Abstract
-
1.
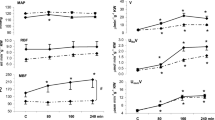
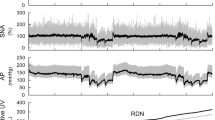
The effect of varying renal artery pressure between 160 and 40 mm Hg on renal blood flow and renin release was studied in seven conscious foxhounds under β-adrenergic blockade receiving a normal sodium diet (4.1 mmol/kg/day). Pressure was either increased by bilateral common carotid occlusion or reduced in steps and maintained constant by a control-system using an inflatable renal artery cuff. Carotid occlusion itself had no influence on renal blood flow and renin release when renal artery pressure was kept constant and the β-receptors in the kidney were blocked.
-
2.
Between 160 mm Hg and resting pressure there was no change in renal blood flow; between resting blood pressure and the lower limit of autoregulation (average 63.9 mm Hg) renal blood flow increased slightly (average 7%) indicating a high efficiency of renal blood flow autoregulation.
-
3.
The relationship between renal artery pressure and renin release could be approximated by two linear sections:a low sensitivity to a pressure change (average slope: −0.69 ±0.26ng AI/min/mm Hg) was found above a threshold pressure (average: 89.8±3.3 mm Hg) and a high sensitivity to a pressure change (average slope: −64.4±20.8 ng AI/ min/mm Hg) was observed between threshold pressure and 60 mm Hg. There was no further increase of renin release between 60 and 40 mm Hg.
-
4.
It is concluded that within the autoregulatory plateau the kidney of a conscious β-blocked dog receiving a normal sodium diet releases only negligible amounts of renin until renal artery pressure falls below a threshold pressure of 90 mm Hg which is close to the animals resting systemic pressure. Since beyond that a decrease of systemic pressure by as little as 1.3 mm Hg below threshold can raise resting renin release (84.8±29.8 ng/min) by 100%, it is suggested that systemic blood pressure tends to stabilize at a level at which renin release is minimal.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe Y Kishimoto T, Yamamoto K (1976) Relationship between renin secretion and renal autoregulation in the dog. Jpn Circ J 40:935–943
Aukland K (1976) Renal blood flow. In: Thurau K (ed) International review of physiology, kidney and urinary-tract physiology II, vol 11. University Park Press, Baltimore, pp 23–79
Blaine EH, Davis JO, Prewitt RL (1971) Evidence for a renal vascular receptor in control of renin secretion. Am J Physiol 220:1593–1597
Blaine EH, Zimmermann MB (1979) Renin secretion during dynamic changes in renal perfusion pressure. Am J Physiol 236:F546-F551
Boknam L, Ericson AC, Åberg B, Ulfendahl HR (1981) Flow resistance of the interlobular artery in the rat kidney. Acta Physiol Scand 111:159–163
Cowley AW, Guyton AC (1972) Quantification of intermediate steps in the renin-angiotensin-vasoconstrictor feedback loop in the dog. Circ Res 30:557–566
Davis JO, Freeman RH (1976) Mechanisms regulating renin release. Physiol Rev 56:1–56
Eide I, Løyning E, Kiil F (1973) Evidence for hemodynamic autoregulation of renin release. Circ Res 32:237–245
Eide I, Løyning E, Langard O, Kiil F (1977) Mechanism of renin release during acute ureteral constriction in dogs. Circ Res 40:293–299
Fahri ER, Cant JR, Barger AC (1982a) Interactions between intrarenal epinephrine receptors and the renal baroreceptor in the control of PRA in conscious dogs. Circ Res 50:477–485
Fahri ER, Cant JR, Barger AC (1982b) Changes in salt intake affect the stimulus-response curve of the renal baroreceptor controlling plasma renin activity in conscious dogs. Fed Proc 41:1670, Abstr. 8186
