Abstract
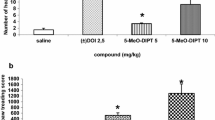
The effect of prolonged administration of the potent and specific 5-HT uptake inhibitor citalopram on behavioural measures of dopaminergic and serotonergic activity has been studied in rats. Administration of citalopram in the diet at a daily dose of 99 μmol/kg led to supersensitivity to d-amphetamine-induced hypermotility and stereotypy and to subsensitivity to apomorphine-induced hypomotility 2 h after withdrawal. Forepaw clonus induced by 5-methoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine was decreased 2 h and 24 h after withdrawal and the number of head shakes induced by 1-5-HTP and citalopram were decreased 24 h after withdrawal. The d-amphetamine potentiation was still seen after 24 h, whereas the response had returned to normal 3 and 7 days after withdrawal. The content of amphetamine in three different brain regions was about 50% higher compared with controls 24 h after withdrawal of prolonged citalopram administration. At this time citalopram had been eliminated, and citalopram itself could not affect amphetamine metabolism. Other experiments indicated a linear relation between d-amphetamine brain concentration and motility level. Thus, a 50% increase in citalopram-treated rats cannot alone account for 3-fold increase in d-amphetamine-induced motility. Potentiation of d-amphetamine-induced hypermotility was also found after citalopram in a daily dietary dose of 25 μmol/kg for 13 days and after oral bolus injection (49 μmol/kg twice daily for 14 days). Acute citalopram injection had no effect in any of these models. The results suggest increased responsiveness of dopaminergic mechanisms mediating hypermotility, and decreased sensitivity of dopamine receptors mediating sedation (proposed autoreceptors). Sensitivity of 5-HT receptors was also decreased. The mechanisms by which citalopram induces d-amphetamine supersensitivity as well as subsensitivity to apomorphine and 5-HT agonists are presently unknown, since no changes in dopaminergic and serotonergic receptor binding have been found after an identical dose regimen.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson JL (1983) Serotonin receptor changes after chronic antidepressant treatments: Ligand binding, electrophysiological, and behavioral studies. Life Sci 32:1791–1801
Anggård E, Gunne L-M, Niklasson F (1970) Gas chromatographic determination of amphetamine in blood, tissue, and urine. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 26:137–144
Antelman SM, Chiodo LA (1981) Dopamine autoreceptor subsensitivity: A mechanism common to the treatment of depression and the induction of amphetamine psychosis? Biol Psychiatry 16:717–727
Arnt J, Bøgesø KP, Christensen AV, Hyttel J, Larsen J-J, Svendsen O (1983) Dopamine receptor agonistic and antagonistic effects of 3-PPP enantiomers. Psychopharmacology 81:199–207
Arnt J, Hyttel J, Fredricson Overø K (1984) Prolonged treatment with the specific 5-HT-uptake inhibitor citalopram: Effect on dopaminergic and serotonergic functions. Pol J Pharmacol Pharm 36:221–230
Blier P, De Montigny C (1983) Electrophysiological investigations on the effect of repeated zimelidine administration on serotonergic neurotransmission in the rat. J Neurosci 3:1270–1278
De Montigny C, Aghajanian GK (1978) Tricyclic antidepressants: Long-term treatment increases responsivity of rat forebrain neurons to serotonin. Science 202:1303–1306
Fredricson Overø K (1981) Fluorescence assay of citalopram and its metabolites in plasma by scanning densitometry of thin-layer chromatograms. J Chromatogr 224:526–531
Fredricson Overø K (1982a) Kinetics of citalopram in test animals; drug exposure in safety studies. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 6:297–309
Fredricson Overø K (1982b) Kinetics of citalopram in man; plasma levels in patients. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 6:311–318
Friedman E, Dallob A (1979) Enhanced serotonin receptor activity after chronic treatment with imipramine or amitriptyline. Commun Psychopharmacol 3:89–92
Friedman E, Cooper TB, Dallob A (1983) Effects of chronic antidepressant treatment on serotonin receptor activity in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 89:69–76
Fuxe K, Ogren S-O, Agnati LF, Benfenati F, Fredholm B, Andersson K, Zini I, Eneroth P (1983) Chronic antidepressant treatment and central 5-HT synapses. Neuropharmacology 22:389–400
Green AR, Hall JE, Rees AR (1981) A behavioural and biochemical study in rats of 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor agonists and antagonists, with observations on structure-activity requirements for the agonists. Br J Pharmacol 73:703–719
Hjorth S, Carlsson A, Clark D, Svensson K, Wikström H, Sanchez D, Lindberg P, Hacksell U, Arvidsson L-E, Johansson A, Nilsson JLG (1983) Central dopamine receptor agonist and antagonist actions of the enantiomers of 3-PPP. Psychopharmacology 81:89–99
Horn AS, Philipson OT (1976) A noradrenaline sensitive adenylate cyclase in the rat limbic forebrain: Preparations, properties and the effects of agonists, adrenolytics and neuroleptic drugs. Eur J Pharmacol 37:1–11
Hwang EC, Van Woeft MH (1980) Acute versus chronic effects of serotonin uptake blockers on potentiation of the “serotonin syndrome”. Commun Psychopharmacol 4:161–167
Hyttel J (1982) Citalopram — pharmacological profile of a specific serotonin uptake inhibitor with antidepressant activity. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 6:277–295
