Summary
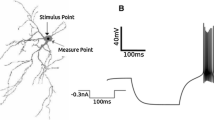
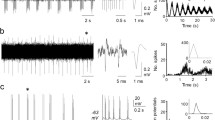
Antidromically activated intracellular and field potentials in the lateral reticular nucleus (LRN) of cat were recorded with microelectrode following stimulation of the inferior cerebellar peduncle.
LRN antidromic field potentials were well synchronized and relatively short duration negative waves. These potentials were observed only when the recording electrode was within the nucleus. No reversal of the negative potentials was detected outside of the nucleus.
Intracellular analysis revealed that antidromic firing of the LRN neuron is composed of M-IS-SD spikes. The IS-SD spike duration was short and sometimes followed by an afterpotential sequence of depolarization and hyperpolarization. Effects of depolarizing and hyperpolarizing currents, injected through the recording electrode, on the antidromic spike, membrane resistance and firing pattern were studied. Findings demonstrated that LRN cells are capable of high frequency firing with little accomodation. The membrane also displayed rectification properties. These results imply that LRN neurons are highly sensitive to depolarization signals and possess characteristics for providing background depolarization and tonic activation of their target neurons.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agree, S.T., Kitai, S.T.: Decending influence on single units of the cat lateral reticular nucleus. Anat. Rec. 157, 203–204 (1967)
Azzena, G.B., Ohno, T.: Influence of spino-reticulo-cerebellar pathway on Purkynê cells of paramedian lobule. Exp. Brain Res. 17, 63–74 (1973)
Baker, R., Precht, W.: Electrophysiological properties of trochlear motoneurons as revealed by IVth nerve stimulation. Exp. Brain Res. 14, 127–157 (1972)
Brock, L.G., Coombs, J.S., Eccles, J.C.: The recording of potentials from motoneurons with an intracellular electrode. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 117, 431–460 (1952)
Brock, L.G., Coombs, J.S., Eccles, J.C.: Intracellular recording from antidromically activated motoneurons. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 122, 429–461 (1953)
Brodal, A.: The cerebellar connections of the LRN (nucleus funiculi lateralis) in rabbit and cat. Experimental investigations. Acta psychiat. (Kbh.) 18, 171–233 (1943)
Brodal, A.: Spinal afferents to the lateral reticular nucleus of the medulla oblongata in the cat. An experimental study. J. comp. Neurol. 91, 259–295 (1949)
Brodal, P., Marsala, J., Brodal, A.: The cerebral cortical projection to the lateral reticular nucleus in the cat, with special reference to the sensorimotor cortical areas. Brain Res. 6, 252–274 (1967)
Bruckmoser, P., Hepp-Reymond, M.C., Wiesendanger, M.: Effects of peripheral, rubral, and fastigial stimulation on neurons of the lateral reticular nucleus of the cat. Exp. Neurol. 27, 288–298 (1970a)
Bruckmoser, P., Hepp-Reymond, M.C., Wiesendanger, M.: Cortical influence on single neurons of the lateral reticular nucleus of the cat. Exp. Neurol. 26, 239–252 (1970b)
Burke, R., Lundberg, A., Weight, F.: Spinal border cell origin of the ventral spinocerebellar tract. Exp. Brain Res. 12, 283–294 (1971)
Burton, J.E., Bloedel, J.R., Gregory, R.S.: Electrophysiological evidence for an input to lateral reticular nucleus from collaterals of dorsal spinocerebellar and cuneocerebellar fibers. J. Neurophysiol. 34, 885–897 (1971)
Busch, H.F.M.: An anatomical analysis of the white matter in the brain stem of the cat. Assen, N.V.: Van Gorcum and Co. 1961
