Abstract
Objective: This study was performed to assess whether a new formulation of felodipine extended release (FER) tablets with a 9 mm diameter is similar to the presently used 11 mm diameter FER formulation with respect to antihypertensive effect and tolerability in patients with essential hypertension. A randomised, double-blind, placebo controlled, three-way cross-over study design was used.
Patients: Twenty-four patients with a supine diastolic blood pressure (DBP) of 95–115 mmHg after a 4-week placebo run-in period were given FER 5 mg 9 mm tablets, FER 5 mg 11 mm tablets and placebo in randomised order. The tablets were given once daily and each double-blind treatment period lasted for two weeks.
Methods: Twenty-four hour ambulatory blood pressure monitoring was performed at the end of each treatment period. The primary effect variable was mean DBP over 24 hours. Nineteen patients had 24-hour blood pressure data valid for analysis using an analysis of variance with patient, treatment, period and carry-over as factors.
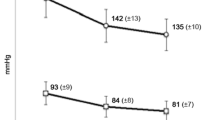
Results: Both formulations of FER 5 mg tablets significantly reduced the mean 24-hour DBP compared to placebo. The 9 and 11 mm tablets resulted in, on average, 4.7 and 3.4 mmHg lower mean 24-hour DBP than placebo. There was, however, no significant difference between the two different FER formulations. Both FER formulations were well tolerated and similar to placebo in this respect.
Conclusion: Both FER 5 mg tablet formulations (9 and 11 mm diameter), given once daily, were clinically equivalent with respect to antihypertensive effect and tolerability in patients with mild to moderate essential hypertension.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ljung B (1985) Vascular selectivity of felodipine. Drugs 29 [Suppl 2]:46–58
Todd PA, Faulds D (1992) Felodipine. A review of the pharmacology and therapeutic use of the extended release formulation in cardiovascular disorders. Drugs 44:251–277
Elvelin L, Kennerfalk A, Elmfeldt D (1993) Tolerability and safety of felodipine. Cardiovasc Drug Rev 11:126–147
Weber MA, Goldberg Al, Faison EP, Lipschutz K, Shapiro DA, Nelson EB, Irvin JD (1994) Extended-release felodipine in patients with mild to moderate hypertension. Clin Pharmacol Ther 55:346–352
Bergstrand R (1990) A bioequivalence study of two reduced size felodipine ER tablet formulations. Data on file, Astra Haessle Report
Ahnoff M (1984) Determination of felodipine in plasma by capillary gas chromatography with electron-capture detection. J Pharmacol Biomed Anal 2:519–526
Blychert E, Wingstrand K, Edgar B, Lidman K (1990) Plasma concentration profiles and antihypertensive effect of conventional and extended-release felodipine tablets. Br J Clin Pharmacol 29:39–45
Blychert E (1992) Felodipine pharmacokinetics and plasma concentration vs effect relationships. Blood pressure 1 [Suppl 2]:1–30
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McGrath, B.P., Watts, R.W. & Elmfeldt, D.B. Clinical equivalence of two tablet formulations of felodipine. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 49, 169–172 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00192375
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00192375