Hyttel J, Fredricson Overø K, Arnt J (1984) Biochemical effects and drug levels in rats after long-term treatment with the specific 5-HT-uptake inhibitor, citalopram. Psychopharmacology 83:20–27
Kopanski C, Türck M, Schultz JE (1983) Effects of long-term treatment of rats with antidepressants on adrenergic-receptor sensitivity in cerebral cortex structure activity. Neurochem Int 5:649–659
Kragh-Sørensen P (1983) A controlled, double-blind multicentre trial comparing clomipramine and a new, highly selective 5-HT-uptake-inhibitor, citalopram (Lu 10-171). Abstract. VII World Congress in Psychiatry, Vienna, July 11–16, p 482
Lucki I, Frazer A (1982) Prevention of the serotonin syndrome in rats by repeated administration of monoamine oxidase inhibitors but not tricyclic antidepressants. Psychopharmacology 77:205–211
Maj J, Rogóz Z, Skuza G, Sowińska H (1982) Effects of chronic treatment with antidepressants on aggressiveness induced by clonidine in mice. J neural Transm 55:19–25
Mertens C (1983) A controlled double-blind clinical trial with a new highly selective 5-HT-re-uptake inhibitor, citalopram (Lu 10–171) versus mianserin in depressed patients. Abstract. VII World Congress in Psychiatry, Vienna, July 11–16, p 441
Mogilnicka E, Klimek V (1979) Mianserin, danitracen and amitriptyline withdrawal increases the behavioural responses of rats to 1-5-HTP. J Pharm Pharmacol 31:704–705
Ogren S-O, Fuxe K, Archer T, Johansson G, Holm AC (1982) Behavioural and biochemical studies on the effects of acute and chronic administration of antidepressant drugs on central serotonergic receptor mechanisms. In: Langer SZ, Takahashi R, Segawa T, Briley M (eds) New vistas in depression. Advances in the Biosciences 40: 11–19
Olpe H-R (1981) Differential effects of clomipramine and clorgyline on the sensitivity of cortical neurons to serotonin: Effect of chronic treatment. Eur J Pharmacol 69:375–377
Olpe H-R, Schellenberg A (1980) Reduced sensitivity of neurons to noradrenaline after chronic treatment with antidepressant drugs. Eur J Pharmacol 63:7–13
Ortmann R, Waldmeier PC, Radeke E, Felner A, Delini-Stula A (1980) The effects of 5-HT uptake- and MAO-inhibitors on 1-5-HTP-induced excitation in rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 311:185–192
Pawlowski L, Stach R, Kacz D (1982) Chronic treatment with amitriptyline and zimelidine: Attenuation of serotonin-induced changes in the light-evoked responses from the occipital cortex. In: Langer SZ, Takahashi R, Segawa T, Briley M (eds) New vistas in depression. Advances in the Biosciences 40: 73–80
Peroutka S-J, Lebowitz RM, Snyder SH (1981) Two distinct central serotonin receptors with different physiological functions. Science 212:827–829
Randrup A, Munkvad I, Fog R, Gerlach J, Molander L, Kjellberg B, Scheel-Krüger J (1975) Mania, depression, and brain dopamine. Curr Dev Psychopharmacol 2:206–247
Rolinski Z, Scheel-Krüger J (1973) The effect of dopamine and noradrenaline antagonists on amphetamine induced locomotor activity in mice and rats. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol 33:385–399
Serra G, Argiolas A, Klimek V, Fadda F, Gessa GL (1979) Chronic treatment with antidepressants prevents the inhibitory effect of small doses of apomorphine on dopamine synthesis and motor activity. Life Sci 25:415–424
Serra G, Argiolas A, Fadda F, Melis MR, Gessa GL (1981) Repeated electroconvulsive shock prevents the sedative effect of small doses of apomorphine. Psychopharmacology 73:194–196
Siegel S (1956) Non-parametric statistics for the behavioural sciences. McGraw-Hill Inc., New York
Snyder SH, Peroutka SJ (1982) A possible role of serotonin receptors in antidepressant drug action. Pharmacopsychiatr 15:131–134
Spyraki C, Fibiger HC (1981) Behavioural evidence for supersensitivity of postsynaptic dopamine receptors in the mesolimbic system after chronic administration of desipramine. Eur J Pharmacol 74:195–206
Stoltz JF, Marsden CA, Middlemiss DN (1983) Effect of chronic antidepressant treatment and subsequent withdrawal on 3H-5-hydroxytryptamine and 3H-spiperone binding in rat frontal cortex and serotonin receptor mediated behaviour. Psychopharmacology 80:150–155
Sulser F, Mishra R (1982) Regulation of central noradrenergic receptor function and its relevance to the therapy of depression. In: Langer SZ, Takahashi R, Segawa T, Briley M (eds) New vistas in depression. Advances in the Biosciences 40: 37–47
Van der Waerden BL, Nievergelt E (1956) Tables for comparing two samples by X-test and sign test. Springer Verlag, Berlin
Welch J, Kim H, Fallon S, Liebman J (1982) Do antidepressants induce dopamine autoreceptor subsensitivity? Nature 298:301–302
Wielosz M (1981) Increased sensitivity to dopaminergic agonists after repeated electroconvulsive shock (ECS) in rats. Neuropharmacology 20:941–945
Willner P (1983) Dopamine and depression: A review of recent evidence III. The effects of antidepressant treatments. Brain Res Rev 6:237–246
Yuwiler A, Plotkin S, Geller E, Ritvo ER (1970) A rapid accurate procedure for the determination of serotonin in whole human blood. Biochem Med 3:426–431
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arnt, J., Fredricson Overø, K., Hyttel, J. et al. Changes in rat dopamine- and serotonin function in vivo after prolonged administration of the specific 5-HT uptake inhibitor, citalopram. Psychopharmacology 84, 457–465 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00431450
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00431450