1968) Increase of “antianxiety” activity and tolerance of behavioral depression during chronic administration of oxazepam. Psychopharmacology 13:74–80
Shemer A, Feldon J (1982) Chlordiazepoxide and the long term partial reinforcement extinction effect. Behav Brain Res 5:120
Stein L, Wise CD, Belluzzi JC (1975) Effects of benzodiazepines on central serotonergic mechanism. In: Costa E, Greengard P (eds) Mechanism of action of benzodiazepines. Raven Press, New York, pp 29–44
Tallman JF, Paul SM, Skolnick P, Gallager DW (1980) Receptors for the age of anxiety: pharmacology of the benzodiazepines. Science 207:274–281
Wise CD, Berger BD, Stein L (1972) Benzodiazepines. Anxiety reducing activity by reduction of serotonin turnover in the brain. Science 177:180–183
Zbinden G, Randall LO (1967) Pharmacology of benzodiazepines: Laboratory and clinical correlations. Adv Pharmacol 5:213–291
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shemer, A., Tykocinski, O. & Feldon, J. Long term effects of chronic chlordiazepoxide (CDP) administration. Psychopharmacology 83, 277–280 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00464794
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00464794