Summary
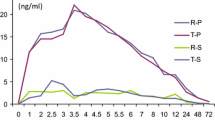
The correlation between serum and saliva levels of theophylline was investigated in seven healthy volunteers after multiple dose administration of a low dose (300 mg/day) and a high dose (900 mg/day) of a sustained release theophylline preparation (Theo-Dur®). Tablets were taken for five days, at 8 a.m. and 8 p.m. and a last dose was taken on Day 6 at 8 a. m. Fourteen serum and saliva samples were collected simultaneously during the dosing period and for up to 32 h after the last dose. On the 300 mg/day regimen the level in saliva was 55.3% of the serum level, with an overall variability of 6.7% and an intrasubject variability of 10.5%. After 900 mg/day, the saliva concentration was 55.5% of the serum concentration, with an overall variability of 7.6% and an intrasubject variability of 12.7%. A good correlation was found between both determinations (r=0.99), which suggests that saliva levels could be used to monitor theophylline after administration of a sustained release tablet.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aranda JV, Sitar DS, Parsons WD, Loughnan PM, Neims AH (1976) Pharmacokinetic aspects of theophylline in premature newborns. N Engl J Med 295: 413–416
Boobis S, Trembath PW (1978) Plasma-saliva ratio of theophylline following oral theophylline derivatives. Br J Clin Pharmacol 6: 456 P
Cohen A, Johnson C, Re O (1975) A rapidly dissolving theophylline tablet. Curr Ther Res 17: 497–505
Danhof M, Breimer DD (1978) Therapeutic drug monitoring in saliva. Clin Pharmacokinet 3: 39–57
Eney RD, Goldstein EO (1976) Compliance of chronic asthmatics with oral administration of theophylline as measured by serum and salivary levels. Pediatrics 57: 513–517
Galant SP, Gillman SA, Cummins LH, Kozak PP, Orcutt JJ (1977) Reliability of salivary theophylline as a guide to plasma theophylline levels. Am J Dis Child 131: 970–972
Hendeles L, Burkey S, Bighley L, Richardson R (1977) Unpredictability of theophylline saliva measurements in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol 60: 335–338
Jonkman JHG, Schoenmaker R, Greving JE, De Zeeuw RA (1980a) Rapid and selective theophylline serum and saliva assay by means of high pressure liquid chromatography. Pharm Weekbl (Sci Ed) 2: 49–53
Jonkman JHG, Berg WC, Schoenmaker R, De Zeeuw RA, Greving JE, Orie NGM (1980b) Disposition and clinical pharmacokinetics of microcrystalline theophylline. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 17: 379–384
Khanna NN, Bada HS, Somani SM (1980) Use of salivary concentrations in the prediction of serum caffeine and theophylline concentrations in premature infants. J Pediatrics 96: 494–499
Knop HJ, Kalafusz R, Knols AJF, Van der Kleyn E (1975) Preliminary report on the saliva/plasma ratio of theophylline after administration of theophylline derivatives in suppositories. Pharm Weekbl 110: 1297–1299
Koëter GH, Jonkman JHG, De Vries K, Schoenmaker R, Greving JE, De Zeeuw RA (1981) Pharmacokinetics of sustained release theophylline at low and high multidose regimen. Br J Clin Pharmacol (in press).
Koysooko R, Ellis EF, Levy G (1974) Relationship between theophylline concentration in plasma and saliva in man. Clin Pharmacol Ther 15: 454–460
Lena SM, Hutchins P, Wood CBS, Turner P (1980) Salivary theophylline estimation in the management of asthma in children. Postgrad Med J 56: 85–87
Levy G, Ellis EF, Koysooko R (1974) Indirect plasma-theophylline monitoring in asthmatic children by determination of theophylline concentration in saliva. Pediatrics 53: 873–876
Mangione A, Imhoff TE, Lee RV, Shum LY, Jusko WJ (1978) Pharmacokinetics of theophylline in liver disease. Chest 73: 616–622
Piafsky KM, Sitar DS, Rangno RE, Ogilvie RI (1977) Theophylline disposition in patients with hepatic cirrhosis. N Engl J Med 296: 1495–1497
Posti J (1979) Arzneimittelkonzentrationen in Plasma und in Speichel. Physiologische und pharmacokinetische Betrachtungen. Pharm Acta Helv 54: 191–196
Schack JA, Waxler SH (1949) An ultraviolet spectrophotometric method for the determination of theophylline and theobromine in blood and tissues. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 97: 283–291
Weinberger M, Hendeles L, Bighley L (1978) The relation of product formulation to absorption of oral theophylline. N Engl J Med 299: 852–857
Zuidema J (1978) Biofarmaceutische en farmacokinetische aspecten van theofylline en acefylline. Ph D Thesis, University of Amsterdam
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jonkman, J.H.G., Koëter, G.H., Schoenmaker, R. et al. Correlation of serum and saliva theophylline concentrations after administration of a sustained release preparation. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 20, 73–78 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00554670
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00554670