Coombs, J.S., Curtis, D.R., Eccles, J.C.: The interpretation of spike potentials of motoneurons. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 139, 198–231 (1957)
Coombs, J.S., Curtis, D.R., Eccles, J.C.: The electrical constants of the motoneurone membrane. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 145, 505–528 (1959)
Courville, J.: Rubrobulbar fibers to the facial nucleus and the lateral reticular nucleus (nucleus of the lateral funiculus). An experimental study in the cat with silver impregnation methods Brain Res. 1, 317–337 (1986)
Crichlow, E.C., Kennedy, T.T.: Functional characteristics of neurons in the lateral reticular nucleus with reference to localized cerebellar potentials. Exp. Neurol. 18, 141–153 (1967)
Crichlow, E.C.: Influence of sensorimotor cortices on lateral reticular nucleus cells. Exp. Neurol. 32, 184–194 (1971)
Eccles, J.C., Hubbard, J.I., Oscarsson, O.: Intracellular recording from cells of the ventral spino-cerebellar tract. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 158, 486–516 (1961)
Eccles, J.C., Sabah, N.H., Táboříková, H.: Responses evoked in neurones of fastigial nucleus by cutaneous mechanoreceptors. Brain Res. 35, 523–527 (1971)
Eccles, J.C.: The cerebellum as a computer: Patterns in space and time. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 229, 1–32 (1973)
Eide, E., Fedina, L., Jansen, J., Lundberg, A., Vyklický, L.: Properties of Clarke's Column neurones. Acta physiol. scand. 77, 125–144 (1969)
Frank, K., Fuortes, M.G.F.: Stimulation of spinal motoneurones with intracellular electrodes. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 134, 451–470 (1958)
Grant, G., Oscarsson, O., Rosén, I.: Functional organization of the spinoreticulo-cerebsllar path with identification of its spinal component. Exp. Brain Res. 1, 306–319 (1966)
Ito, M., Hongo, T., Yoshida, M., Okada, Y., Obata K.: Antidromic and trans-synaptic activation of Deiter's neurones induced from the spinal cord. Jap. J. Physiol. 14, 638–858 (1964)
Kernell, D.: The delayed depolarization in cat and rat motoneurons. In: Progr. Brain Res. 12, p. 42–55. Ed. by J. C. Eccles and J. P. Schadé. Amsterdam: Elsevier 1964
Kernell, D.: High frequency repetitive firing of cat lumber sacral motoneurones stimulated by long-lasting injected currents. Acta physiol. scand. 65, 74–86 (1986)
Kitai, S.T., Kennedy, D.T., Morin, F., Gardner, E.: The lateral reticular nucleus of the medulla oblongata of the cat. Exp. Neurol. 17, 65–73 (1967)
Kitai, S.T., Hatada, H., Cassy, W.: Intracellular analysis of antidromically and synaptically activated lateral reticular neurons. Brain Res. 43, 629–634 (1972a)
Kitai, S.T., Tanaka, T., Tsukahara, N., Yu, H.: The facial nucleus of cat: Antidromic and synaptic activation and peripheral nerve representation. Exp. Brain Res. 16, 161–183 (1972b)
Kitai, S.T., DeFrance, J.F., Hatada, K., Kennedy, D.T.: Electrophysiological properties of lateral reticular nucleus cells: II. Synaptic activation. Exp. Brain Res. 21, 419–432 (1974)
Kuno, M., Miyahara, J.T.: Factors responsible for multiple discharge of neurones in Clarke's Column. J. Neurophysiol. 31, 624–638 (1968)
Kuno, M., Llinás, R.: Enhancement of synaptic transmission by dendritic potentials in chromatolysed motoneurons of the cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 210, 807–821 (1970)
Künzle, H.: The topographic organization of spinal afferents to the lateral reticular nucleus of the cat. J. comp. Neurol. 149, 103–116 (1973)
Kuypers, H.G.J.M.: An anatomical analysis of corticobulbar connections to the pons and lower brain stem in the cat. J. Anat. (Lond.) 92, 198–218 (1958)
