Summary
Following a cross-over design propranolol 20 mg p.o. was given to 7 healthy subjects at 09.00 h and 21.00 h at an interval of 1 week. Heart rate (HR) during submaximal ergometer exercise was measured at four intervals during 10 h after treatment. Plasma propranolol concentrations were also determined.
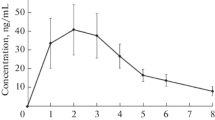
The suppressive effect (%R) of propranolol on the rise in HR during exercise after the morning dosage was significantly greater at 1.5 h and tended to be greater 3 h after administration than at comparable times in the evening trial. Mean plasma propranolol concentrations during the early phase were higher after the morning than the evening dose. The maximum plasma concentration (Cmax), area under the plasma concentration-time curve from 0 to 10 h (AUC (0–10)) and absorption rate constant (ka) were significantly greater after the morning dose. The time to maximum concentration (tmax) and elimination half-life (t1/2) of the morning and evening dosages did not differ. A significant correlation was observed between plasma propranolol concentration and %R in HR during exercise in the morning (r=0.74) and evening (r=0.63) trials, and the regression lines of the morning and evening treatments did not differ.
The data indicate that the suppressive effect of propranolol on exercise-induced tachycardia was relatively greater after a morning than an evening dose; that propranolol was more rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract after the morning than the evening dosage; that diurnal changes in the activity of propranolol depend in part on the time of administration and its subsequent effect on plasma concentrations of the drug; and that the antagonist activity of propranolol relative to a given drug concentration may not differ between morning and evening treatments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fujimura A, Ebihara A (1986) Chronopharmacological study of furosemide in rats. Life Sci 38: 1215–1220
Fujimura A, Ebihara A (1988) Chronopharmacological study of furosemide in rats: (II) influence of β-adrenoceptor blockade. Life Sci 42: 1431–1437
Tateishi T, Fujimura A, Miura T, Ebihara A (1987) Chronopharmacological study of furosemide in human subjects. Jpn J Clin Pharmacol Ther 18: 379–385
Simpson HW (1979) Hydrochlorothiazide diuresis in healthy man: Review of the circadian mediation. Nephron 23: 98–105
Lemmer B, Bathe K, Charrie A, Neuwann G, Schulz D, Winkler H (1982) On the chronopharmacology of beta-adrenoceptor blocking drugs. In: Takahashi R, Halberg F, Walker CA (ed) Toward chronopharmacology. Pergamon Press, London, pp 183–190
Fujimura A, Kumagai Y, Kajiyama H, Ebihara A (1986) Circadian variations in the acute toxicity of adrenoceptor blocking agents in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol 59: 432–433
Fujimura A, Ebihara A (1987) Chronotoxicity of β-adrenoceptor blocking agent in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 14: 805–807
Smolensky M, Jovonovich JA, Kyle GM, Hsi B (1979) Chronotoxicity in rodents challenged with propranolol HCl. In: Reinberg A, Halberg F (ed) Chronopharmacology. Pergamon Press, London, pp 263–271
Hrushesky WJM, Borch R, Levi F (1982) Circadian time dependence of cisplatin urinary kinetics. Clin Pharmacol Ther 32: 330–339
Levi F, Louarn CL, Reinberg A (1985) Timing optimizes sustained-release indomethacin treatment of osteoarthritis. Clin Pharmacol Ther 37: 77–84
Regazzi MB, Rondanelli R, Vida E, Farinelli F, Upton RA (1987) A theophylline dosage regimen which reduces round-the-clock variations in plasma concentrations resulting from diurnal pharmacokinetic variation. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 33: 243–247
Langner B, Lemmer B (1988) Circadian changes in the pharmacokinetics and cardiovascular effects of oral propranolol in healthy subjects. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 33: 619–624
Markiewicz A, Semenowicz K, Korczynska J, Boldys H (1980) Temporal variations in the response of ventilatory and circulatory functions to propranolol in healthy man. In: Smolensky MH, Reinberg A, McGorern JP (ed) Recent advances in the chronobiology of allergy and immunology. Pergamon Press, Oxford, pp 185–193
Semenowicz-Siuda K, Markiewicz A, Korczyńska-Wardecka J (1984) Circadian bioavailability and some effects of propranolol in healthy subjects and in liver cirrhosis. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther Toxicol 22: 653–658
Kawashima K, Levy A, Spector S (1976) Stereospecific radioimmunoassay for propranolol isomers. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 196: 517–523
Carruthers SG, Pacha WL, Aellig WH (1985) Contrasts between pindolol and propranolol concentration-response relationships. Br J Clin Pharmacol 20: 417–420
Reinberg A, Smolensky MH (1982) Circadian changes of drug disposition in man. Clin Pharmacokinet 7: 401–420
Fagard R, Amery A, Reybrouck T, Lijnen P, Billiet L (1979) Response of the systemic and pulmonary circulation to alpha- and beta-receptor blockade (labetalol) at rest and during exercise in hypertensive patients. Circulation 60: 1214–1219
Ohashi K, Ebihara A, Kondo K, Usami M (1984) Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacological actions of a long-acting formulation of propranolol. Arzneim-Forsch/Drug Res 34: 507–517
Jack DB, Quarterman CP, Zaman R, Kendall MJ (1982) Variability of beta-blocker pharmacokinetics in young volunteers. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 23: 37–42
Nakano S, Hollister LE (1983) Chronopharmacology of amitriptyline. Clin Pharmacol Ther 33: 453–459
Watanabe H, Nakano S, Nagai K, Ogawa N (1984) Time-dependent absorption of theophylline in man. J Clin Pharmacol 24: 509–514
Prichard PJ, Yeomans ND, Mihaly GW, Jones DB, Buckle PJ, Smallwood RA, Louis WJ (1985) Omeprazole: A study of its inhibition of gastric pH and oral pharmacokinetics after morning or evening dosage. Gastroenterology 88: 64–69
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fujimura, A., Kumagai, Y., Sugimoto, K. et al. Circadian influence on effect of propranolol on exercise-induced tachycardia in healthy subjects. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 38, 133–137 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00265971
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00265971