Abstract
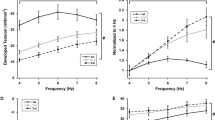
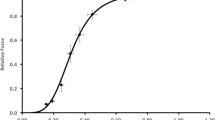
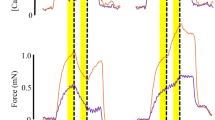
This study compares changes in contractile properties, Parvalbumin content, and Ca2+-uptake by the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) of low-frequency stimulated rat and rabbit tibialis anterior (TA) muscles. Time to peak tension increased 1.8-fold in 35-day stimulated rabbit TA, while no change occurred in rat TA. Isometric twitch tension increased 2-fold in rabbit TA, but was unaltered in rat TA. Parvalbumin (PA) content was more than 90% reduced in rabbit TA, but only 60% in rat TA after 35 days. At this time, PA content of the stimulated rat TA was still higher than that of normal rabbit TA. Taking into account the suggested role of PA as a cytosolic Ca2+ buffer, its decrease could lead to an impaired free Ca2+-decay with a prolonged active state and a higher tension output during a single twitch. This would explain why chronic stimulation led to an increase in isometric twitch tension in rabbit TA, but not in rat TA. The 1.6-fold rise in half-relaxation time of 35-day stimulated rat and rabbit TA most likely resulted from a 50% reduced Ca2+-uptake by the SR, due to a still unknown modification of the Ca2+-transport ATPase.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bär A, Simoneau J-A, Pette D (1989) Altered expression of myosin light chain isoforms in chronically stimulated fast-twitch muscle of the rat. Eur J Biochem 178:591–594
Brown WE, Salmons S, Whalen RG (1983) The sequential replacement of myosin subunit isoforms during muscle type transformation induced by long term electrical stimulation. J Biol Chem 258:14686–14692
Eisenberg BR, Salmons S (1981) The reorganization of subcellular structure in muscle undergoing fast-to-slow type transformation: a stereological study. Cell Tissue Res 220:449–471
Exner GU, Staudte HW, Pette D (1973) Isometric training of rats-Effects upon fast and slow muscle and modification by an anabolic hormone (Nandrolone Decanoate). I. Female rats Pflügers Arch 345:1–14
Gerday C, Gillis JM (1976) The possible role of parvalbumin in the control of contraction. J Physiol (Lond) 258:96P
Gillis JM, Thomason D, Lefèvre J, Kretsinger RH (1982) Parvalbumin and muscle relaxation: a computer simulation study. J Muscle Res Coll Motil 3:377–398
Härtner K-T, Kirschbaum BJ, Pette D (1989) The multiplicity of troponin T isoforms. Normal rabbit muscles and effects of chronic stimulation. Eur J Biochem 179:31–38
Heilmann C, Pette D (1979) Molecular transformations in sarcoplasmic reticulum of fast-twitch muscle by electro-stimulation. Eur J Biochem 93:437–446
Kirschbaum BJ, Simoneau J-A, Bär A, Barton PJR, Buckingham ME, Pette D (1989) Chronic stimulation-induced changes of myosin light chains at the mRNA and protein levels in rat fast-twitch muscle. Eur J Biochem 179:23–29
Klug G, Reichmann H, Pette D (1983) Rapid reduction in parvalbumin concentration during chronic stimulation of rabbit fast-twitch muscle. FEBS Lett 152:180–182
Klug GA, Leberer E, Leisner E, Simoneau J-A, Pette D (1988) Relationship between parvalbumin content and the speed of relaxation in chronically stimulated rabbit fast-twitch muscle. Pflügers Arch 411:126–131
Kwong WH, Vrbová G (1981) Effects of low-frequency electrical stimulation on fast and slow muscles of the rat. Pflügers Arch 391:200–207
Leberer E, Pette D (1986) Neural regulation of parvalbumin expression in mammalian skeletal muscle. Biochem J 235:67–73
Leberer E, Härtner K-T, Pette D (1987a) Reversible inhibition of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca-ATPase by altered neuromuscular activity in rabbit fast-twitch muscle. Eur J Biochem 162:555–561
Leberer E, Klug GA, Seedorf U, Pette D (1987b) Regulation of parvalbumin concentration in mammalian muscle. In: Means AR, Conn PM (eds) Cellular regulators, part A, calcium- and calmodulin-binding proteins, methods in enzymology, vol 139. Academic Press, New York London pp 763–776
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Mabuchi K, Szvetko D, Pinter K, Sréter FA (1982) Type IIB to IIA fiber transformation in intermittently stimulated rabbit muscles. Am J Physiol. 242:C373-C381
Maier A, Gambke B, Pette D (1986) Degeneration-regeneration as a mechanism contributing to the fast to slow conversion of chronically stimulated fast-twitch rabbit muscle. Cell Tissue Res 244:635–643
Maier A, Gorza L, Schiaffino S, Pette D (1988) A combined histochemical and immunohistochemical study on the dynamics of fast to slow fiber transformation in chronically stimulated rabbit muscle. Cell Tissue Res 254:59–68
Pette D, Smith ME, Staudte HW, Vrbová G (1973) Effects of longterm electrical stimulation on some contractile and metabolic characteristic of fast rabbit muscles. Pflügers Arch 338:257–272
Pette D, Müller W, Leisner E, Vrbová G (1976) Time dependent effects on contractile properties, fibre population, myosin light chains and enzymes of energy metabolism in intermittently and continuously stimulated fast twitch muscle of the rabbit. Pflügers Arch 364:103–112
Salmons S, Vrbová G (1969) The influence of activity on some contractile characteristics of mammalian fast and slow muscles. J Physiol (Lond) 201:535–549
Schachat F, Williams RS, Schnurr CA (1988) Coordinate changes in fast thin filament and Z-line protein expression in the early response to chronic stimulation. J Biol Chem 263:13975–13978
Schwarz G, Leisner E, Pette D (1983) Two telestimulation systems for chronic indirect muscle stimulation in caged rabbits and mice. Pflügers Arch 398:130–133
Seedorf K, Seedorf U, Pette D (1983) Coordinate expression of alkali and DTNB myosin light chains during transformation of rabbit fast muscle by chronic stimulation. FEBS Lett 158:321–324
Simoneau J-A, Pette D (1988) Species-specific effects of chronic nerve stimulation upon tibialis anterior muscle in mouse, rat, guinea pig, and rabbit Pflügers Arch 412:86–92
Simoneau J-A, Pette D (1989) Species-specific responses of muscle lactate dehydrogenase isozymes to increased contractile activity. Pflügers Arch 413:679–681
Sréter FA, Gergely J, Salmons S, Romanul F (1973) Synthesis by fast muscle of myosin light chains characteristic of slow muscle in response to long-term stimulation. Nature 241:17–19
Staron RS, Gohlsch B, Pette D (1987) Myosin polymorphism in single fibers of chronically stimulated rabbit fast-twitch muscle. Pflügers Arch 408:444–450
Sweeney LH, Kushmerick MJ, Mabuchi K, Sréter FA, Gergely J (1988) Myosin alkali light chain and heavy chain variations correlate with altered shortening velocity of isolated skeletal muscle fibers. J Biol Chem 263:9034–9039
Tyler KR, Wright AJA (1980) Light weight portable stimulators for stimulation of skeletal muscles at different frequencies and for cardiac pacing. J Physiol 307:6P-7P
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Simoneau, JA., Kaufmann, M., Härtner, KT. et al. Relations between chronic stimulation-induced changes in contractile properties and the Ca2+-sequestering system of rat and rabbit fast-twitch muscles. Pflugers Arch. 414, 629–633 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00582127
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00582127