Lorente de Nó, R.: A study of nerve physiology. Studies from Rockefeller Inst. 132, Chapt. 16, 1947
Mannen, H.: Contribution to the morphological study of dendritic arborization in the brain stem. In: Progr. Brain Res. 21A, p. 131–162. Ed. by Tokizane, J.P. Schadé. Amsterdam: Elsevier 1966
Morin, F., Kennedy, D.T., Gardner, E.: Spinal afferents to the lateral reticular nucleus. I. An histological study. J. comp. Neurol. 126, 511–522 (1966)
Nelson, P.G., Frank, K.: Anomalous rectification in cat spinal motoneurons and effect of polarizing currents on excitatory postsynaptic potential. J. Neurophysiol. 30, 1097–1113 (1967)
Oscarsson, O., Rosén, I.: Response characteristics of reticulo-cerebellar neurones activated from spinal afferents. Exp. Brain Res. 1, 320–328 (1966)
Porter, R.: Antidromic responses of hypoglossal motoneurons. Exp. Neurol. 20, 624–634 (1968)
Ramón-Moliner, E., Nauta, W.J.H.: The isodendritic core of the brain stem. J. comp. Neurol. 126, 311–336 (1966)
Rosén, I., Scheid, P.: Cutaneous afferent responses in neurones of the lateral reticular nucleus. Brain Res. 43, 259–263 (1972)
Rosén, I., Scheid, P.: Patterns of afferent input to the lateral reticular nucleus of the cat. Exp. Brain Res. 18, 242–255 (1973a)
Rosén, I., Scheid, P.: Responses in the spino-cerebellar pathway to stimulation of cutaneous mechanoreceptors. Exp. Brain Res. 18, 268–278 (1973b)
Sasaki, K.: Electrophysiological studies on oculomotor neurons of the cat. Jap. J. Physiol. 13, 287–302 (1963)
Sasaki, K., Strata, P.: Responses evoked in the cerebellar cortex by stimulating mossy fiber pathways to the cerebellum. Exp. Brain Res. 3, 95–110 (1967)
Szentágothai, J.: Anatomical aspects of junctional transformation. In: Information processing in the nervous system. Ed. by R.W. Gerard, p. 119–136. Amsterdam 1964
Thomas, R.C., Wilson, V.J.: Precise localization of Renshaw cells with a new marking technique. Nature (Lond.) 206, 211–213 (1965)
Thomas, R.C., Wilson, V.J.: Marking single neurons by staining with intracellular recording microelectrodes. Science 151, 1538–1539 (1986)
Tsukahara, N., Toyama, K., Kosaka, K.: Electrical activity of red nucleus neurons investigated with intracellular microelectrodes. Exp. Brain Res. 4, 18–33 (1967)
Valverde, F.: Reticular formation of pons and medulla oblongata. A Golgi study. J. comp. Neurol. 116, 71–99 (1961)
Verhaart, W.J.C.: The lateral reticular nucleus of the medulla oblongata and the passing fiber systems of the lateral funiculus. Acta psychiat. scand. 32, 211–229 (1957)
Walberg, F.: The lateral reticular nucleus of the medulla oblongata in mammals. A comparative anatomical study. J. comp. Neurol. 96, 283–344 (1952)
Walberg, F.: Descending connections to the lateral reticular nucleus. An experimental study in the cat. J. comp. Neurol. 109, 363–389 (1958)
Zangger, P., Wiesendanger, M.: Excitation of lateral reticular neurones by collaterals of the pyramidal tract. Exp. Brain Res. 17, 144–151 (1973)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This study was supported by U.S. Public Health Service Grants NB 00405, RR 5384 and National Science Foundation Grant GB 35532.
The authors express their gratitude to Mss. D. Agresta, C. Casper and B. Pantelis for their patient and skillful assistance in histology, photography and preparation of this manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kitai, S.T., Kennedy, D.T., Defrance, J.F. et al. Electrophysiological properties of lateral reticular nucleus cells: I. Antidromic activation. Exp Brain Res 21, 403–418 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00237903
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00237903