Abstract
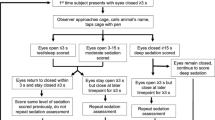
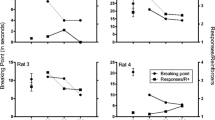
The behaviour of partially pre-satiated rats consuming a sweet palatable food and treated with either vehicle or the specific kappa receptor agonist U-50,488H (0.1–3 mg/kg) was recorded on videotape. Analysis revealed that the hyperphagia induced by the kappa agonist (0.3–3 mg/kg) resulted from an increase in the duration of feeding and not from an increase in the local rate of eating. The increase in duration was due, in turn, to a greater frequency of bouts of feeding. The kappa agonist also increased the latency to the final feeding bout. The effect of U-50,488H was consistent with de-satiation, so that the increase in feeding duration was in evidence from the start of the test period, while the temporal pattern of later satiation was preserved but lagged behind that of control animals. At the largest dose, other recorded activities (rearing, locomotor activity, grooming) were suppressed, with a marked increased in inactivity. At the lowest dose (0.1 mg/kg) there was a significant increase in grooming behaviour. The results are discussed with reference to an hypothesis of opioid function in the control of food intake.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aloyo VJ, Spruijt B, Zwiers H, Gispen WH (1983) Peptide-induced excessive grooming in the rat: the role of opiate receptors. Peptides 4:833–836
Blundell JE, Latham CJ (1978) Pharmacological manipulation of feeding behaviour: possible influences of serotonin and dopamine on food intake. In: Garattini S, Samanin R (eds) Central mechanisms of anorectic drugs. Raven, New York, pp 83–108
Castellano C, Pavone F, Sansone M (1984) Locomotor depression by the opioid benzodiazepine tifluadom in mice. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 270:318–323
Chavkin C, James IF, Goldstein A (1982) Dynorphin is a specific endogenous ligand of the opioid receptor. Science 215:413–415
Cooper SJ, Jackson A, Kirkham TC (1985a) Endorphins and food intake: kappa opioid receptor agonists and hyperphagia. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 23:889–901
Cooper SJ, Jackson A, Morgan R, Carter R (1985b) Evidence for opiate receptor involvement in the consumption of a high palatability diet in nondeprived rats. Neuropeptides 5:345–348
Dourish CT, Cooper SJ, Philips SR (1985) Yawning elicited by systemic and intrastriatal injection of piribedil and apomorphine in the rat. Psychopharmacology 86:175–181
Gosnell BA, Morley JE, Levine AS (1984) Lesions of the globus pallidus and striatum attenuate ketocyclazocine-induced feeding. Physiol Behav 33:349–355
Gwynn GJ, Domino EF (1984) Genotype-dependent behavioural sensitivity to mu vs. kappa opiate agonists. I. Acute and chronic effects on mouse locomotor activity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 231:306–311
Jackson A, Cooper SJ (1985) Effects of kappa opiate agonists on palatable food consumption in non-deprived rats, with and without food preloads. Brain Res Bull 15:391–396
Jackson HC, Sewell RDE (1984) The role of opioid receptor subtypes in tifluadom-induced feeding. J Pharm Pharmacol 36:683–686
Katz RJ (1980) Behavioural effects of dynorphin — a novel opioid neuropeptide. Neuropharmacology 19:801–803
Kavaliers M, Teskey GC, Hirst M (1985) The effects of aging on day-night rhythms of kappa opiate-mediated feeding in the mouse. Psychopharmacology 87:286–291
Kirkham TC (1985) Investigation of opioid mechanisms in the control of feeding behaviour. Unpublished PhD thesis, University of Leeds
Lynch WC, Watt J, Krall S, Paden CM (1985) Autoradiographic localisation of kappa opiate receptors in CNS taste and feeding areas. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 22:699–705
Morley JE, Levine AS, Grace M, Kniep J (1982) An investigation of the role of kappa opiate receptor agonists in the initiation of feeding. Life Sci 2617–2626
Morley JE, Levine AS, Kniep J, Grace M, Zeugner H, Shearman GT (1985) The opioid receptor and food intake. Eur J Pharmacol 112:17–25
Mulder AH, Wardeh G, Hogenboom F, Frankhuyzen AL (1984) K-and δ;-opioid receptor agonists differentially inhibit striatal dopamine and acetylcholine release. Nature 308:278–280
Sanger DJ, McCarthy PSD (1981) Increased food and water intake produced in rats by opiate receptor agonists. Psychopharmacology 74:217–220
Ukai M, Kameyama T (1984) The antagonistic effect of naloxone on hypermotility in mice induced by dynorphin (1–13) using a multi-dimensional behavioural analysis. Neuropharmacology 23:165–168
Ukai M, Yamada S, Kameyama T (1984) Naloxone reverses the inhibitory effects of dynorphin A on motor activity in the mouse. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 20:815–818
VonVoigtlander PF, Lahti RA, Ludens JH (1983) U-50,488: a selective and structurally novel non-mu (kappa) opioid agonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 224:7–12
Walker JM, Katz RJ, Akil H (1980) Behavioural effects of dynorphin (1–13) in the mouse and rat: initial observations. Peptides 1:341–345
Yamada K, Furukawa T (1980) Direct evidence for involvement of dopaminergic inhibition and cholinergic activation in yawning. Psychopharmacology 67:39–43
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jackson, A., Cooper, S.J. An observational analysis of the effect of the selective kappa opioid agonist, U-50,488H, on feeding and related behaviours in the rat. Psychopharmacology 90, 217–221 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00181245
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00181245