Fiorentini C, Guazzi MD Olivari MT, Bartotelli A, Necchi G, Magrini F (1981) Selective reduction of renal perfusion pressure and blood flow in man: humoral and hemodynamic effects. Circulation 63:973–978
Fojas JF, Schmid HE (1970) Renin release, renal autoregulation, and sodium excretion in the dog. Am J Physiol 219:464–468
Fray JCS (1976) Stretch receptor model for renin release with evidence from perfused rat kidney. Am J Physiol 231:936–944
Gilmore JP, Cornish KG, Rogers SD, Joyner WL (1980) Direct evidence for myogenic autoregulation of the renal microcirculation in the hamster. Circ Res 47:226–230
Gotshall RW, Davis JO, Blaine EH, Musacchia XJ, Braverman R, Freeman R, Johnson JA (1974) Increased renin release during renal arteriolar dilatation in dogs. Am J Physiol 227:251–255
Gross R, Kirchheim H, Brandstetter K (1976) Basal vascular tone in the kidney. Evaluation from the static pressure-flow relationship under normal autoregulation and at maximal dilation in the dog. Circ Res 38:525–531
Gross R, Ruffmann K, Kirchheim H (1979) The separate and combined influence of common carotid occlusion and nonhypotensive hemorrhage on kidney blood flow. Pflügers Arch 379:81–88
Gross R, Kirchheim H (1980) Effects of carotid occlusion and auditory stimulation on renal blood flow and sympathetic nerve activity in the conscious dog. Pflügers Arch 383:233–239
Gross R, Hackenberg H, Hackenthal E, Kirchheim H (1981a) Interaction between perfusion pressure and sympathetic nerves in renin release by carotid baroreflex in conscious dogs. J Physiol (Lond) 313:237–250
Gross R, Kirchheim H, Ruffmann K (1981b) Effect of carotid occlusion and of perfusion pressure on renal function on conscious dogs. Circ Res 48:777–784
Gutmann FD, Tagawa H, Haber E, Barger AC (1973) Renal artery pressure, renin secretion and blood pressure control in trained dogs. Am J Physiol 224:66–72
Hackenthal E, Hackenthal R, Hofbauer KG (1977) No evidence for product inhibition of the renin-angiotensiongen reaction in the rat. Circ Res 41 (Suppl II):49–54
Hall JE, Guyton AC, Jackson TE, Granger JP, Kastner PhR (1981) Autoregulation of glomerular filtration: role of renin-angiotensin system. Proc 8th Int Congr Nephrol (Athens), pp 162–169
Harris RC, Ayers CR (1972) Renal hemodynamics and plasma renin activity after renal artery constriction in conscious dogs Circ Res 31:520–530
Heller J, Horacek V, Kasalicky J (1979) Renal blood flow distribution at varying perfusion pressure in the alloperfused dog kidney. Pflügers Arch 382:91–98
Heller J, Horacek V (1979) Autoregulation of superficial nephron function in the alloperfused dog kidney. Pflügers Arch 382:99–104
Herd J, Barger AC (1964) Simplified technique for chronic catheterization of blood vessels. J Appl Physiol 19:791–792
Heyeraas-Tønder KJ, Aukland K (1979) Interlobular arterial pressure in the rat kidney. Renal Physiol 2:214–221
Johnson PC (1980) The myogenic response. In: Handbook of physiology, section II: The cardiovascular system, vol 2: Vascular smooth muscle. Am Physiol Soc, Bethesda, Maryland, pp 409–442
Kaloyanides GJ, Bastron RD, DiBona GF (1973) Effect of ureteral clamping and increased renal arterial pressure on renin release. Am J Physiol 225:95–99
Källskog Ö, Lindbom LO, Ulfendahl HR Wolgast M (1976) Hydrostatic pressures within the vascular structures of the rat kidney. Pflügers Arch 363:205–210
Keeton TK, Campell WB (1980) The pharmacologic alterations of renin release. Pharmacol Rev 31:81–227
Kiil F (1975) Influence of autoregulation on renin release and sodium excretion. Kidney Int 8 (Suppl):208–218
