Summary
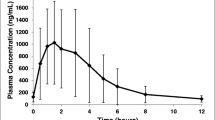
The pharmacokinetics and oral biovailability of dexamethasone were studied in 6 patients with neurological disease being treated with high dosages of the drug. A specific high performance liquid chromatographic assay was used to measure dexamethasone concentrations. Unlike the previously published mean figure of 0.78 for the oral bioavailability of the drug given in single doses to healthy volunteers, the mean bioavailability of dexamethasone in the patients studied was 0.53±SD 0.40. It appeared more likely that this incomplete bioavailability was due to presystemic elimination than to poor absorption. The intravenous clearance of the drug was relatively high (0.4902±SD 2291 l kg−1, approximately 65% of expected hepatic plasma flow), the oral clearance higher (2.5804±SD 3.2181 l kg−1 h−1) while the absorption rate constant (4.8729±8.4998 h−1), suggested rapid absorption after oral administration. Prior phenytoin and possibly prior dexamethasone therapy is likely to have contributed to the higher clearance values of the drug in these patients than the values reported in healthy volunteers after single dose studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown RD, Manno JE (1978) ESTRIP, a Basic computer program for obtaining initial polyexponential parameter estimates. J Pharm Sci 67: 1687–1691
Cham BE, Sadowski B, O'Hagan JM, DeWytt CN, Bochner F, Eadie MJ (1980) High performance liquid chromatographic assay of dexamethasone in plasma and tissue. Ther Drug Monit 2: 373–377
Duggan DE, Yeh KC, Matalia N, Ditzler CA, McMahon FG (1975) Bioavailability of oral dexamethasone. Clin Pharmacol Ther 18: 205–209
Gibaldi M, Perrier D (1975) Pharmacokinetics. Marcel Dekker, New York
Haque N, Thrasher K, Werk EE, Knowles HC, Sholiton LJ (1972) Studies on dexamethasone metabolism in man. Effect of diphenylhydantoin. J Clin Endocrinol 34: 44–50
Horwitz DL, Homer LD (1970) Analysis of biomedical data by time-sharing computers. 1. Non-linear regression analysis. Project No. MR005.20-0287. Naval Medical Research Institute, National Naval Medical Centre, Bethesda, Maryland 20014, USA
Jubiz W, Meikle AW, Levinson RA, Mizutani S, West CD, Tyler FH (1970) Effect of diphenylhydantoin on the metabolism of dexamethasone. Mechanism of abnormal dexamethasone suppression in humans. N Engl J Med 283: 11–14
McCafferty J, Brophy TRO'R, Yelland JD, Cham BE, Bochner F, Eadie MJ (1981) Intraoperative pharmacokinetics of dexamethasone. Br J Clin Pharmacol 12: 434–435
Peck CC, Barrett BB (1979) Nonlinear least-squares programs for microcomputers. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 7: 537–541
Tsuei SE, Moore RG, Ashley JI, McBride WG (1979) Disposition of synthetic glucocorticoids. I. Pharmacokinetics of dexamethasone in healthy adults. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 7: 249–264
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brophy, T.R.O., McCafferty, J., Tyrer, J.H. et al. Bioavailability of oral dexamethasone during high dose steroid therapy in neurological patients. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 24, 103–108 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00613935
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00613935