Summary
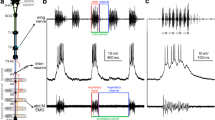
Extracellular recordings from neurones in the lateral septum were performed in urethane anaesthetised lactating rats to study the eventual role of the septum in the control of suckling-induced oxytocin release. The connections of these neurones with the supraoptic nucleus, which contains cells secreting oxytocin, were assessed electrophysiologically by single pulse stimulation of the ipsilateral supraoptic nucleus. The neurones were thus classified into four categories: antidromically activated, orthodromically activated or inhibited, and unresponsive neurones. One hundred septal neurones were recorded in animals not exposed to suckling. A second group of 40 cells were analysed during suckling and one or more reflex milk ejections.
The mean firing rates of each category of septal neurone did not differ significantly during suckling from the values observed in the absence of suckling. During suckling, almost all the recorded septal cells showed no significant alteration in their level of firing in relation to milk ejections. Two neurones presented an activation in the period between two milk ejections that seemed related to arousal. One neurone was clearly inhibited at the time of milk ejection.
Our observations suggest that the septum does not represent an essential component of the pathways necessary for the milk ejection reflex induced by suckling, although it could exert an inhibitory action modulating either the intervals between two successive milk ejections, or the amount of oxytocin released.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Assaf SY, Miller JJ (1978) The role of a raphe serotonin system in the control of septal unit activity and hippocampal desynchronization. Neuroscience 3: 539–550
Aulsebrook LH, Holland RC (1969) Central inhibition of oxytocin release. Am J Physiol 216: 830–842
Brimble MJ, Dyball REJ, Forsling ML (1978) Oxytocin release following osmotic activation of oxytocin neurones in the paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei. J Physiol (Lond) 278: 69–78
Cross BA (1955) Neurohormonal mechanisms in emotional inhibition of milk ejection. J Endocrinol 12: 29–37
Cross BA, Dyball REJ (1974) Central pathways for neurohypophysial hormone release. In: Knobil EL, Sawyer WH (eds) Handbook of physiology, endocrinology IV, part 1. American Physiology Society, Washington DC, pp 269–285
De Groot J (1959) The rat forebrain in stereotaxic coordinates. North Holland, Amsterdam
Gogolak G, Stumpf C, Petsche H, Sterc J (1968) The firing pattern of septal neurons and the form of the hippocampal theta wave. Brain Res 7: 201–207
Green JD, Arduini AA (1954) Hippocampal electrical activity in arousal. J Neurophysiol 17: 533–557
Koizumi K, Yamashita H (1972) Studies of antidromically identified neurosecretory cells of the hypothalamus by intracellular and extracellular recordings. J Physiol (Lond) 221: 683–705
Lincoln DW (1969) Correlation of unit activity in the hypothalamus with the EEG patterns associated with the sleep cycle. Exp Neurol 24: 1–18
Lincoln DW, Wakerley JB (1974) Electrophysiological evidence for the activation of supraoptic neurones during the release of oxytocin. J Physiol (Lond) 242: 533–554
Lincoln DW, Hentzen K, Hin T, van der Schoot P, Clarke G, Summerlee AJS (1980) Sleep: A prerequisite for reflex milk ejection in the rat. Exp Brain Res 38: 151–162
McLennan H, Miller JJ (1974) The hippocampal control of neuronal discharges in the septum of the rat. J Physiol (Lond) 237: 607–624
Morales FR, Roig JA, Monti JM, Macadar O, Budelli R (1971) Septal unit activity and hippocampal EEG during the sleepwakefulness cycle of the rat. Physiol Behav 6: 563–567
Negoro H, Visessuwan S, Holland RC (1973) Inhibition and excitation of units in paraventricular nucleus after stimulation of the septum, amygdala, and neurohypophysis. Brain Res 57: 479–483
Newton M, Newton NR (1948) The let-down reflex in human lactation. J Paediatr 33: 698–704
Peeters G, Stormorken H, Vanschoubroek F (1960) The effect of different stimuli on ejection and diuresis in the lactating cow. J Endocrinol 20: 163–172
Petsche H, Stumpf Ch, Gogolak G (1962) The significance of the rabbit's septum as a relay station between the midbrain and the hippocampus: I. The control of hippocampus arousal activity by the septum cells. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 14: 202–211
Poulain DA, Wakerley JB, Dyball REJ (1977) Electrophysiological differentiation of oxytocin- and vasopressin-secreting neurones. Proc R Soc Lond [Biol] 196: 367–384
Poulain DA, Ellendorff F, Vincent JD (1980) Septal connections with identified oxytocin and vasopressin neurones in the supraoptic nucleus of the rat. An electrophysiological investigation. Neuroscience 5: 379–387
Poulain DA, Lebrun CJ, Vincent JD (1981) Electrophysiological evidence for connections between septal neurones and the supraoptic nucleus of the hypothalamus of the rat. Exp Brain Res 42: 260–268
Poulain DA, Theodosis DT, Lebrun CJ (1982) Septal lesions do not disrupt the milk ejection reflex in the rat. J Physiol (Paris) (in press)
Richard P, Urban I, Denamur R (1970) The role of the dorsal tracts of the spinal cord and of the mesencephalic and thalamic lemniscal system in the milk ejection reflex during milking in the ewe. J Endocrinol 47: 45–53
Sundsten JW (1971) Septal inhibition of antidromically activated hypothalamic paraventricular neurons in the monkey. Anat Rec 169: 439
Taleisnik S, Deis RP (1964) Influence of cerebral cortex inhibition of oxytocin release induced by stressful stimuli. Am J Physiol 207: 1394–1398
Voloschin LM, Tramezzani JH (1979) Milk ejection reflex linked to slow wave sleep in nursing rats. Endocrinology 105: 1202–1207
Wakerley JB, Lincoln DW (1973) The milk ejection reflex of the rat: A 20- to 40-fold acceleration in the firing of paraventricular neurones during oxytocin release. J Endocrinol 57: 477–493
Wakerley JB, Poulain DA, Brown D (1978) Comparison of firing patterns in oxytocin- and vasopressin-releasing neurones during progressive dehydration. Brain Res 148: 425–440
Zaborsky L, Leranth C, Makara GB, Palkovits M (1975) Quantitative studies on the supraoptic nucleus in the rat. II. Afferent fiber connections. Exp Brain Res 22: 525–540
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by grant INSERM CRL 79.5.372.6
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lebrun, C.J., Poulain, D.A. Electrical activity of septal neurones during suckling and the milk ejection reflex in the lactating rat. Exp Brain Res 47, 203–208 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00239379
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00239379