Summary
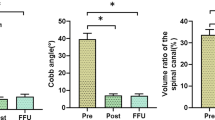
Surgical reconstruction and fusion form the treatment of choice for unstable thoracolumbar fractures. It remains difficult, however, to prove that surgical treatment provides an increased potential for neurological recovery. Also, the role of a decompressive laminectomy is still unclear. To address these issues, 93 consecutive cases of thoracolumbar fractures treated with dorsal instrumentation were reviewed. The neurological status at the time of admission and at a mean of 26 months postinjury was graded according to a modified Frankel scale. By using preoperative radiographs and computed tomography scans, we differentiated between fracture-dislocation lesions, dislocation lesions, flexion-distraction lesions, complete and incomplete burst fractures. Spinal stenosis was classified from grade 0 (no stenosis) to grade 3 (> 66% stenosis). All thoracolumbar fractures were treated with posterior instrumentation, using Dick's fixateur interne and Steffee's VSP plates and screws. During this procedure, laminectomy was performed in 33 patients (35%). In 17 cases (52% of the laminectomies), a surgically treatable lesion (dural tear, trapped nerve root, etc.) was found, especially in patients with a combination of a neurological deficit and a dislocation lesion, a fracture-dislocation lesion or a complete burst fracture with spinal stenosis grade 2 or 3. The neurological and functional outcome was excellent: none of the patients deteriorated, 68% made a complete neurological recovery, and 61% regained their previous level of activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aebi M, Etter C, Kehl T, Thalgott J (1987) Stabilization of the lower thoracic and lumbar spine with the internal spine skeletal fixation system: indications, techniques and first results. Spine 12:544–551
Braakman R (1986) The value of more aggressive management in traumatic paraplegia. Neurosurg Rev 141–147
Daniaux H (1986) Transpedikuläre Reposition und Spongiosaplastik bei Wirbelkötperbrüchen der unteren Brust- und Lendenwirbelsäule. Unfallchirurgie 89:197–213
Denis F (1983) The three column spine and its significance in the classification of acute-thoracolumbar spinal injuries. Spine 8:817–831
Denis F (1984) Spinal instability as defined by the three-column spine concept in acute spinal trauma. Clin Orthop 189:65–76
Dick W (1987) The ‘fixateur interne’ as a versatile implant for spine surgery. Spine 12:882–890
Dick W, Kluger P, Magerl F, Woersdörfer O, Zäch G (1985) A new device for internal fixation of thoracolumbar and lumbar spine fractures: the ‘fixateur interne’. Paraplegia 23:225–232
Eysel P, Meinig G (1991) Comparative study of different dorsal stabilization techniques in recent thoraco-lumbar spine fractures. Acta Neurochir 109:12–19
Frankel HL, Hancock G, Hyslop G, Melzak J, Michaelis LS, Ungar GH, Vernon JDS, Walsh JJ (1969) The value of postural reduction in the initial management of closed injuries of the spine with paraplegia and tetraplegia. Paraplegia 7:179–192
Jacobs RR, Asher MA, Snider RK (1980) Dorso-lumbar spine fractures: recumbent versus operative treatment. Paraplegia 18:358–376
Jodoin A, Dupuis P, Fraser M, Beaumont P (1985) Unstable fractures of the thoracolumbar spine: a 10 years experience at the Sacré-Coeur Hospital. J Tauma 25:197–202
Kornberg M, Rechtine GR, Herndon WA, Reinert CM, Dupuy TE (1984) Surgical stabilization of thoracic and lumbar spine fracutes: a retrospective study in a military population. J Trauma 24:140–146
Lemons VR, Wagner FC, Montesano PX (1992) Management of thoracolumbar fractures with accompanying neurological injury. Neurosurgery 30:667–671
Lindsey RW, Dick W (1991) The fixateur interne in the reduction and stabilization of thoracolumbar spine fractures in patients with neurologic deficit. Spine 16 (Suppl):S140-S145
McEvoy RD, Bradford DS (1985) The management of burst fractures of the thoracic and lumbar spine: experience in 53 patients. Spine 10:631–637
Miller CA, Dewey RC, Hunt WE (1980) Impaction fracture of the lumbar vertebrae with dural tear. J Neurosurg 53:765–771
Wiberg J, Hauge HN (1988) Neurological outcome after surgery for thoracic and lumbar spine injuries. Acta Neurochir 91:106–112
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weyns, F., Rommens, P.M., Van Calenbergh, F. et al. Neurological outcome after surgery for thoracolumbar fractures. Eur Spine J 3, 276–281 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02226579
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02226579