Summary
-
1.
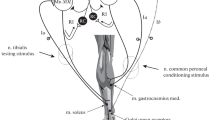
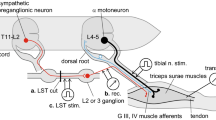
Electrical stimulation of extensor nerves of the ankle has been used to investigate the presynaptic inhibition in a synergic monosynaptic reflex arc.
-
2.
Depression of monosynaptic reflex response as well as increase in excitability of Ia afferent terminals in the MG (medial gastrocnemius) reflex arc is found following the conditioning stimulation of LGS (lateral gastrocnemius-soleus) nerve at Group I strength.
-
3.
Excitability increase of the Ia terminals of the LGS nerve is also found following the conditioning stimulation of either a group of fibres of the same nerve or the MG nerve.
-
4.
Conditioning by Group I afferent volleys from either the LGS or the PBST (posterior biceps-semitendinosus) muscles produces comparable changes in excitability of the Ia terminals from MG muscle.
-
5.
The hypothesis is advanced that the depression of the monosynaptic reflex discharge during repetitive stimulation is mainly caused by the depolarization of the Ia afferent terminals, i.e. by presynaptic inhibition.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvord, E.C., and M.G.F. Fuortes: Reflex activity of extensor motor units following muscular afferent excitation. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 122, 302–321 (1953).
Beswick, F.B., and J.M. Evanson: Homosynaptic depression of the monosynaptic reflex following its activation. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 135, 400–411 (1957).
Bracchi, F., M. Decandia and T. Gualtierotti: Frequency stabilization in the motor centers of spinal cord and caudal brain stem. Amer. J. Physiol. 210, 1170–1177 (1966).
Cook, jr. W.A., D.R. Neilson jr. and J.M. Brookhart: Primary afferent depolarization and monosynaptic reflex depression following succinylcholine administration. J. Neurophysiol. 28, 290–311 (1965).
Decandia, M., and L. Provini: Motoneurone excitability during repetitive stimulation of Group I afferent fibres. Experientia (Basel) 22, 187 (1966).
— and H. Táboříková: Excitability changes in the Ia extensor terminals induced by stimulation of agonist afferent fibres. Brain Res. 2, 402–404 (1966).
—: Mechanisms of the reflex discharge depression in the spinal motoneurone during repetitive orthodromic stimulation. Brain Res. 4, 284–291 (1967).
Devanandan, M.S., R.M. Eccles and D. Stenhouse: Presynaptic inhibition evoked by muscle contraction. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 185, 471–485 (1966).
— and T. Yokota: Depolarization of afferent terminals evoked by muscle stretch. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 179, 417–429 (1965).
Eccles, J.C.: Synaptic potentials of motoneurones. J. Neurophysiol. 9, 87–120 (1946).
—: The physiology of synapses, pp. 220–238. Berlin-Göttingen-Heidelberg: Springer 1964.
—, R.M. Eccles and A. Lundberg: Synaptic actions on motoneurones in relation to the two components of the Group I muscle afferent volleys. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 136, 527–546 (1957a).
—: Synaptic actions on motoneurones caused by impulses in Golgi tendon organ afferents. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 138, 227–252 (1957b).
— and F. Magni: Central inhibitory action attributable to presynaptic depolarization produced by muscle afferent volleys. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 159, 147–166 (1961).
—, P. Fatt and K. Koketsu: Cholinergic and inhibitory synapses in a pathway from motor-axon collaterals to motoneurones. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 126, 524–562 (1954).
—, W. Kozak and F. Magni: Dorsal root reflexes of muscle Group I afferent fibres. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 159, 128–146 (1961).
—, F. Magni and W.D. Willis: Depolarization of central terminals of Group I afferent fibres from muscle. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 160, 62–93 (1962).
—, R.F. Schmidt and W.D. Willis: Presynaptic inhibition of the spinal monosynaptic reflex pathway. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 161, 282–297 (1962).
—: The location and the mode of action of the presynaptic inhibitory pathways on the group I afferent fibres from muscle. J. Neurophysiol. 26, 506–522 (1963).
—: Inhibition of discharges into the dorsal and ventral spinocerebellar tracts. J. Neurophysiol. 26, 635–645 (1963b).
Granit, R.: Reflex self regulation of muscle contraction and autogenic inhibition. J. Neurophysiol. 13, 351–372 (1950).
Hagbarth, K.E.: Excitatory and inhibitory skin areas for flexor and extensor motoneurones. Acta physiol. scand. 26, Suppl. 94 (1952).
Jansen, J.K.S., and T. Rudjord: On the silent period and Golgi tendon organs of the soleus muscle of the cat. Acta physiol. scand. 62, 364–379 (1964).
Laporte, Y., and D.P.C. Lloyd: Nature and significance of the reflex connections established by large afferent fibres of muscular origin. Amer. J. Physiol. 169, 609–621 (1952).
Lloyd, D.P.C.: Facilitation and inhibition of spinal motoneurones. J. Neurophysiol. 9, 421–438 (1946).
—: Monosynaptic reflex response of individual motoneurones as a function of frequency. J. gen. Physiol. 40, 435–450 (1957).
Renshaw, B.: Central effects of centripetal impulses in axons of spinal ventral roots. J. Neurophysiol. 9, 191–204 (1946).
Roberts, T.D.M.: Separation of the effects on the muscle servo of the alpha-, gamma-, and Renshaw-control pathways. In: Muscular Afferents and Motor Control. Nobel Symposium I., pp. 457–459. Ed. by R. Granit. Stockholm: Almqvist and Wiksell 1966.
Wall, P.D.: Excitability changes in afferent fibre terminations and their relation to slow potentials. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 142, 1–21 (1958).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Decandia, M., Provini, L. & Táboříková, H. Presynaptic inhibition of the monosynaptic reflex following the stimulation of nerves to extensor muscles of the ankle. Exp Brain Res 4, 34–42 (1967). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00235215
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00235215