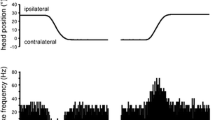
Summary
Single-unit activities were recorded from floccular Purkinje cells in 29 alert pigmented rabbits. The floccular areas specifically related to horizontal eye movement (H-zone) were identified by the effects of local stimulation and later confirmed histologically. Most of the 53 H-zone Purkinje cells responded to both vestibular stimulation with turntable oscillation (5° peak-to-peak, 0.1 Hz) in darkness and optokinetic stimulation with dot screen oscillation (2.5°, 0.33 Hz), often showing a preference either for turntable oscillation or screen oscillation. Since these responses were not correlated with the velocity of evoked eye movements or eye position shift, it is concluded that the major inputs to flocculus H-zone Purkinje cells are head velocity or retinal slip signals rather than eye velocity or position signals.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balaban DC, Watanabe E (1984) Functional representation of eye movements in the flocculus of monkeys (Macaca fuscata). Neurosci Lett 49:199–205
Buettner U, Waespe W (1984) Purkinje cell activity in the primate flocculus during optokinetic stimulation, smooth pursuit eye movements and VOR-suppression. Exp Brain Res 55:97–104
Dufossé M, Ito M, Miyashita Y (1977) Functional localization in the rabbit's cerebellar flocculus determined in relationship with eye movements. Neurosci Lett 5:273–277
Dufossé M, Ito M, Jastreboff PJ, Miyashita Y (1978) A neuronal correlate in the rabbit's cerebellum to adaptive modification of the vestibulo-ocular reflex. Brain Res 150:611–616
Ito M (1982) Cerebellar control of the vestibulo-ocular reflex around the flocculus hypothesis. Ann Rev Neurosci 5:275–296
Ito M (1984) Vestibulo-ocular reflex. In: The cerebellum and neural control. Raven, New York, pp 354–373
Jastreboff PJ (1979) Evaluation and statistical judgment of neural responses to sinusoidal stimulation in cases with superimposed drift and noise. Biol Cybern 33:113–120
Leonard CS, Simpson JI (1986) Eye velocity related simple spike modulation of rabbit flocculus Purkinje cells during horizontal compensatory eye movements. In: Developments in oculomotor research. Satellite symposium XXXth International Congress of IUPS, Gleneden Beach, Oregon, p 45
Lisberger SG, Fuchs AF (1978) Role of primate flocculus during rapid behavioral modification of vestibulo-ocular reflex. I. Purkinje cell activity during visually guided horizontal smooth-pursuit eye movements and passive rotation. J Neurophysiol 41:733–763
Lisberger SG, Pavelko TA (1988) Brain stem neurons in modified pathways for motor learning in the primate vestibulo-ocular reflex. Science 242:771–773
Miles FA, Fuller JH, Brightman DJ, Dow BM (1981) Long-term adaptive changes in primate vestibulo-ocular reflex. III. Electrophysiological observations in flocculus of normal monkey. J Neurophysiol 43:1437–1476
Miles FA, Lisberger SG (1981) Plasticity in vestibulo-ocular reflex: a new hypothesis. Ann Rev Neurosci 4:273–299
Miyashita Y (1984) Eye velocity responsiveness and its proprioceptive component in the floccular Purkinje cells of the alert pigmented rabbits. Exp Brain Res 55:81–90
Miyashita Y, Nagao S (1984) Analysis of signal content of Purkinje cell responses to optokinetic stimuli in the rabbit cerebellar flocculus by selective lesions of brain stem pathways. Neurosci Res 1:223–241
Nagao S (1988a) Behavior of floccular Purkinje cells correlated with adaptation of horizontal optokinetic eye movement response. Exp Brain Res 73:489–497
Nagao S (1988b) Eye velocity and position responses of rabbit floccular Purkinje cells in the horizontal eye movement field (H-zone). Neurosci Res Suppl 7:S101
Nagao S (1989a) Behavior of floccular Purkinje cells correlated with adaptation of vestibulo-ocular reflex. Exp Brain Res 77:531–540
Nagao (1989b) Role of cerebellar flocculus in the adaptive interaction between horizontal optokinetic eye movement response and vestibulo-ocular reflex. Exp Brain Res 77:541–551
Nagao S, Ito M, Karachot L (1985) Eye fields in the rabbit flocculus determined with local stimulation. Neurosci Res 3:39–52
Noda H, Suzuki DA (1979) The role of the flocculus of monkey in fixation and smooth pursuit eye movements. J Physiol 294:335–348
Noda H, Warabi T (1982) Eye position signals in the flocculus of the monkey during smooth pursuit eye movements. J Physiol 324:187–202
Waespe W, Henn V (1981) Visual-vestibular interaction in the flocculus of the alert monkey. Exp Brain Res 43:349–360
Titterington DM, Smith AFM, Makov VE (1985) Learning about the parameters of a mixture. In: statistical analysis of fixed mixture distribution. John Wily & Sons, Chichester New York Brisbane Toronto Singapore, pp 52–147
Watanabe E (1985) Role of primate flocculus in adaptation of the vestibulo-ocular reflex. Neurosci Res 3:20–38
Zee DS, Yamazaki A, Butler PH, Gücer G (1981) Effects of ablation of flocculus and paraflocculus on eye movements in primate. J Neurophysiol 46:878–899
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagao, S. Eye velocity is not the major factor that determines mossy fiber responses of rabbit floccular Purkinje cells to head and screen oscillation. Exp Brain Res 80, 221–224 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00228867
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00228867