Summary
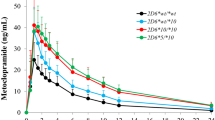
The kinetics of mefloquine were studied in 12 healthy Thai male and 12 healthy Thai female volunteers. Mefloquine (MQ) was administered either alone (750 mg orally) or in combination (MSP) with sulphadoxine (1.5 g) and pyrimethamine (75 mg) to each of 6 male and 6 female subjects. Plasma concentrations of MQ were measured by HPLC at intervals for 42 days. There was considerable interindividual variability in the pharmacokinetic parameters; for example in the male subjects receiving MQ alone peak concentrations ranged between 638 and 2494 ng·ml−1 with a mean concentration of 1442 ng·ml−1. Compared to previously published data on MQ concentrations in Caucasian male subjects, the present study indicates that higher concentrations are achieved in Thai subjects. The only significant difference in kinetic parameters between male and female subjects receiving MQ alone was in the mean residence time (MRT) which was greater in females. However, an analysis of pharmacokinetic parameters following administration of the combination preparation showed that the time to peak (tmax) was significantly reduced in females receiving MSP compared to the corresponding females given MQ alone and males given MSP. When data obtained from all subjects (male and female) receiving either MQ alone or MSP were combined, both MRT and half-life were significantly greater in subjects given MSP. There is therefore some evidence that therapeutic concentrations of MQ are maintained for a longer period of time following MSP administration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Harinasuta T, Dixon KE, Warrell DA, Doberstyn EB (1982) Recent advances in malaria with special reference to South East Asia. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Hyg 13: 1–34
Chongsuphajaisiddhi T, Sabcharoen A, Attanath P (1981) In vivo and in vitro sensitivity of falciparum malaria to quinine in Thai children. Ann Trop Paediatr 1: 21–26
Ohnmacht CJ, Patel AR, Lutz RE (1971) Antimalarials, 7-bis (Trifluoro methyl)-α-(2-piperidyl)-4-quinoline methanols. J Med Chem 14: 926–928
Strube RE (1975) The search for new antimalarial drugs. J Trop Med Hyg 78: 171–185
Rieckmann KH, Trenholme GM, Williams RL, Carson PE, Frischer M, Desjardins RE (1974) Prophylactic activity of mefloquine hydrochloride (WR 142,490) in drug resistant malaria. Bull WHO 51: 375–378
Trenholme GM, Williams RL, Desjardins RE, Frischer M, Carson PE, Rieckman KH, Canfield CJ (1975) Mefloquine (WR 142,490) in the treatment of human malaria. Science 190: 792–794
Clyde DF, McCarthy VC, Miller RM, Hornick RB (1976) Suppressive activity of mefloquine in sporozoit induced human malaria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 9: 384–386
Hall AP, Doberstyn EB, Karnchanachetanee C, Samransamruajkit S, Laisuthai B, Pearlman EJ, Lampe RM, Miller CF, Phintuyothin P (1977) Sequential treatment with quinine and mefloquine or quinine and pyrimethamine sulphadoxine for falciparum malaria. Br Med J 1: 1626–1628
Rozman RS, Canfield CS (1979) New experimental antimalarial drugs. Adv Pharmacol Chemother 16: 1–43
Harinasuta T, Bunnag D, Wernsdorfer WH (1983) A phase II clinical trial of mefloquine in patients with chloroquine resistant falciparum malaria in Thailand. Bull WHO 61: 299–305
Ekue JMK, Ulrich AM, Rwabwogo-Atenyi J, Sheth UK (1983) A double-blind comparative clinical trial of mefloquine and chloroquine in symptomatic falciparum malaria. Bull WHO 61: 713–718
Peters W, Portus JH, Robinson BL (1977) The chemotherapy of rodent malaria XXVIII. The development of resistance to melfoquine (WR 142,490). Ann Trop Med Parasitol 71: 419–427
Kazim M, Peri SK, Dutta GP (1979) Chemotherapeutic studies with mefloquine and selection of a mefloquine resistant strain of plasmodium berghei. Indian J Med Res 70 [Suppl]: 95–102
Merkli B, Richle R, Peters W (1980) The inhibitory effect of a drug combination on the development of mefloquine resistance in plasmodium berghei. Ann Trop Med Parsitol 74: 1–9
Peters W (1974) Prevention of drug resistance in rodent malaria by the use of drug mixture. Bull WHO 51: 379–383
Peters W, Robinson BL (1984) The chemotherapy of rodent malaria XXXV. Further studies on the retardation of drug resistance by the use of a triple combination of mefloquine, pyrimethamine and sulphadoxine in mice infected with P. berghei NS. Ann Trop Med Parsitol 78: 459–466
Desjardins RE, Pamplin CL, von Bredow J, Barry KG, Canfield CJ (1979) Kinetics of a new antimalarial, mefloquine. Clin Pharmacol Ther 27: 372–379
Schwartz DE, Weber W, Richard-Lenoble D, Gentilini M (1980) Kinetic studies of mefloquine and one of its metabolites in the dog and in man. Acta Tropica 37: 238–242
Schwartz DE, Eckert G, Hartmann D, Weber B, Richard-Lenoble D, Ekue JMK, Gentilini M (1982) Single dose kinetics of mefloquine in man. Chemotherapy 28: 70–84
Mimica I, Fry W, Eckert G, Schwartz DE (1983) Multiple-dose kinetic study of mefloquine in healthy male volunteers. Chemotherapy 29: 184–187
Riviere JH, Back DJ, Breckenridge AM, Howells RE (1985) The pharmacokinetics of mefloquine in man. Lack of effect of mefloquine on antipyrine metabolism. Br J Clin Pharmacol 20: 469–474
Gibaldi M, Perrier D (1982) Pharmacokinetics. Marcel Dekker, New York, p 494
White NJ (1985) Clinical pharmacokinetics of antimalarial drugs. Clin Pharmacokinet 10: 187–215
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karbwang, J., Bunnag, D., Breckenridge, A.M. et al. The pharmacokinetics of mefloquine when given alone or in combination with sulphadoxine and pyrimethamine in Thai male and female subjects. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 32, 173–177 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00542191
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00542191