Abstract
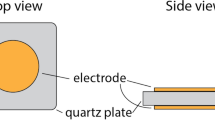
A method for the manufacture of ion-sensitive micro-electrodes, which can be readily used with small single cells, is described in detail. A glass pipette with a tip size of 1 μm, essentially similar to those used as suction electrodes in whole-cell recording, when silanized and with its tip filled with a suitable ion-sensitive resin, producesan ion-sensitive electrode with fast electrical and chemical response times. These electrodes can be applied to the cell membrane of isolated myocytes and penetration achieved without cell damage, by the application of suction. For the estimation of intracellular ionic activities they can be used in conjunction with a separate conventional KCl-filled micro-electrode or a suction voltage electrode. The technique is illustrated by the measurement of intracellular Na+, Ca2+ and pH. It is possible that these electrodes can also be used to measure local changes in ionic activity in restricted areas.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bountra C, Powell T, Vaughan-Jones RD (1987) Comparison of micro-electrode measurement of intracellular pH in cardiac ventricular tissue and isolated ventricular cells of guinea-pig. J Physiol (Lond) 390:58 P
Boyett MR, Capogrossi MC, DuBell WH, Lakatta EG, Spurgeon AJ (1989) Cytosolic Ca2+ modulation of the action potential in rat ventricular myocytes. J Physiol (Lond) 415:109P
Chapman RA (1986) Sodium/calcium exchange and intracellular calcium buffering in ferret myocardium: an ion-sensitive microelectrode study. J Physiol (Lond) 373:163–179
Chapman RA, Tunstall J (1987) The calcium paradox of the heart. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 50:67–96
Chapman RA, Rodrigo Glenn C (1987) Intracellular sodium activity in isolated guinea-pig myocytes in normal Tyrode solution and during exposure to calcium-free solution. J Physiol (Lond) 386:116P
Chapman RA, Rodrigo Glenn C (1989) An estimate of the Ca influx associated with the calcium repletion phase of the calcium paradox of isolated guinea-pig ventricular myocytes. J Physiol (Lond) 410:70 P
Donoso P, Eisner DA, O'Neill SC (1989) Measurement of [Na]i in isolated rat cardiac myocytes using the fluorescent indicator SBFI. J Physiol (Lond) 418:48P
Dunlop W, Gillespie JI, Greenwell JR, Otun H (1989) Measurement of intracellular calcium (Ca 2+i ) and sodium (Na+) in single cultured rat smooth muscle cells (A10) using the fluorescent dyes Fura-2 and SBFI. J Physiol (Lond) 418:201P
Eisner DA, Lederer WJ, Vaughan-Jones RD (1981) The dependence of sodium pumping and tension on intracellular sodium activity in voltage clamped sheep Purkinje fibres. J Physiol (Lond) 317:163–187
Fozzard HA, Chapman RA, Friedlander IR (1985) Measurement of intracellular calcium ion activity with neutral exchanger ion sensitive microelectrodes. Cell Calcium 6:57–68
Isenberg G, Klockner U (1982) Calcium tolerant ventricular myocytes prepared by preincubation in a “KB-medium”. Pflügers Arch 395:6–18
January CT, Fozzard HA (1984) The effects of membrane potential, extracellular potassium and tetrodotoxin on the intracellular sodium activity of sheep cardiac muscle. Circ Res 54:652–665
Lambert MR, Johnson JD, Lamka KG, Brierley GP, Altschuld RA (1986) Intracellular free Ca and the hypercontracture of adult rat heart myocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys 245:426–435
Lee CO (1981) Ionic activities in cardiac muscle cells an application of ion-sensitive micro-electrodes. Am J Physiol 241: H459-H478
Mitra R, Morad M (1985) A uniform enzymatic method for dissociation of myocytes from hearts and stomachs of vertebrates. Am J Physiol 249:H1056-H1060
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodrigo, G.C., Chapman, R.A. A novel resin-filled ion-sensitive micro-electrode suitable for intracellular measurements in isolated cardiac myocytes. Pflügers Arch 416, 196–200 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00370242
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00370242