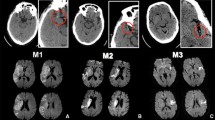
Summary
Information obtained from CT scan after contrast administration was evaluated in 59 consecutive stroke patients. CT scans before and after contrast administration were performed 3 days and 21/2 weeks after stroke. A plain CT scan was repeated 6 months later. Contrast enhancement was practically not seen on the first examination, but was seen in 46% on the second examination. There was a close relationship between the occurrence of contrast enhancement and the socalled “fogging effect”. Contrast scanning gave additional information only when this effect was present. Plain CT scans 3 days after stroke were superior to contrast scans taken at any time for detecting and visualizing cerebral infarcts.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Becker H, Desch H, Hacker H, Pencz A (1979) CT fogging effect with ischemic cerebral infarcts. Neuroradiology 18: 185–192
Brahme FJ (1978) CT diagnosis of cerebrovascular disorders — a review. Comput Tomogr 2: 173–181
Caillé JM, Guibert F, Bidabe AM, Billerey J, Piton J (1980) Enhancement of cerebral infarcts with CT. Comput Tomogr 4: 73–77
Cambell JK, Houser OW, Stewens JC, Wahner HW, Baker HL, Folger WN (1978) Computed tomography and radionuclide imaging in the evaluation of ischemic stroke. Radiology 126: 695–702
Constant P, Renou AM, Caillé JM, Vernhiet J (1977) CAT studies of cerebral ischemia. In: du Boulay GH, Moseley IF (eds) The first European seminar on computerized asial tomography in clinical practise. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 227–236
Constant P, Renou AM, Caillé JM, Vernhiet J, Dop A (1977) Cerebral ischemia with CT. Comput Tomogr 1: 235–248
Davis KR, Ackerman RH, Kistler JP, Mohr JP (1977) Computed tomography of cerebral infarction. Hemorhagic contrast enhancement and time of appearance. Comput Tomogr 1: 71–86
Drayer PD, Dujovny M, Boehnke M, Wolfson SK, Barrionuevo PJ, Cook EE, Rosenbaum AE (1977) The capacity for computed tomography diagnosis of cerebral infarction. Radiology 125: 393–402
Harrison MJG (1977) The use of CAT in cerebral infarction. In: du Boulay GH, Moseley IF (eds) The first European seminar on computerized axial tomography in clinical practise. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 221–226
Kendall BE, Pullicino P (1980) Intravascular contrast injection of ischemic lesions. II. Effect on prognosis. Neuroradiology 19: 241–243
Kinkel WR, Jacobs L, Kinkel PR (1980) Gray matter enhancement. A computerized tomographic sign of cerebral hypoxia. Neurology 30: 810–819
Lee KF, Chambers RA, Diamond C, Park CH, Thompson NL, Schnapf D, Pripstein S (1978) Evaluation of cerebral infarction by computed tomography with special emphasis on microinfarction. Neuroradiology 16: 156–158
Norton GA, Kishore RS, Lin J (1978) CT contrast enhancement in cerebral infarction. AJR 131: 881–885
Palmers Y, Staelens B, Baert AL, Termote L (1978) Cerebral ischemia. In: Baert A, Jeanmart L, Wackenheim A (eds) Clinical computer tomography head and trunk. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 113–127
Pullicino P, Kendall BE (1980) Contrast enhancement in ischemic lesions. Neuroradiology 19: 235–239
Skriver EB, Olsen TS (1981) Transient disappearance of cerebral infarcts on CT scan, the socalled fogging effect. Neuroradiology 22: 61–65
Wing SD, Norman D, Pollock JA, Newton TH (1976) Contrast enhancement of cerebral infarcts in computed tomography. Radiology 121: 89–92
Yock DH, Marshall WH (1975) Recent ischemic brain infarcts at computed tomography: appearances pre- and postcontrast infusion. Radiology 117: 599–608
Yock D, Norman D, Newton TH (1978) Pitfalls in the diagnosis of ischemic cerebral infarcts by computed tomography. In: Bories J (ed) The diagnostic limitations of computerized axial tomography. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 90–104
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Skriver, E.B., Olsen, T.S. Contrast enhancement of cerebral infarcts. Incidence and clinical value in different states of cerebral infarction. Neuroradiology 23, 259–265 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00339392
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00339392