Summary
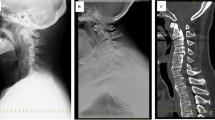
In this study, the authors evaluate the importance of computed tomography (CT) in 15 patients who underwent surgical treatment for cervical disc disease. In nine operated on by an anterior approach, all CT examinations were interpreted as positive for disc herniation and correlated precisely with surgical observations. CT demonstrated protrusion of the disc, centrally in four and posterolaterally in five in all of whom disc material was found posterior to the vertebral body. Of six who underwent laminectomy, either thickening or calcification of the ligamentum flavum was demonstrated by CT and confirmed at surgery in five. Vacuum phenomenon in the intervertebral space and hypertrophy of the intervertebral joint were not infrequently associated. CT can exactly delineate cervical disc lesions and associated pathological changes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Crandall PH, Batzdorf U (1966) Cervical spondylotic myelopathy. J Neurosurg 25: 57–66
Shapiro R (1975) Myelography. Year Book Medical Publishers, Chicago, pp 348–462
Baker RA, Hilman BJ, McLennan JE, Strand RD, Kaufman SM (1978) Sequelae of metrizamide myelography in 200 examinations. AJR 130: 499–502
Skalpe IO (1977) Adverse effects of water-soluble contrast media in myelography, cisternography and ventriculography. Acta Radiol (Suppl) 355: 359–370
Carella A, Federico F, DiCuonzo F, Vinjau E, Lamberti P (1982) Adverse side effects of metrizamide and Iopamidolo in myelography. Neuroradiology 22: 247–249
Haughton VM, Syvertsen A, Williams AL (1980) Soft tissue anatomy within the spinal canal as seen on computed tomography. Radiology 134: 649–655
Ethier R, King DG, Melancon D, Bélanger G, Thompson C (1980) Diagnosis of intra- and extramedullary lesions by CT without contrast achieved through modifications applied to the EMI CT 5005 body scanner. In: Post MJD (ed) Radiographic evaluation of the spine. Masson, New York, pp 377–393
Williams AL, Haughtom VM, Syvertsen A (1980) Computed tomography in the diagnosis of herniated nucleus pulposus. Radiology 135: 95–99
Carrera GF, Williams AL, Haughton VM (1980) Computed tomography in scietica. Radiology 137: 433–437
Glenn WV Jr, Rhodes ML, Altschuler EM (1980) Multi-planer computerized tomography of lumbar disc abnormalities: the proponent's viewpoint. In: Post MJD (ed) Radiographic evaluation of the spine. Masson, New York, pp 108–138
Coin CG, Coin JT (1981) Computed tomography of cervical disk disease: technical considerations with representative case reports. J Comput Assist Tomogr 5: 275–280
Beamer YB, Garner JT, Shelden CH (1973) Hypertrophied ligamentum flavum. Clinical and surgical significance. Arch Surg 106: 289–292
Penning L, v.d. Zwag P (1966) Biomechanical aspects of spondylotic myelopathy. Acta Radiol 5: 1090–1103
Resnick D, Niwayama G, Guerra J Jr, Vint V, Usselman J (1981) Spinal vacuum phenomena: anatomical study and review. Radiology 139: 345–348
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miyasaka, K., Isu, T., Iwasaki, Y. et al. High resolution computed tomography in the diagnosis of cervical disc disease. Neuroradiology 24, 253–257 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00333176
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00333176