Summary
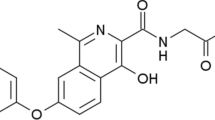
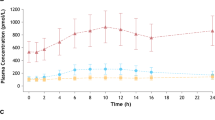
The haemodynamic response and pharmacokinetics of single dose oral tolmesoxide were studied at various dose levels in 4 patients with severe hypertension. There was a reproducible fall in mean arterial pressure from baseline of 24.2% and a rise in heart rate of 37.6% following administration of tolmesoxide. The onset of antihypertensive action occurred within 1 h, with a peak effect at 3 h after dosing. The mean duration of action was up to 12.0 h. Tolmesoxide had a mean half-life of 3.0 h. It was rapidly absorbed with a mean peak plasma level occurring at 1.0 h. Plasma levels correlated well with the doses administered. Side-effects included mild nausea, facial flushing and postural symptoms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buylla JA, Clifford JM, Wynne RD (1979) The Action of tolmesoxide on certain cardiovascular measurements in healthy normal volunteers. Br J Clin Pharmacol 8: 402
Chidsey CA, Gottlieb TB (1974) The Pharmacological basis of antihypertensive therapy: the role of vasodilator drugs. Prog Cardiovasc Dis XVII: 99–113
Collier JG, Lorge RE, Robinson BF (1978) Comparison of effects of tolmesoxide (RX71107), diazoxide, hydrallazine, prazosin, glyceryl trinitrate and solium nitroprusside on forearm arteries and dorsal hand veins of man. Br J Clin Pharmacol 5: 35–44
Doxey JC (1978) Tolmesoxide, a drug that lowers blood pressure by a direct relaxant effect on vascular smooth muscle. Br J Pharmacol 63: 111–118
Freis ED, Rose JC, Higgins TF, Finnerty Jr FA, Kelley RT, Partenope EA (1953) The haemodynamic effects of hypotensive drugs in man. IV. I-hydrazinophthalazine. Circulation 8: 199–204
Lloyd-Jones JG, Henson RA, Nichols JD, Greenslade D, Clifford JM (1981) Pharmacokinetics of intravenous and oral tolmesoxide, 19: 119–125
Lowenthal DT, Onesti G, Mutterperl R, Affrime M, Martinez EW, Kim KE, Busby P, Shirk J, Swartz C (1978) Long-term clinical effects, bioavailability and kinetics of minoxidil in relation to renal function. J Clin Pharmacol 18: 500–508
Moore-Jones D, Perry Jr HM (1966) Radio-autographic localization of hydralazine — I — C14 in arterial walls. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 122: 576–579
O'Malley K, O'Boyle C, McGarry K, O'Brien ET (1980) Vasodilators and α-adrenoceptor blocking drugs in the treatment of hypertension. The Royal Society of Medicine, Int. Congress and Symposium Series 26: 73–81
Pluss RG, Orcutt J, Chidsey CA (1972) Tissue distribution and hypotensive effects of minoxidil in normotensive rats. J Lab Clin Med 79: 639–647
Reidenberg MM, Drayer D, DeMarco AL, Bello CT (1973) Hydralazine elimination in man. Clin Pharmacol Ther 14: 970–977
Ueda H, Yagi S, Kaneko Y (1968) Hydralazine and plasma renin activity. Arch Intern Med 122: 387–391
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
O'Boyle, C.P., Laher, M., O'Brien, E.T. et al. The clinical pharmacology of tolmesoxide. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 23, 93–97 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00545961
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00545961