Abstract
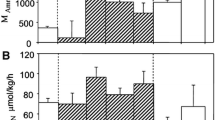
Ammonia excretion was investigated in relation to oxygen consumption during a feeding regime and during shortterm starvation in two mature male Octopus vulgaris, trawled in spring 1983 off Banyuls-sur-mer. In our study, ammonia excretion is taken to include renal and gill loss. The excretion of primary amines was also studied, but proved to be negligible under our experimental conditions. Ammonia excretion and oxygen consumption are repetitive linear processes over 1 to 2 h incubation periods at 15° to 16°C, in both fed and starved conditions. Starvation induces a decline in ammonia excretion and oxygen consumption and an increase in the atomic O:N ratio, suggesting that O. vulgaris uses up other reserves (lipids) before utilizing an exclusively protein substrate.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Bayne, B. L. and C. Scullard: Rates of nitrogen excretion by species of Mytilus (Bivalvia: Mollusca). j. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 57, 355–369 (1977)
Buckley, S. K. L.: Oogenesis and its hormonal control in Octopus vulgaris, PhD. thesis, University of Cambridge 1976
Conover, R. J. and E. D. S. Corner: Respiration and nitrogen excretion by some marine zooplankton in relation to their life cycle. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 48, 49–75 (1968)
Delaunay, H.: L'excrétion azotée des invertébrés. Biol. Rev. 6, 265–301 (1931)
Harrison, F. M. and A. W. Martin: Excretion in the cephalopod Octopus dofleini. J. exp. Biol. 42, 71–98 (1965)
Martin, A. W.: The renopericardial canal as the reabsorptive structure of an octopus urinary tract. Am. Zool. 5, p. 207 (1965)
Mayzaud, P.: Respiration and nitrogen excretion of zooplankton. II. Studies of the metabolic characteristics of starved animals. Mar. Biol. 21, 19–28 (1973)
Mayzaud, P.: Respiration and nitrogen excretion of zooplankton. IV. The influence of starvation on the metabolism and the biochemical composition of some species. Mar. Biol. 37, 47–58 (1976)
O'Dor, R. K., K. Mangold, R. Boucher-Rodoni, M. J. Wells and J. Wells. Nutrient absorption, storage and remobilization in Octopus vulgaris. Mar. Behav. Physiol. 11, 239–258 (1984)
O'Dor, R. K. and M. J. Wells: Yolk protein synthesis in the ovary of Octopus vulgaris and its control by the optic gland gonadotropin. J. exp. Biol. 59, 665–674 (1973)
O'Dor, R. K. and M. J. Wells: Control of yolk protein synthesis by octopus gonadotropin in vivo and in vitro. Gen. comp. Endocr. 27, 129–135 (1975)
O'Dor, R. K. and M. J. Wells: Reproduction versus somatic growth: hormonal control in Octopus vulgaris. J. exp. Biol. 77, 15–31 (1978)
Potts, W. T. W.: Ammonia excretion in Octopus dofleini. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 14, 339–355 (1965)
Potts, W. T. W.: Excretion in the molluscs. Biol. Rev. 42, 1–41 (1967)
Regnault, M.: Respiration and ammonia excretion of the shrimp Crangon crangon L. Metabolic responses to prolonged starvation. J. comp. Physiol. 141, 549–555 (1981)
Schipp, R. and S. v. Boletzky: Morphology and function of the excretory organs in dibranchiate cephalopods. Fortschr. Zool. 23, 89–111 (1975)
Schipp, R., S. Mollenhauer and S. v. Boletzky: Electron microscopical and histochemical studies of differentiation and function of the cephalopod gill (Sepia officinalis). Zoomorphologie 93, 193–207 (1979)
Solórzano, L.: Determination of ammonia in natural waters by the phenolhypochlorite method. Limnol. Oceanogr. 14, 799–801 (1969)
Stickle, W. B. and B. L. Bayne: Effects of temperature and salinity on oxygen consumption and nitrogen excretion in Thais (Nucella) lapillus (L.). J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 58, 1–17 (1982)
Udenfriend, S., S. Stein, P. Bohlen, W. Dairman, W. Leimgruber and M. Weigele: Fluorescamine: a reagent for assay of amino acids, peptides, proteins and primary amines in the picomole range. Science, N.Y. 178, 871–872 (1972)
Wells, M. J., R. K. O'Dor, K. Mangold and J. Wells: Diurnal changes in activity and metabolic rate in Octopus vulgaris. Mar. Behav. Physiol. 9, 275–287 (1983a)
Wells, M. J., R. K. O'Dor, K. Mangold and J. Wells: Feeding and metabolic rate in Octopus. Mar. Behav. Physiol. 9, 305–317 (1983 b)
Wood, E. D., F. A. J. Armstrong and F. A. Richards: Determination of nitrate in seawater by cadmium-copper reduction to nitrite. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 47, 23–31 (1967)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by J. M. Pérès, Marseille
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boucher-Rodoni, R., Mangold, K. Ammonia excretion during feeding and starvation in Octopus vulgaris . Mar. Biol. 86, 193–197 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00399026
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00399026