Abstract
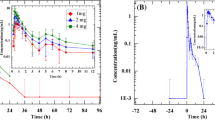
The pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of enalapril, an angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor, are reported to vary with the time of administration. The present study was undertaken to examine whether the effect of enalapril on plasma bradykinin (BK), substance P and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), which are likely to be involved in the mechanism of enalaprilinduced cough, might also be affected by its time of administration. Enalapril 5 mg or placebo was given orally at 10:00 h (day trial) or 22:00 h (night trial) to 12 patients with essential hypertension. Serum concentrations of total drug (enalapril + enalaprilat, its active metabolite) during the day and night trials did not differ significantly at any time. However, serum enalaprilat tended to be higher and its maximum concentration greater in the day trial than in the night trial. Blood pressure 24 h after administration of enalapril was reduced at 22:00 h, but not at 10:00 h. Plasma BK tended to increase following enalapril administration at 10:00 h, but not at 22:00 h. Remarkable increases in plasma BK were observed in two patients in the day trial and one of them also complained of cough. However, no such increase in plasma BK or subsequent adverse effect were recorded in the night trial. Plasma substance P and PGE2 did not change significantly following enalapril administration either in the day or night trial. The results suggest that the response of BK to enalapril is affected by the time of administration. In patients who complain of cough during treatment with enalapril during the daytime, this adverse effect might be dminished or eliminated by a switch to night-time administration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Todd PA, Goa KL (1992) Enalapril. A reappraisal of its pharmacology and therapeutic use in hypertension. Drugs 43:346–381
Morice AH, Brown MJ, Higenbottam T (1989) Cough associated with angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 13 [Suppl 3]:S59-S62
Lemmer B (1989) Chronopharmacology. Cellular Clocks Series vol 3. Dekker, New York
Weissen K, Schloos J, Lehmann K, Dusing R, Vetter H, Mutschler E (1991) Pharmacokinetics and converting enzyme inhibition after morning and evening administration of oral enalapril to healthy subjects. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 40:95–99
Witte K, Weisser K, Neubeck M, Mutschler E, Lehmann K, Hopf R, Lemmer B (1993) Cardiovascular effects, pharmacokinetics, and converting enzyme inhibition of enalapril after morning versus evening administration. Clin Pharmacol Ther 54:177–186
Ishizaki T, Baba T, Murabayashi S, Kubota K, Hara K, Kurimoto F (1988) Effect of cimetidine on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of enalapril in normal volunteers. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 12:512–519
Ikeda I, Iinuma K, Takai M (1982) Measurement of plasma renin activity by a simple solid phase radioimmunoassay. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 54:423–428
Ando T, Shimamoto K, Nakahashi Y, Nishitani T, Hosoda S, Ishida H, Tanaka S, Iimura O (1982) Blood kinin measurement by sensitive kinin radioimmunoassay and its clinical application. In: Fritz H, Dietz G, Fiedler F, Haberland GL (eds) Recent progress on kinins. Birkhäuser, Basel, pp 222–226
Yanaihara C, Sato H, Hirohashi M, Sakagami M, Yamamoto K, Hashimoto T, Yanaihara N, Abe K, Kaneko T (1976) Substance P radioimmunoassay using Nα-tyrosyl-substance P and demonstration of the presence of substance P-like immunoreactivities in human blood and porcine tissue extracts. Endocrinol Japon 23:457–463
Powell WS (1980) Rapid extraction of oxygenated metabolites of arachidonic acid from biological samples using octadecylsilyl silica. Prostaglandins 20:947–957
Bruguerolle B (1989) Temporal aspect of drug absorption and drug distribution. In: Lemmer B (ed) Chronopharmacology. Dekker, New York, pp 3–13
Fujimura A, Kajiyama H, Kumagai Y, Nakashima H, Sugimoto K, Ebihara A (1989) Chronopharmacokinetic studies of pranoprofen and procainamide. J Clin Pharmacol 29:786–790
Shiga T, Fujimura A, Tateishi T, Ohashi K, Ebihara A (1993) Difference of chronopharmacokinetic profiles between propranolol and atenolol in hypertensive subjects. J Clin Pharmacol 33:756–761
Dollery C (1991) Enalapril maleate. In: ⊠ (ed) Therapeutic drugs. Livingstone, Edinburgh, pp E9-E12
Belanger PM, Labrecque G (1989) Temporal aspect of drug metabolism. In: Lemmer B. (ed) Chronopharmacology. Dekker, New York, pp 15–34
Palatini P, Racioppa A, Raule G, Zaninotto M, Penzo M, Pessina AC (1992) Effect of timing of administration on the plasma ACE inhibitory activity and the antihypertensive effect of quinapril. Clin Pharmacol Ther 52:378–383
Puolijoki H, Nieminen MM, Moilanen E, Nurmi AK, Vappatalo H, Siitonen L, Lahdensuo A (1992) Bradykinin: a putative mediator of enalapril-induced cough. Curr Ther Res 51:844–847
Campbell DJ, Kladis A, Duncan A (1994) Effects of converting enzyme inhibitors on angiotensin and bradykinin peptides. Hypertension 23:439–449
Kaufman MP, Coleridge HM, Coleridge JCG (1980) Bradykinin stimulates afferent C fibers in the intrapulmonary airways of dogs. J Appl Physiol 48:511–517
Veglio F, Pietrandrea R, Ossola M, Vignami A, Angeli A (1987) Circadian rhythm of the angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) activity in serum of healthy adult subjects. Chronobiologia 14:21–25
Stocker M, Hornung J (1978) Application of bradykinin radio-immunoassay for the measurement of urinary kallikrein activity in rats. Klin Wochenschr 56 [Suppl 1]:127–129
Skidgel RA (1992) Bradykinin-degrading enzymes: structure, function, distribution, and potential roles in cardiovascular pharmacology. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 20 [Suppl 9]:S4-S9
Thysell H, Andersson KE, Anderson SI, Ekman R (1988) Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition, cough and the serum concentration of substance P. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 34:649–650
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sunaga, K., Fujimura, A., Shiga, T. et al. Chronopharmacology of enalapril in hypertensive patients. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 48, 441–445 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00194332
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00194332