Abstract
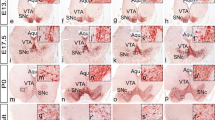
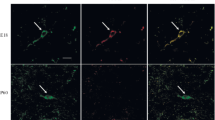
Immunocytochemical labeling for tyrosine hydroxylase and [3H]thymidine autoradiography were combined in wild-type mice and in mice homozygous for the weaver mutant gene (wv) to see whether the neurogenetic patterns of midbrain dopaminergic neurons was normal in the mutants and whether the degeneration of dopaminergic neurons was linked to their time of origin. Dams of wild-type and homozygous weaver mice were injected with [3H]thymidine on embryonic days (E) 11–E12, E12–E13, E13–E14, and E14-E15 to label neurons in the retrorubral field, the substantia nigra pars compacta, the ventral tegmental area, and the interfascicular nucleus as they were being generated. The quantitatively determined time of origin profiles indicated that wv/wv mice have the same time span of neurogenesis as +/+ mice (E10 to E14), but have significant deficits in the proportion of late-generated neurons in each dopaminergic population. In the retrorubral field and substantia nigra, weaver homozygotes had substantial losses of dopaminergic neurons and had a greater deficit in the proportion of neurons generated late while, in the ventral tegmental area and interfascicular nucleus, there were slight losses of dopaminergic neurons and only slight deficits in the proportion of late-generated neurons. These findings lead to the conclusion that the weaver gene is specifically targeting dopaminergic neurons that are generated late, mainly on E13 and E14.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altman J, Bayer SA (1981) Development of the brain stem in the rat. V. Thymidine-radiographic study of the time of origin of neurons in the midbrain tegmentum. J Comp Neurol 198:677–716
Bayer SA (1984) Neurogenesis in the rat neostriatum. Int J Dev Neurosci 2:163–175
Bayer SA, Altman J (1987) Directions in neurogenetic gradients and patterns of anatomical connections. Prog Neurobiol 29:57–106
Bayer SA, Altman J, Russo RJ, Zhang X (1993) Timetables of neurogenesis in the human brain based on experimentally determined patterns in the rat. Neurotoxicology 14:83–144
Bayer SA, Triarhou LC, Thomas JD, Ghetti B (1994a) Correlated quantitative studies of the neostriatum, nucleus accumbens, substantia nigra, and ventral tegmental area in normal and weaver mutant mice. J Neurosci 14:6901–6910
Bayer SA, Triarhou LC, Thomas JD, Ghetti B (1994b) The weaver gene targets dopaminergic neurons generated during a specific temporal window in substantia nigra neurogenesis. Soc Neurosci Abstr 292.5 20:688
Bayer SA, Wills KV, Triarhou LC, Ghetti B (1995a) Time of neuron origin and gradients of neurogenesis in midbrain dopaminergic neurons in the mouse. Exp Brain Res 105:191–199
Bayer SA, Wills KV, Triarhou LC, Verina T, Thomas JD, Ghetti B (1995b) Selective vulnerability of late-generated dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra in weaver mutant mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA (in press)
Gaspar P, Ben Jelloun N, Febvret A (1994) Sparing of the dopaminergic neurons containing calbindin-D28k and of the dopaminergic mesocortical projections in weaver mutant mice. Neuroscience 61:293–305
Gerfen CR, Baimbridge KG, Thibault J (1987) The neostriatal mosaic. III. Biochemical and developmental dissociation of patch-matrix mesostriatal systems. J Neurosci 7:3935–3944
Ghetti B, Triarhou LC (1992a) Degeneration of mesencephalic dopamine neurons in weaver mutant mice. Neurochem Int [Suppl 20]:305S–307S
Ghetti B, Triarhou LC (1992b) Combined degeneration of cerebellar granule cells and of midbrain dopamine neurons in the weaver mutant mouse. In: Hefti F, Weiner WJ (eds) Progress in Parkinson's disease research. Futura, Mount Kisko, NY, pp 375–388
Ghetti B, Triarhou LC (1992c) Nigrostriatal aberrations induced by weaver gene are present at birth. Soc Neurosci Abstr 69.1 18:156
