Abstract
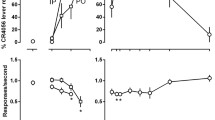
In experiment 1, rats (n=12) were trained to discriminate the benzodiazepine (BDZ) compound chlordiazepoxide (CDP, 20 mg/kg, IP) from saline in a two-lever food-reinforced procedure, and subsequently were tested for stimulus control with different doses of CDP, Ro 15-1788 (a proposed BDZ receptor antagonist) and Ro 15-1788 plus 20 mg/kg CDP. Ro 15-1788 (0.63–40 mg/kg) dose-dependently antagonized CDP, and induced predominantly saline appropriate responding when administered alone. Thereafter, the same rats were retrained by progressively decreasing the training dose, to discriminate 2.5 mg/kg CDP from saline, and were tested again with the same compounds. Ro 15-1788 (0.16–40 mg/kg) now failed to antagonize CDP (2.5 mg/kg) and increased the percentage of drug-appropriate responding in a dose-related manner when administered alone. In experiment 2, separate groups of rats (n=10) were similarly trained to discriminate either 15 or 3 mg/kg CDP from saline. Tests with CDP, Ro 15-1788 and Ro 15-1788 plus CDP (either 15 or 3 mg/kg) yielded similar results to experiment 1, suggesting that the training dose effects on generalization and antagonism of Ro 15-1788 were not affected by the manner in which the lower CDP dose acquired drug stimulus control. It is concluded that mixed agonist-antagonist properties are apparent after-variations of the BDZ training dose in a drug discrimination procedure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albertson TE, Bowyer JF, Paule MG (1982) Modification of the anticonvulsant efficacy of diazepam by Ro 15-1788 in the kindled amygdaloid seizure model. Life Sci 31:1597–1601
Bonetti EP, Pieri L, Cumin R, Schaffner R, Pieri M, Gamzu ER, Müller RKM, Haefely W (1982) Benzodiazepine antagonist Ro 15-1788: neurological and behavioral effects. Psychopharmacology 78:8–18
Colpaert FC (1977) Discriminative stimulus properties of benzodiazepines and barbiturates. In: Lal H (ed) Discriminative stimulus properties of drugs. Plenum Press, New York, pp 93–106
Colpaert FC, Niemegeers CJE, Janssen PAJ (1976) Theoretical and methodological considerations on drug discrimination learning. Psychopharmacologia 46:169–177
Colpaert FC, Niemegeers CJE, Janssen PAJ (1980) Factors regulating drug cue sensitivity: the effect of training dose in fentanylsaline discrimination. Neuropharmacology 19:705–713
Colpaert FC, Slangen JL (eds) (1982) Drug discrimination: Applications in CNS pharmacology. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Corda MG, Costa E, Guidotti A (1982) Specific proconvulsant action of an imidazobenzodiazepine (Ro 15-1788) in isoniazid convulsions. Neuropharmacology 21:91–94
Dantzer R, Pério A (1982) Behavioral evidence for partial agonist properties of Ro 15-1788, a benzodiazepine receptor antagonist. Eur J Pharmacol 81:655–658
De Vry J, Slangen JL (1985a) Differential interactions between chlordiazepoxide, pentobarbital and benzodiazepine antagonists Ro 15-1788 and CGS 8216 in a drug discrimination procedure. Pharmacol Biochem Behav (in press)
De Vry J, Slangen JL (1985b) Effects of training dose on discrimination and cross-generalization of chlordiazepoxide, pentobarbital and ethanol in the rat. Psychopharmacology (in press)
De Vry J, Slangen JL (1985c) Stimulus control induced by benzodiazepine antagonist Ro 15-1788 in the rat. Psychopharmacology 85:483–485
File SE, Lister RG, Nutt DJ (1982a) The anxiogenic actions of benzodiazepine antagonists. Neuropharmacology 21:1033–1037
File SE, Lister RG, Nutt DJ (1982b) Intrinsic actions of benzodiazepine antagonists. Neurosci Lett 32:165–168
Gherezghiher T, Lal H (1982) Ro 15-1788 selectively reverses antagonism of pentylenetetrazol-induced discriminative stimuli by benzodiazepines but not by barbiturates. Life Sci 31:2955–2960
Haefely W, Bonetti EP, Burkard WP, Cumin R, Laurent JP, Möhler H, Pieri L, Polc P, Richards JG, Schaffner R, Scherschlicht R (1983) Benzodiazepine antagonists. In: Costa E (ed) The benzodiazepines: From molecular biology to clinical practice. Raven Press, New York, pp 137–146
Haug T, Götestam KG (1982) The diazepam stimulus complex: specificity in a rat model. Eur J Pharmacol 80:225–230
Herling S, Shannon HE (1982) Ro 15-1788 antagonizes the discriminative stimulus effects of diazepam in rats but not similar effects of pentobarbital. Life Sci 31:2105–2112
Holtzman SG (1982) Discriminative stimulus properties of opioids in the rat and squirrel monkey. In: Colpaert FC, Slangen JL (eds) Drug discrimination: Applications in CNS pharmacology. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 17–36
