Summary
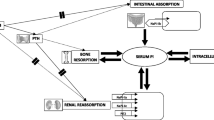
The effects on plasma and skeletal muscle electrolytes of the combination of triamterene 37.5 mg and hydrochlorothiazide 25 mg daily were studied in 19 patients on prior long-term (>1 year) diuretic therapy for arterial hypertension and/or congestive heart failure. A further 20 patients fulfilling the same admission criteria were used as controls. Blood samples and skeletal muscle biopsies were taken before the study and after 6 months on therapy.
The diuretic-treated group had a significant increase in skeletal muscle potassium and magnesium after 6 months on therapy as compared to the controls.
Thus, the combination of triameterene and hydrochlorothiazide appeared effective in preserving the cellular content of potassium and magnesium on a long-term basis in the type of patient studied.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bender AD, Carter CL, Hansen KB (1967) Use of a diuretic combination of triamterene and hydrochlorothiazide in elderly patients. J Am Geriat Soc 15: 166–173
Devane J, Ryan MP (1981) The effects of amiloride and triamterenc on urinary magnesium excretion in conscious salineloaded rats. Br J Pharmacol 72: 285–289
Dyckner T, Wester PO (1979) Ventricular extrasystoles and intracellular electrolytes before and after potassium and magnesium infusions in patients on diuretic treatment. Am Heart J 97: 12–18
Dyckner T, Wester PO, Widman L (1986) Effects of spironolactone on serum and muscle electrolytes in patients on long-term diuretic therapy for congestive heart failure and/or arterial hypertension. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 30: 535–540
Fisch C (1973) Relation of electrolyte disturbances to cardiac arrhythmias. Circulation 47: 408–419
Gatzy JT (1971) The effect of potassium-sparing diuretics on ion transport across the excised toad bladder. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 176: 580–594
Gettes LS (1976) Possible role of ionic changes in the appearance of arrhythmias. Pharmacol Ther [B] 2: 787–810
Helgeland A (1980) Treatment of mild hypertension: A five year controlled drug trial. Am J Med 69: 725–732
Hänze S, Seyberth H (1967) Untersuchungen zur Wirkung der Diuretika Furosemid, Etakrynsäure und Triamteren auf die renale Magnesium- und Calciumausscheidung. Klin Wochenschr 45: 313–314
Morgan DB, Davidson C (1980) Hypokalemia and diuretics: An analysis of publications. Br Med J 280: 905–908
Multiple Risk Factor Intervention Trial Research Group (1982) Multiple risk factor intervention trial. Risk factor changes and mortality results. Am Med Assoc 248: 1465–1477
Reyes AJ, Leary WP (1982) Urinary volume and solute flows after a single dose of hydrochlorothiazide-triamterene in healthy adults. Curr Ther Res 32: 439–444
Swales JD (1982) Magnesium deficiency and diuretics. Br Med J 285: 1377–1378
Whang R, Welt L (1963) Observations in experimental magnesium depletion. J Clin Invest 42: 305–313
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Widmann, L., Dyckner, T. & Wester, PO. Effects of triameterene on serum and skeletal muscle electrolytes in diuretic-treated patients. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 33, 577–579 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00542490
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00542490