Summary
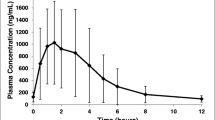
The pharmacokinetics of naproxen after a single oral dose of 250 mg has been studied in 8 subjects with normal renal function and 16 patients with varying degrees of chronic renal insufficiency. Unchanged naproxen and its main unconjugated metabolite, 6-0-desmethylnaproxen, were determined fluorometrically in serum. In healthy subjects the elimination half-life of naproxen was 17.7± 3.0 h (mean±SD) and it was not significantly prolonged in patients with renal failure (18.1±5.3) h. No accumulation of naproxen in serum occurred in uraemic patients. On the contrary, serum drug levels were slightly but significantly lower in patients with severe renal failure. The total body clearance and apparent volume of distribution of naproxen were significantly increased in this group of patients. Decreased binding of naproxen to serum proteins was observed in patients with renal failure. The apparent half-life of desmethylnaproxen was of the same order of magnitude as that of naproxen (18.6± 4.4 h), and was also independent of renal function. A good correlation was found between the area under the curve (AUC), the peak concentration of the metabolite and the serum creatinine concentration. These observations suggest increased metabolism and an increased apparent volume of distribution of naproxen in severe renal failure, probably caused by decreased serum protein binding of the drug. However, it is proposed that in naproxen therapy no adjustment of the dosage regimen is necessary in patients with impaired renal function.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson RJ, Berl T, McDonald KM, Schrier RW (1976) Prostaglandins: Effects on blood pressure, renal blood flow, sodium and water excretion. Kidney Int 10: 205–215
Anttila M (1977) Fluorometric determination of naproxen in serum. J Pharm Sci 66: 433–434
Cockcroft DW, Gault MH (1976) Prediction of creatinine clearance from serum creatinine. Nephron 16: 31–41
Gibaldi M (1977) Drug distribution in renal failure. Am J Med 62: 471–474
Greenblatt DW, Koch-Weser J (1975) Clinical Pharmacokinetics. N Engl J Med 293: 702–705
Letteri JM, Mellk H, Louis S, Kutt H, Durante P, Glazko A (1971) Diphenylhydantoin metabolism in uremia. N Engl J Med 285: 648–652
Lichter M, Black M, Arias JM (1973) The metabolism of antipyrine in patients with chronic renal failure. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 187: 612–619
Lunde PKM, Rane A, Yaffe SJ, Lund L, Sjöqvist F (1970) Plasma protein binding of diphenylhydantoin in man. Interaction with other drugs and the effect of temperature and plasma dilution. Clin Pharmacol Ther 11: 846–855
Maddocks JL, Wake CJ, Harber MM (1975) The plasma half-life of antipyrine in chronic uraemic and normal subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol 2: 339–343
Odar-Cederlöf I, Borgå O (1974) Kinetics of diphenylhydantoin in uraemic patients: Consequences of decreased plasma protein binding. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 7: 31–37
Reidenberg, MM (1976) The binding of drugs to plasma proteins from patients with poor renal function. Clin Pharmacokinet 1: 121–125
Rollins DE, Klaassen CD (1979) Biliary excretion of drugs in man. Clin Pharmacokinet 4: 368–379
Runkel RA, Kraft KS, Boost G, Sevelius H, Forchielli E, Hill R, Magoun R, Szakacs JK, Segre E (1972) Caproxen oral absorption charasteristics. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 20: 1457–1466
Runkel R, Forchielli E, Boost G, Chaplin M, Hill R, Sevelius H, Thompson G, Segre E (1973) Naproxen — metabolism excretion and comparative pharmacokinetics. Scand J Rheumatol Suppl 2: 29–36
Runkel R, Forchielli E, Sevelius H, Chaplin M, Segre E (1974) Nonlinear plasma level response to high doses of naproxen. Clin Pharmacol Ther 15: 261–266
Runkel R, Chaplin MD, Sevelius H, Ortega E, Segre E (1976) Pharmacokinetics of naproxen overdoses. Clin Pharmacol Ther 20: 269–277
Runkel R, Mroszczak E, Chaplin M, Sevelius H, Segre E (1978) Naproxen-probenecid interaction. Clin Pharmacol Ther 24: 706–713
Segre EJ (1975) Naproxen metabolism in man. J Clin Pharmacol 15: 316–323
Stein G, Kunze M, Zaumseil J, Traeger A (1977) Zur Pharmakokinetik von Indometazin und Indometazin-metaboliten bei wiederholter Applikation an nierengesunden und nierengeschädigten Patienten. Int J Clin Pharmacol 15: 470–473
Thompson G, Collins J (1973) Urinary metabolic profiles for choosing test animals for chronic toxicity studies: Application to naproxen. J Pharm Sci 62: 937–941
Traeger A, Stein G, Kunze M, Zaumseil J (1972) Zur Pharmakokinetik von Indometazin bei nierengeschädigten Patienten. Int J Clin Pharmacol 6: 237–242
Weber SS, Troutman WC, Trujeque L (1979) Effect of hemodialysis on plasma naproxen concentration. Am J Hosp Pharm 36: 1567–1569
Wibell L (1977) The metabolism of naproxen in renal insufficiency. Scand J Rheumatol 6: 71–72
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anttila, M., Haataja, M. & Kasanen, A. Pharmacokinetics of naproxen in subjects with normal and impaired renal function. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 18, 263–268 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00563009
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00563009