Summary
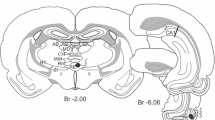
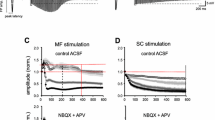
Previous electrophysiological experiments in rabbits have suggested that medial septal stimulation activates dentate granule cells and evokes an associated negative field response at the granule cell layer, without an associated “dendritic” response. Anatomical studies have suggested that septal input to the granule cells may be to stratum moleculare, or close to the cell layer, or may not exist at all. The present experiments confirmed in rats anaesthetised with urethane that medial septal stimulation elicits single action potentials from cells in the granule layer. The associated negative field potential was maximal in the granule cell layer and there was no sign of a separate dendritic potential. The fibres responsible for this potential travel to the dorsal hippocampus in the fornix superior rather than the fimbria, taking the same course as the fibres which contribute to the dense cholinesterase staining just above the granule cell layer. Stimulation at 100 Hz for 1 s of either medial septal, or perforant path, input to the dentate granule cell layer produced long term potentiation of the subsequent evoked field responses to the stimulated pathway. The responses to the non-stimulated pathway were unchanged. Paired pulse stimulation produced both homosynaptic and heterosynaptic potentiation. These data suggest that medial septal input synapses close to granule cell bodies and produces a negative field potential which is a combination of dendritic and population spike potentials. Medial septal input also appeared to produce direct activation of hilar neurones, some of which may be basket cells or other interneurones. The data also show that long term potentiation is specific to this input, perhaps dependent on presynaptic mechanisms. Paired pulse potentiation, at least in the heterosynaptic case appears to depend on postsynaptic mechanisms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez-Leefmans FJ, Gardner-Medwin AR (1975) Influences of the septum on the hippocampal dentate area which are unaccompanied by field potentials. J Physiol (London) 249: 14–16
Andersen P, Bland BH, Dudar JD (1973) Organisation of the hippocampal output. Exp Brain Res 17: 152–168
Andersen P, Bruland H, Kaada BR (1961) Activation of the dentate area by septal stimulation. Acta Physiol Scand 51: 17–28
Brust-Carmona H, Alvarez-Leefmans FJ, Arditti L (1973) Differential projections of septal nuclei to ventral and dorsal hippocampus in rabbits. Exp Neurol 40: 553–566
Deadwyler SA, West JR, Cotman CN, Lynch G (1975) A neurophysiological analysis of a commissural projection to the dentate gyrus of the rat. J Neurophysiol 38: 167–184
Douglas RM, McNaughton BL, Goddard GV (1983) Commissural inhibition and facilitation of granule cell discharge in fascia dentata. J Comp Neurol 219: 285–294
Fantie BD, Goddard GV (1982) Septal modulation of the population spike in the fascia dentata produced by perforant path stimulation in the rat. Brain Res 252: 227–237
Ibata Y, Desiraju T, Pappas GD (1971) Light and electron microscopic study of the projection from the medial septal nucleus to the hippocampus of the cat. Exp Neurol 33: 103–122
Kramis R, Vanderwolf CH, Bland BH (1975) Two types of hippocampal rhythmical slow activity in both the rabbit and the rat: relations to behaviour and effects of atropine, diethyl ether, urethane and pentobarbital. Exp Neurol 49: 58–85
Krug M, Ott T, Matthies H (1980) The septo-hippocampal pathway: Electrophysiological observations. Acta Physiol Acad Sci Hung 55: 261–272
Lynch GS, Rose G, Gall CM (1978) Anatomical and functional aspects of the septo-hippocampal projections. In Elliot K, Whelan J (eds) Functions of the septo-hippocampal system. CIBA Foundation Symposium 58 (new series): Elsevier, Amsterdam
Macadar O, Roig JA, Monti JM, Budelli R (1970) The functional relationship between septal and hippocampal unit activity and hippocampal theta rhythm. Physiol Behav 5: 1443–1449
Mosko S, Lynch GS, Cotman CW (1973) The distribution of septal projections to the hippocampus of the rat. J Comp Neurol 152: 163–174
Petsche H, Gogolak G, Stumpf C (1968) Septal unit firing and shape of theta waves in rabbit hippocampus. EEG 24: 390
Rawlins JNP, Feldon J, Gray JA (1979) Septo-hippocampal connections and the hippocampal theta rhythm. Exp Brain Res 37: 49–63
Robinson GB, Racine RJ (1982). Heterosynaptic interactions between septal and entorhinal inputs to the dentate gyrus: long-term potentiation effects. Brain Res 249: 162–166
Rudell AP, Fox SE, Ranck JB (1980) Hippocampal excitability phase-locked to the theta rhythm in walking rats. Exp Neurol 68: 87–96
Swanson LW, Cowan WM (1979) The connections of the septal region in the rat. J Comp Neurol 186: 621–656
Vinogradova OS (1975) Functional organisation of the limbic system in the process of registration of information: facts and hypotheses. In: Isaacson RL, Pribram KH (eds) The Hippocampus, Vol II. Plenum Press, New York
Von Euler C, Green JD (1960) Excitation, inhibition and rhythmical activity in the hippocampal pyramidal cells in rabbit. Acta Physiol Scand 48: 110–125
Wheal HV, Miller JJ (1980) Pharmacological identification of acetylcholine and glutamate excitatory systems in the dentate gyrus of the rat. Brain Res 182: 145–155
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McNaughton, N., Miller, J.J. Medial septal projections to the dentate gyrus of the rat: electrophysiological analysis of distribution and plasticity. Exp Brain Res 56, 243–256 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00236280
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00236280