Abstract
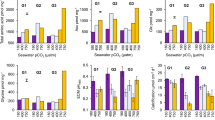
The relationship between various experimental concentrations of CO2 and calcification in Bossiella orbigniana (Decaisne) was studied by measuring Ca-45 incorporation into the crystalline matrix. Air containing CO2 at partial pressures (PCO 2) of 0.04 to 5.5% was bubbled through synthetic seawater in incubation vessels. The resultant pH values in the presence of plants ranged from 6.5 to 8.7. The maximum calcification rate appears to lie between 0.11 and 1.05% PCO 2. The data suggest that calcification is controlled by a biological process that may be sensitive to pH and/or to the relative bicarbonate concentration. The data also suggest that a severalfold increase in CO2 over the present atmospheric level might lead to increased calcification in this marine alga.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Abelson, P.: Energy and climate. Science, N.Y. 197, p. 941 (1977)
Adams, J.A.S., M.S.M. Mantovani and L.L. Lundell: Wood versus fossil fuel as a source of excess carbon dioxide in the atmosphere: a preliminary report. Science, N.Y. 196, 54–56 (1977)
Baes, C.F., Jr., H.E. Goeller, J.S. Olson and R.M. Rotty: Carbon dioxide and climate: the uncontrolled experiment. Am. Scient. 65, 310–320 (1977)
Bolin, B.: Changes of land biota and their importance for the carbon cycle. Science, N.Y. 196, 613–615 (1977)
Borowitzka, M.A.: Algal calcification. Oceanogr. mar. Biol. A. Rev. 15, 189–223 (1977)
— and A.W.D. Larkum: Calcification in the green alga Halimeda. II. The exchange of Ca2+ and the occurrence of age gradients in calcification and photosynthesis. J. exp. Bot. 27, 864–878 (1976a)
—: Calcification in the green alga Halimeda. II. The exchange of Ca2+ and the occurrence of age gradients in calcification and photosynthesis. J. exp. Bot. 27, 864–878 (1976a)
——: Calcification in the green alga Halimeda. III. The sources of inorganic carbon for photosynthesis and calcification and a model of the mechanism of calcification. J. exp. Bot. 27, 879–893 (1976b)
——: Calcification in the green alga Halimeda. I. An ultrastructure study of thallus development. J. Phycol. 13, 6–16 (1977)
Clark, G.R., II: Shell growth in the marine environment: approaches to the problem of marginal calcification. Am. Zool. 16, 617–626 (1976)
Clausen, C.D. and A.A. Roth: Effect of temperature and temperature adaptation on calcification rate in the hermatypic coral Pocillopora damicornis. Mar. Biol. 33, 93–100 (1975)
Coyne, L.: Chemistry in natural water systems. J. chem. Educ. 52, 796–800 (1975)
Crenshaw, M.A.: Coccolith formation by two marine coccolithophorids, Coccolithus huxleyi and Hymenomonas sp., 82 pp. Ph.D. dissertation, Duke University 1964
Culberson, C., R.M. Pytkowicz and J.E. Hawley: Seawater alkalinity determination by the pH method. J. mar. Res. 28, 15–21 (1970)
Darley, W.M.: Silicification and calcification. In: Algal physiology and biochemistry, pp 655–675. Ed. by W.D.P. Stewart. Berkeley and Los Angeles: University of California Press 1974. (Bot. Monogr. No. 10)
Digby, F.S.B.: Photosynthesis and respiration in the coralline algae Clathromorphum circumscriptum and Corallina officinalis and the metabolic basis of calcification. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 57, 1111–1124 (1977)
Dixon, W.J. (Ed.) BMD Biomedical computer programs, 773 pp. Berkeley: University of California Press 1974
Goreau, T.F.: Calcium carbonate deposition by coralline algae and corals in relation to their roles as reef-builders. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 109, 127–167 (1963)
Ikemori, M.: Relation of calcium uptake to photosynthetic activity as a factor controlling calcification in marine algae. Bot. Mag., Tokyo 83, 152–162 (1970)
