Summary
Seven patients undergoing routine thrice weekly haemodialysis for endstage renal failure participated in 12 investigations of dichloroacetate (DCA) pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. DCA doses were 50 mg/kg by i. v. infusion over 30 min. In each investigation single doses were administered to each subject on two consecutive days, one being a day during which the patient was dialyzed. The timing of drug administration, relative to dialysis, was varied to assess the effect of dialysis on the apparent volume of distribution and elimination rate constants of DCA and on its effect on blood glucose and lactate.
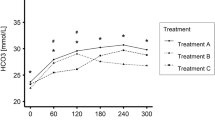
Dialysis increased the clearance of DCA by approximately 60%, but had no effect on its apparent volume of distribution. Dialysis did not reduce the maximal lactate-lowering effect of DCA, but slightly decreased the duration of this effect. Blood glucose levels were not significantly altered by DCA and no adverse drug effects were observed.
We conclude that dialysis increases plasma clearance of DCA, but has little influence on the metabolic effects of the drug when given at 50 mg/kg doses. DCA can safely and effectively be given to hemodialysis patients who may require the drug for treatment of lactic acidosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stacpoole PW (1989) The pharmacology of dichloroacetate. Metabolism 38: 1124–1144
Stacpoole PW, Harman EM, Curry SH, Baumgartner TG, Misbin RI (1983) Treatment of lactic acidosis with dichloroacetate. N Engl J Med 309: 390–396
Stacpoole PW, Lorenz A, Thomas RG, Harman EM (1988) Dichloroacetate in the treatment of lactic acidosis. Ann Intern Med 100: 58–63
DCA-Lactic Acidosis Collaborative Study Group (1987) The design of a randomized, multicenter study of sodium dichloroacetate (DCA) as a treatment for lactic acidosis. Controll Clin Trials 8: 291–292
Curry SH, Chu PI, Baumgartner TG, Stacpoole PW (1985) Plasma concentrations and metabolic effects of intravenous sodium dichloroacetate. Clin Pharmacol Ther 37: 89–93
Wells PG, Moore GW, Rabin D, Wilkinson GR, Oates JA, Stacpoole PW (1980) Metabolic effects and pharmacokinetics of intravenously administered dichloroacetate in humans. Diabetologia 19: 109–113
Lukas G, Vyas KH, Brindle SD, LeSher AR, Wagner WE Jr (1980) Biological disposition of sodium dichloroacetate in animals and humans after intravenous administration. J Pharm Sci 69: 419–421
Stansbie D (1976) Regulation of the human pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Clin Sci Mol Med 54: 445–452
Whitehouse S, Cooper RH, Randle PJ (1974) Mechanism of activation of pyruvate dehydrogenase by dichloroacetate and other halogenated carboxylic acids. Biochem J 141: 761–774
Evans OB (1982) Dichloroacetate tissue concentrations and its relationship to hypolactatemia and pyruvate. Biochem Pharmacol 31: 3124–3126
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Curry, S.H., Lorenz, A., Henderson, G.N. et al. Haemodialysis studies with dichloroacetate. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 40, 613–617 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00279980
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00279980