Kirchheim H, Gross R, Hackenberg HM, Hackenthal E, Huber J (1981) Autoregulation of renin release and its modification by renal sympathetic nerves in conscious dogs. Kidney Int 20 (Abstract) 152
Kopp U, Aurell M, Nilsson IM, Åblad B (1980) The role of beta-1-adrenoceptors in the renin release response to graded renal sympathetic nerve stimulation. Pflügers Arch 387:107–113
Kopp U, Aurell M, Sjölander M, Åblad B (1981) The role of prostaglandins in the alpha- and beta-adrenoceptor mediated renin release response to graded renal nerve stimulation. Pflügers Arch 391:1–8
La Grange RG, Sloop ChH, Schmid HE (1973) Selective stimulation of renal nerves in the anaesthetized dog. Circ Res 33:704–712
Lalone BJ, Sullivan SM, Johnson PC (1977) Blood flow autoregulation in cat sartorius muscle (Abstract). Fed Proc 36:526
Langård O, Holdaas H, Eide I, Kiil F (1981) Condition for humoral alpha-adrenoceptor stimulation of renin release in anaesthetized dogs. Scand J Clin Invest 41:527–534
Mangelsen EL, Malvin RL (1978) Renin secretion: transient response to a step reduction in arterial pressure. Renal Physiol 1:247–253
Navar LG, Bell PD, White RW, Watts RL, Williams RH (1977) Evaluation of the single nephron glomerular filtration coefficient in the dog kidney. Kidney Int 12:137–149
Osborn J, DiBona GF, Thames MD (1981) Beta-1-receptor mediation of renin secretion elicited by low-frequency renal nerve stimulation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 216:265–269
Oster P, Bauknecht H, Hackenthal E (1975) Active and passive immunization against angiotensin II in the rat and rabbit Evidence for a normal regulation of the renin-angiotensin-system. Circ Res 37:607–614
Schmid HE (1972) Renal autoregulation and renin release during changes in renal perfusion pressure. Am J Physiol 2221132–1137
Skinner SL, McCubbin JW, Page IH (1964) Control of renin secretion. Circ Res 15:64–76
Taher MS, McLain LG, Donald KM, Schrier RW (1976) Effect of betaadrenergic blockade on renin response to renal nerve stimulation. J Clin Invest 57:459–465
Taugner Ch, Poulsen K, Hackenthal E, Taugner R (1979) Immunocytochemical localization of renin in mouse kidney. Histochemistry 62:19–27
Taugner R, Hackenthal E, Nobiling R, Harlacher M, Reb G (1981) The distribution of renin in the different segments of the arterial tree. Immunocytological investigations in the mouse kidney. Histochemistry 73:75–88
Thurau K, Dahlheim M, Grüner A, Mason J, Granger P (1972) Activation of renin in the single juxtaglomerular apparatus by sodium-chloride in the tubular fluid at the macula densa. Circ Res 30/31, Suppl II:182–186
Tobian L, Tomboulian A, Janacek J (1959) Effect of high perfusion pressure on the granulation of juxtaglomerular cells in an isolated kidney. J Clin Invest 38:605–610
Wallenstein S, Zucker ChL, Fleiss JL (1980) Some statistical methods useful in circulation research. Circ Res 47:1–9
Zschiedrich H, Hofbauer KH, Baron GD, Hackenthal E, Gross F (1975) Relationship between perfusion pressure and renin release in the isolated rat kidney. Pflügers Arch 360:255–266
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This study was supported by the German Research Foundation within the SFB 90, Heidelberg
A preliminary report of a part of this investigation has been presented to the meeting of the German Society of Nephrology, Würzburg, October 1980 (Kidney Int. 20, 152, 1981)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Finke, R., Gross, R., Hackenthal, E. et al. Threshold pressure for the pressure-dependent renin release in the autoregulating kidney of conscious dogs. Pflugers Arch. 399, 102–110 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00663904
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00663904