Jolliffe, E.A. and E.B., Tregunna: Studies on HCO3 - ion uptake during photosynthesis in benthic marine algae. Phycologia 9, 293–303 (1970)
Kolesar, P.T.: Factors affecting the magnesium content of calcite secreted by some articulated coralline algae, 131 pp. Ph.D. dissertation. University of California, Riverside 1973
Lehman, J.T.: Enhanced transport of inorganic carbon into algal cells and its implications for the biological fixation of carbon. J. Phycol. 14, 33–42 (1978)
Leyendekkers, J.V.: The ionic activity function of water and the activity coefficient of the hydrogen ion in seawater. Limnol. Oceanogr. 18, 784–787 (1973)
Lucas, W.J.: Photosynthetic fixation of 14carbon by internodal cells of Chara corallina. J. exp. Bot. 26, 331–346 (1974)
Moss, D.N.: Studies on increasing photosynthesis in crop plants. In: CO2 metabolism and plant productivity, pp 31–41. Ed. by R.H. Burris and C.C. Black. Baltimore: University Park Press 1976
Paasche, E.: A tracer study of the inorganic carbon uptake during coccolith formation and photosynthesis in the coccolithophorid Coccolithus huxleyi. Physiologia P1. 3 (Suppl.), 1–82 (1964)
—: Biology and physiology of coccolithophorids. A. Rev. Microbiol. 22, 71–86 (1968)
Park, P.K.: Oceanic CO2 system: an evaluation of ten methods of investigation. Limnol. Oceanogr. 14, 179–186 (1969)
Pearse, V.B.: Radioisotopic study of calcification in the articulated coralline alga Bossiella orbigniana. J. Phycol. 8, 88–97 (1972)
Plass, G.N.: Carbon dioxide and the climate. Am. Scient. 44, 302–316 (1956)
Robbins, J.V.: The effects of total carbon supply, irradiance, pH, temperature and salinity on short term photosynthesis of Palmaria palmata (L.) Grev. J. Phycol. 13 (Suppl.), p. 58 (1977)
Silva, P.C.: Notes on Pacific marine algae. Madroño 14, 41–51 (1957)
Skirrow, G.: The dissolved gases — carbon dioxide. In: Chemical oceanography. 2nd ed. Vol. II. pp 1–192. Ed. by J.P. Riley and G. Skirrow. London: Academic Press 1975
Smith, A.D.: The effect of carbon dioxide concentration on calcification in the red coralline alga Bossiella orbigniana, 54 pp. Ph.D. dissertation, Loma Linda University 1977
Smith, W.H., Jr. and D.W. Hood: pH measurement in the ocean: a sea water secondary buffer system. In: Ken Sugawara festival volume. Recent researches in the fields of the hydrosphere, atmosphere and nuclear geochemistry, pp 185–202. Ed. by Y. Miyake and T. Koyama. Tokyo: Maruzen Co. 1964
Stark, L.M., L. Almodovar and R.W. Krauss: Factors affecting the rate of calcification in Halimeda opuntia (L.) Lamouroux and Halimeda discoidea Decaisne. J. Phycol. 5, 305–312 (1969)
Steemann Nielsen, E.: Marine photosynthesis, 142 pp. New York: American Elsevier Publishing Co. 1975
Suess, H.E.: Natural radiocarbon. Endeavour 32, 34–38 (1973)
Swift, E. and W.R. Taylor: The effect of pH on the division rate of the coccolithophorid Cricosphaera elongata. J. Phycol. 2, 121–125 (1966)
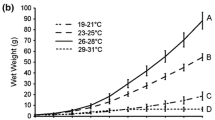
Thomas, C.M.: Effects of temperature on calcium uptake in Bossiella orbigniana, 101 pp. M.A. thesis, Loma Linda University 1976
Wilbur, K.M., L.H. Colinvaux and N. Watabe: Electron microscope study of calcification in the alga Halimeda (order Siphonales). Phycologia 8, 27–35 (1969)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by N.D. Holland, La Jolla
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smith, A.D., Roth, A.A. Effect of carbon dioxide concentration on calcification in the red coralline alga Bossiella orbigniana . Mar. Biol. 52, 217–225 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00398135
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00398135