Abstract
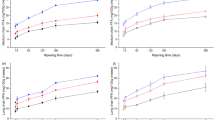
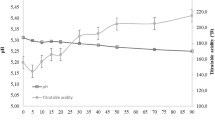
Ten batches of Arzúa, a soft cow's-milk cheese produced in northwest Spain, were prepared from pasteurized milk. Two (control) batches (CB) were made with a commercial starter containingLactococcus lactis subspecieslactis andcremoris. Another eight batches (MB) were made with the commercial starter plus one of eightMicrococcus spp. strains previously isolated from raw-milk Arzúa cheeses. In all MB, β-casein degradation over the 30-day ripening period was more pronounced (mean 31%) than in the CB (mean 12%). αS1-Casein degradation was highly variable in the MB, though mean degradation over the ripening period (75%) was similar to that observed in the CB (73%). Similarly, volatile fatty acid (VFA) content was highly variable in the MB, with the mean content at 30 days (3.8 mEq per 100 g) being higher than in the CB (1.6 mEq per 100 g). Rheological characterization of the cheeses (by uniaxial compression) revealed significant differences between batches, with some samples fracturing under the compression pressure applied and others not. Sensory evaluation also revealed significant differences. “Non-milk” aromas were more frequently detected in batches made with lipolytic micrococcal strains. Betweenbatch differences in tastes and texture were also detected. Multiple correlation analysis of the data obtained at day 15 of ripening revealed statistically significant positive correlations (r>0.70) between αS1-casein content and dry matter content, between αS1-casein content and sensorially evaluated firmness, and between VFA content and sensorially evaluated rancidity. Statistically significant negative correlations between sensorially evaluated firmness and the ratio of αS1-I content to αS1-casein content were detected. The results of this study suggest a need for further studies aimed at selecting those strains which could be most suitable for the production of Arzüa cheeses; due to their effects on texture, αS1-caseinolytic strains seem to be more appropriate than β-caseinolytic ones.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gehringer G (1981) Kiel Milchwirtsch Forschungsber 33: 317–323
Bautista L, Bermejo MP, Núñez M (1986) J Dairy Res 53: 1–5
Alford JA, Frazier WC (1950) J Dairy Sci 33: 115–120
Perry KD, Sharpe ME (1961) J Dairy Res 27: 267–275
Ordóñez JA, Burgos J (1977) Lait 57: 150–163
Bhowmik T, Riesterer R, Van Boekel MAJS, Marth EH (1990) Milchwissenschaft 45: 230–235
Marth EH (1963) J Dairy Sci 46: 869–890
Ordóñez JA, Barneto R, Mármol MP (1978) Anal Bromatol 30: 361–376
Bhowmik T, Marth EH (1990) J Dairy Sci 73: 859–866
Devoyod JJ (1969) Lait 49: 20–39
Cousins CM, Bramley AJ (1987) In: Microbiología lactológica. Acribia, Zaragoza, pp 109–150
Speck ML (1947) J Dairy Sci 62: 1865–1871
Speck ML, Lucas HL (1951) J Dairy Sci 34: 333–336
Ortiz de Apodaca MJ, Selgas MD, Ordóñez JA (1993) Rev Esp Cienc Tec Ali 33: 651–663
Vivier D, Ratomahenina R, Galzy P (1994) J Appl Bacteriol 76: 546–552
Devoyod JJ, Muller M (1969) Lait 49: 369–399
Naguib MM, Nour MA, Tohamy MM, Hofi AA (1980) Egypt J Dairy Sci 8: 1–7
Todesco R, Lodi R, Mucchetti G, Carini S (1981) Latte 6: 741–751
