Summary
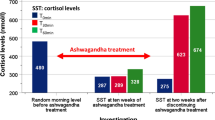
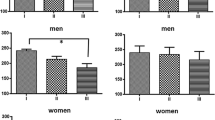
In a model of mental stress the influence of nifedipine and hydrochlorothiazide on stress-induced changes in blood pressure, heart rate, and plasma catecholamines was studied in normal persons. The drugs were used to investigate whether substances with antihypertensive but no particular sympatholytic properties were capable of suppressing emotionally induced stress reactions. In all subjects blood pressure and heart rate increased significantly during mental stress, and this effect was not inhibited either by nifedipine or hydrochlorothiazide. In the hydrochlorothiazide group plasma noradrenaline levels were significantly higher than in controls in the resting state and during the stress reaction, whereas in the nifedipine group no difference was observed. It is concluded that nifedipine or hydrochlorothiazide do not inhibit emotional stress reactions in normotensive persons.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Axelrod J (1957) O-methylation of epinephrine and other catechols in vitro and in vivo. Science 126: 400
Brod J, Fencl V, Hejl Z, Jirka J (1959) Circulatory changes underlying blood pressure elevation during acute emotional stress (mental arithmetic) in normotensive and hypertensive subjects. Clin Sci 18: 269
Corea L, Miele N, Bentivoglio M, Boschetti E, Agabiti RE, Muiesan G (1979) Acute and chronic effects of nifedipine on plasma renin activity and plasma adrenaline and noradrenaline in controls and hypertensive patients. Clin Sci 57 [Suppl 5]: 115s-117s
Funkenstein DH, Kings SH, Drolette ME (1957) Mastery of stress. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, p 44
Heidbreder E, Pagel G, Röckel A, Heidland A (1978) Beta-adrenergic blockade in stress protection. Limited effect of metoprolol in psychological stress reaction. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 14: 391
Heidbreder E, Ziegler A, Heidland A (1982) Verhindern sympathikolytische Antihypertensiva den Blutdruckanstieg bei mentalem Streß? Herz-Kreisl 14: 135
Kirsten R, Heintz B, Hennemann H, Nelson K (1980) Pharmacological approach to the patients with pheochromocytoma. In: Rietbrock N, Woodcock BG, Neuhaus G (eds) Methods in Clinical Pharmacology. Vieweg & Sohn, Braunschweig, p 314
Lake CR, Ziegler MG, Coleman MD, Kopin IJ (1979) Hydrochlorothiazide-induced sympathetic hyperactivity in hypertensive patients. Clin Pharmacol Ther 26: 428
Lederballe-Pedersen O, Mikkelsen E, Christensen NJ, Kornerup JJ, Pedersen EB (1979) Effect of nifedipine on plasma renin, aldosterone and catecholamines in arterial hypertension. J Clin Pharmacol 15: 235–240
Lee BS (1950) Effects of delayed speech feed-back. J Acoust Soc Am 22: 822
Lerche E, Nessel E (1956) Neue Beobachtungen bei Reihen-untersuchungen mit verzögerter Sprachrückkopplung (Lee-Effekt) Arch Hals, Nasen, Ohrenheilkd 169: 505
Lydtin H, Lohmöller G, Lohmöller R, Schmitz H, Walter J (1975) Hemodynamic studies of adalat in healthy volunteers and in patients; In: Lochner W, Braasch H, Kroneberg K (eds) 2nd Int Adalat Symp, New Therapy of Ischemic Heart Disease. Excerpta Medica, Berlin, pp 112–123
Murphy MB, Scriven AJ, Brady H, Dollery CT (1982) Nifedipine reduces blood pressure but not sympathetic activity. In: Int. Symposium on Calcium Modulators, Venice, June 17–18, 1982, Abstract p41, Fondazione Giovanni Lorenzini
Nelson RR, Gobel FL, Jorgensen CR, Wang K, Wang Y, Taylor HL (1974) Hemodynamic predictors of myocardical oxygen consumption during static and dynamic exercise. Circulation 50: 1179
Reid JL (1980) Plasma noradrenaline as an index of sympathetic activity. In: Philipp T, Distler A (eds) Hypertension. Mechanisms and Management. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, p 65
Silverberg AB, Shah SD, Haymond MW, Cryer PE (1978) Norepinephrine: Hormone and neurotransmitter in man. Am J Physiol 234: E 252
Stein G (1976) Antianginal efficacy of different doses of adalat in angina pectoris patients in a double-blind trial. In: Jatene AD (ed) New Therapy of Ischemic Heart Disease, 3. Int. Adalat Symposium, Excerpta Medica, Amsterdam, Oxford, p 233–239
Taylor SH, Silke B, Ahuja RC, Okoli RC (1982) Comparison of two calcium antagonists on the circulatory responses to isometric/dynamic exercise and cold in hypertension. Int Symposium on Calcium Modulators. Venice, June 17–18, 1982, Abstract p44, Fondazione Giovanni Lorenzini
Taylor SH, Silke B, Ahuja RC, Okoli R (1982) Influence of nicardipine on the blood pressure at rest and on the pressor responses to cold, isometric exertion, and dynamic exercise in hypertensive patients. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 4: 803–807
Weidmann P, Grimm M, Meier A, Glück Z, Keusch G, Minder I, Beretta-Piccoli C (1980) Cardiovascular pressor reactivity as related to plasma catecholamines: Role in the pathogenesis of essential hypertension and in the antihypertensive mechanism of diuretic treatment. In: Philipp T, Distler A (eds) Hypertension. Mechanisms and Management. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heidbreder, E., Schafferhans, K., Kirsten, R. et al. Effect of diuretics and calcium antagonists on circulatory parameters and plasma catecholamines during mental stress. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 25, 19–22 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00544008
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00544008