Summary
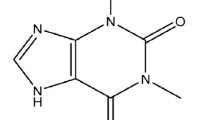
The effects of single oral doses of ketoconazole 400 mg and terbinafine 500 mg on the hepatic microsomal system have been investigated in 8 healthy male volunteers. Microsomal activity caffeine was assessed by following the metabolism of 3 mg/kg bodyweight i.v. administered 1 h after the drug.
The inhibitory effect of terbinafine was more pronounced than that of ketoconazole: clearance was decreased from 1.34 ml·kg−1·min−1 in controls to 1.06 and 1.21 ml·kg−1·min−1, respectively, and the corresponding half-life was increased from 5.8 h in controls to 7.6 and 6.7 h, respectively. The apparent volume of distribution remained unchanged. The serum levels of the antimycotics were within the therapeutic range in each subject.
Although all three substances are metabolised by microsomes, the kinetic parameters (Cmax, half-life, elimination constant) of the antimycotics were poorly if at all correlated with the elimination of caffeine.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnaud MJ, Welsch C (1981) Theophylline and caffeine metabolism in man. In: Rietbrook N, Woodcock BG, Staib AH (eds) Theophylline and other methylxanthines. Vieweg und Sohn Braunschweig Wiesbaden, pp 135–148
Battig FA, Nefzger M, Schulz G (1987) Major biotransformation routes of some allylamine antimycotics. In: Fromtling RA (ed) Recent trends in the discovery, development and evaluation of antifungal agents. JR Prous Science Publishers, Barcelona, pp 479–495
Baxter JG, Brass C, Schentag J, Slaughter RL (1986) Pharmacokinetics of ketoconazole administered intravenously to dogs and orally as tablet and solution to humans and dogs. J Pharm Sci 75: 443–447
Broughton LJ, Rogers HJ (1981) Decreased systemic clearance of caffeine due to cimetidine. Br J Clin Pharmacol 12: 155–159
Brown MW, Maldonado AL, Meredith CG, Speeg KV (1985) Effect of ketoconazole on hepatic oxidative drug metabolism. Clin Pharmacol Ther 37: 290–297
Campbell ME, Grant GM, Inaba T, Kalow W (1987) Biotransformation of caffeine, paraxanthine, theophylline and theobromine by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-inducible cytochrome(s) P-450 in human liver microsomes. Drug Metab Dispos 15: 237–249
DeCoster R, Caers I, Haelterman C, Debroye M (1985) Effect of a single administration of ketoconazole on total and physiologically free plasma testosteron and 17β-oestradiol levels in healthy male volunteers. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 29: 489–493
Gumbleton M, Brown JE, Hawksworth G, Whiting PH (1985) The possible relationship between hepatic drug metabolism and ketoconazole enhancement of cyclosporine nephrotoxicity. Transplantation 40: 454–455
Hawksworth G, Brown JE, Burke MD, Tan K (1986) Inhibition of antipyrine metabolite formation by ketoconazole in rat and in human hepatic microsomes. Biochem Soc Trans 14: 918–919
Joeres R, Klinker H, Heusler H, Epping J, Richter E (1987) Influence of mexiletine on caffeine elimination. Pharmacol Ther 33: 163–169
Lewis JH, Zimmerman HJ, Benson GD, Ishak KI (1984) Hepatic injury associated with ketoconazole therapy. Gastroenterology 86: 503–513
Lin JH, Chremos AN, Chiou R, Yeh KC, Williams R (1987) Comparative effects of famotidine and cimetidine on the pharmacokinetics of theophylline in normal volunteers. Br J Clin Pharmacol 24: 669–672
Meredith CG, Maldonado AL, Speeg KV (1985) The effect of ketoconazole on hepatic oxidative drug metabolism in the rat in vivo and in vitro. Drug Metab Dispos 13: 156–162
Pascucci VL, Bennett J, Narang PK, Chatterji DC (1983) Quantification of ketoconazole in biological fluids using high-performance liquid chromatography. J Pharm Sci 72: 1467–1469
Petranyi G, Ryder NS, Stütz A (1984) Allylamine derivatives: New class of synthetic antifungal agents inhibiting fungal squalene epoxidase. Science 224: 1239–1241
Ryder NS (1984) Selective inhibition of squalene epoxidation by allylamine antimycotic agents. Micr Cell Wall Syn Autolysis 7: 313–321
Schatz F, Haberl H (1989) Arzneimittelforsch/Drug Res (in press)
Schatz F, Millendorfer A, Czok R (1987) Pharmacokinetics of orally applied terbinafine in man. In: Berkarda B (ed) Proc. 15th Int. Congr. Chemotherapy, vol 1. Kümmerle, Munich Tokyo Shanghai, pp 417–419
Schürmeyer Th, Nieschlag E (1984) Effect of ketoconazole and other imidazole fungizides on testosterone biosynthesis. Acta Endocrinol 105: 275–280
Schuster I (1985) The interaction of representative members from two classes of antimycotics — the azoles and the allylamines — with cytochromes P-450 in steroidogenic tissues and liver. Xenobiotica 15: 529–546
Staib AH, Harder S, Mieke S, Beer C, Stille W (1987) Gyraseinhibitors impair caffeine elimination in man. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol 9: 193–198
van Tyle JH (1984) Ketoconazole. Pharmacotherapy 4: 343–373
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wahlländer, A., Paumgartner, G. Effect of ketoconazole and terbinafine on the pharmacokinetics of caffeine in healthy volunteers. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 37, 279–283 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00679784
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00679784