Prasad R, Malik RK, Mathur DK (1983) Asian J Dairy Res 2: 67–70
Massa S, Turtura GC (1989) Milchwissenschaft 44: 219–225
Bhowmik T, Marth EH (1988) J Dairy Sci 71: 2358–2365
Bhowmik T, Marth EH (1990) J Dairy Sci 73: 33–36
Poznanski S, Lenoir J, Mocquot G (1965) Lait 45: 3–13
Paird JC, El Soda M, Alkhalaf W, Rousseau M, Desmazeaud M, Vassal L, Grippon JC (1986) Biotechnol Lett 8: 241–247
Peterson MH, Johnson MJ (1949) J Bacteriol 58: 701–704
Alifax R (1975) L'Alim Vie 63: 22–229
Stadhouders J, Mulder H (1958) Neth Milk Dairy J 12: 237–241
Robertson PS, Perry KD (1961) J Dairy Res 28: 245–253
Lee SK, Johnson ME, Marth EH (1992) Lebensm Wiss Technol 25: 552–558
Dagvin N, Baltadzhiev M, Gruev P, Knani Y (1994) Khranitelna Promishlenost 43: 21–24
Poznanski S, Rymaszewski J (1965) Milchwissenschaft 20: 14–20
Naghmoush MR, Mewtally MM, Aboudawoos AE, Naguib MM, Ali AA (1979) Egyptian J Dairy Sci 7: 117–127
Kasik RL, Luksas AJ (1971) US Patent no. 3, 579, 354
Luksas AJ (1972) US Patent no. 3, 689, 286
Roberts MJ (1972) US Patent no. 3, 650, 768
Deane DD (1951) J Dairy Sci 34: 776–783
Tourneur C, Daudin JJ (1983) Microbiol Aliments Nutr 1: 337–342
Ortiz de Apodaca MJ, Selgas MD, Ordóñez JA (1989) In: Actas XII Congreso Nacional de la Sociedad Española de Microbiología. Pamplona, Spain, pp 144
Centeno JA, Rodríguez-Otero JL, Cepeda A (1994) J Food Saf 14: 229–241
Centeno JA, Cepeda A, Rodríguez-Otero JL (1995) Nahrung 39: 55–62
International Dairy Federation (1982) Standard 4-A, Brussels 42. International Dairy Federation (1986) Standard 5-B, Brussels
American Public Health Association (1992) In: Standard methods for the examination of dairy products, 16th edn. APHA, Washington, pp 504–508
American Public Health Association (1992) In: Standard methods of the examination of dairy products, 16th edn. APHA, Washington, pp 443–445
Centeno JA, Rodríguez-Otero JL, Cepeda A (1994) Milchwissenschaft 14: 319–322
Luyten (1988) In: The rheological and fracture properties of gouda cheese. PhD Thesis, Wageningen Agricultural University, Wageningen, The Netherlands, pp 10–14
Van Vliet T, Peleg M (1991) Bull Int Dairy Fed 268: 26–29
Lavanchy P, Bérodier F, Zannoni M, Noël Y, Adamo C, Squella J, Herrero L (1993) Lebensm Wiss Technol 26: 59–68
Ministerio de la Presidencia (1994) In: Boletín Oficial del Estado no. 229, Madrid, Spain, pp 29492–29511
Obradovic D (1982) In: XXI International Dairy Congress. Mir, Moscow, pp 432–433
Nath KR, Ledford RA (1972) J Dairy Sci 10: 1424–1427
Prasad R, Malik RK, Mathur DK (1986) J Dairy Sci 69: 633–642
García de Fernando GD, Fox PF (1991) Lait 71: 371–383
De Jong L (1976) Neth Milk Dairy J 30: 242–253
Creamer LK, Olson NF (1982) J Food Sci 47: 631–636, 646
Ortiz de Apodaca MJ, Selgas MD, Ordonez JA (1993) Food Res Int 26: 319–325
Visser S, Hup G, Exterkate FA, Stadhouders J (1983) Neth Milk Dairy J 37: 169–182
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Centeno, J.A., Varela, J.A., Almena, M. et al. Effects of variousMicrococcus strains on the ripening and organoleptic characteristics of Arzúa cow's-milk cheese. Z Lebensm Unters Forch 203, 546–552 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01193161
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01193161