Graybiel AM, Ohta K, Roffler-Tarlov S (1990) Patterns of cell and fiber vulnerability in the mesostriatal system of the mutant mouse weaver. I. Gradients and comparisons. J Neurosci 10:720–733
Gupta M, Felten DL, Ghetti B (1987) Selective loss of monoaminergic neurons in weaver mutant mice an immunocytochemical study. Brain Res 402:379–382
Iacopino A, Christakos S, German D, Sonsalla PK, Altar CA (1992) Calbindin-D28k-containing neurons in animal models of neurodegeneration: possible protection from excitotoxicity. Mol Brain Res 13:251–261
Lavoie B, Parent A (1991) Dopaminergic neurons expressing calbindin in normal and parkinsonian monkeys. Neuroreport 2:601–604
Lazzarini AM, Myers RH, Zimmerman TR, Mark MH, Golbe LI, Sage JI, Johnson WG, Duvoisin RCÊ (1994) A clinical genetic study of Parkinson's disease: evidence for dominant transmission. Neurology 44:499–506
Lin L-FH, Doherty DH, Lile JD, Bektesh S, Collins F (1993) GDNF: a glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor for midbrain dopaminergic neurons. Science 260:1130–1132
Mayer E, Dunnett SB, Pellitteri R, Fawcett JW (1993) Basic fibroblast growth factor promotes the survival of embryonic ventral mesencephalic dopaminergic neurons. I. Effects in vitro. Neuroscience 56:379–388
O'Malley EK, Sieber B-A, Morrison RS, Black IB, Dreyfus CF (1994) Nigral type 1 astrocytes release a soluble factor that increases dopaminergic neuron survival through mechanisms distinct from basic fibroblast growth factor. Brain Res 647:83–90
Roffler-Tarlov S, Graybiel AM (1987) The postnatal development of the dopamine-containing innervation of dorsal and ventral striatum: effects of the weaver gene. J Neurosci 7:2364–2372
Schaar DG, Sieber B-A, Dreyfus CF, Black IB (1993) Regional and cell-specific expression of GDNF in rat brain. Exp Neurol 124:368–371
Schmidt MJ, Sawyer BD, Perry KW, Fuller RW, Foreman MM, Ghetti B (1982) Dopamine deficiency in the weaver mutant mouse. J Neurosci 2:376–380
Sidman RL, Angevine JB, Taber Pierce E (1971) Atlas of the mouse brain and spinal cord. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, Mass
Simon J, Richter JA, Ghetti B (1994) Age-dependent alterations in dopamine content, tyrosine hydroxylase activity and dopamine uptake in the striatum of the weaver mutant mouse. J Neurochem 62:543–548
Strömberg I, Björklund L, Hohansson M, Tomac A, Collins F, Olson L, Hoffer B, Humpel C (1993) Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor is expressed in the developing but not adult striatum and stimulates developing dopamine neurons in vivo. Exp Neurol 124:401–412
Takeshima T, Johnston JM, Commissiong JW (1994a) Mesencephalic type 1 astrocytes rescue dopaminergic neurons from death induced by serum deprivation. J Neurosci 14:4769–4779
Takeshima T, Johnston JM, Commissiong JW (1994b) Oligodendrocyte-type-2 astrocyte (O-2A) progenitors increase the survival of rat mesencephalic, dopaminergic neurons from death induced by serum deprivation. Neurosci Lett 166:178–182
Takeshima T, Shimoda K, Suave Y, Commissiong JW (1994c) Astrocyte-dependent and -independent phases of the development and survival of rat embryonic day 14 mesencephalic, dopaminergic neurons in culture. Neuroscience 60:809–823
Triarhou LC, Low WC, Ghetti B (1986) Transplantation of ventral mesencephalic anlagen to hosts with genetic nigrostriatal dopamine deficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:8789–8793
Triarhou LC, Norton J, Ghetti B (1988) Mesencephalic dopamine cell deficit involves areas A8, A9 and A10 in weaver mutant mice. Exp Brain Res 70:256–265
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bayer, S.A., Wills, K.V., Triarhou, L.C. et al. Systematic differences in time of dopaminergic neuron origin between normal mice and homozygous weaver mutants. Exp Brain Res 105, 200–208 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00240956
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00240956