Holtzman SG (1983) Discriminative stimulus properties of opioid agonists and antagonists. In: Cooper SJ (ed) Theory in psychopharmacology. Volume 2. Academic Press, London, pp 1–45
Järbe TUC, McMillan DE (1983) Interaction of the discriminative stimulus properties of diazepam and ethanol in pigeons. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 18:73–80
Jensen LH, Petersen EN, Braestrup C, Honoré T, Kehr W, Stephens DN, Schneider H, Seidelmann D, Schmiechen R (1984) Evaluation of the β-carboline ZK 93 426 as a benzodiazepine receptor antagonist. Psychopharmacology 83:249–256
Koek W, Slangen JL (1982) The role of fentanyl training dose and of the alternative stimulus condition in drug generalization. Psychopharmacology 76:149–156
Koek W, Slangen JL (1984) External stimulus control in a “drug-discrimination” procedure: Drug effects and inter-animal variation. Psychopharmacology 82:168–173
Kuhn DM, Appel JB, Greenberg J (1974) An analysis of some discriminative properties of d-amphetamine. Psychopharmacologia 39:57–66
Lal H, Shearman GT, Ticku M, Bennett DA (1981) Dihydromethylbenzodiazepine (DMB): A possible anxiogenic ligand with a novel neurochemical profile. Fed Proc 40:310
Lloyd KG, Bovier P, Broekkamp C, Worms P (1981) Reversal of the antiaversive and anticonvulsant actions of diazepam, but not of progabide, by a selective antagonist of benzodiazepine receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 75:77–78
McElroy J, Feldman R (1982) Generalization between benzodiazepine — and triazolopyridazine — elicited discriminative cues. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 17:709–713
Nielsen EB, Jepsen SA, Nielsen M, Braestrup C (1985) Discriminative stimulus properties of methyl 6,7-dimethoxy-4-ethyl-β-carboline-3-carboxylate (DMCM), an inverse agonist at benzodiazepine receptors. Life Sci 36:15–23
Nielsen EB, Valentine JD, Holohean A, Appel JB (1983) Benzodiazepine receptor mediated discriminative cues: effects of GABA-ergic drugs and inverse agonists. Life Sci 33:2213–2220
Nutt DJ, Cohen PJ, Little HJ (1982) Unusual interactions of benzodiazepine receptor antagonists. Nature 295:436–438
Overton DA (1976) Discriminable effects of benzodiazepines. Psychopharmacol Commun 2:339–343
Overton DA (1979) Drug discrimination training with progressively lowered doses. Science 205:720–721
Shannon HE, Herling S (1983) Discriminative stimulus effects of diazepam in rats: evidence for a maximal effect. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 227:160–166
Shannon HE, Holtzman SG (1979) Morphine training dose: a determinant of stimulus generalization to narcotic antagonists in the rat. Psychopharmacology 61:239–244
Siegel S (1956) Nonparametric statistics for the behavioral sciences. McGraw-Hill, New York
Stephens DN, Shearman GT, Kehr W (1984) Discriminative stimulus properties of β-carbolines characterized as agonists and inverse agonists at central benzodiazepine receptors. Psychopharmacology 83:233–239
Stolerman IP, D'Mello GD (1981) Role of training conditions in discrimination of central nervous system stimulants by rats. Psychopharmacology 73:295–303
Stolerman IP, Garcha HS, Kumar R (1984) Role of training dose in discrimination of nicotine and related compounds by rats. Psychopharmacology 84:413–419
Tallarida RJ, Murray RB (1981) Manual of pharmacologic calculations. Springer-Verlag, New York
Teal JJ, Holtman SG (1980) Stimulus effects of morphine in the monkey: quantitative analysis of antagonism. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 12:587–593
Wauquier A, Ashton D (1984) The benzodiazepine antagonist, Ro 15-1788, increases REM and slow wave sleep in the dog. Brain Res 308:159–161
White FJ, Appel JB (1982) Training dose as a factor in LSD — saline discrimination. Psychopharmacology 76:20–25
Winer BJ (1971) Statistical principles in experimental design, 2nd edn. McGraw-Hill, New York
Young R, Dewey WL (1982) Differentiation of the behavioral responses produced by barbiturates and benzodiazepines by the benzodiazepine antagonist Ro 15-1788. In: Colpaert FC, Slangen JL (eds) Drug discrimination: Applications in CNS pharmacology. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 235–240
Young R, Rosecrans JA, Glennon RA (1983) Behavioral effects of 5-methoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine and dose-dependent antagonism by BC-105. Psychopharmacology 80:156–160
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Vry, J., Slangen, J.L. Effects of chlordiazepoxide training dose on the mixed agonist-antagonist properties of benzodiazepine receptor antagonist Ro 15-1788, in a drug discrimination procedure. Psychopharmacologia 88, 177–183 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00652236
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00652236