Abstract
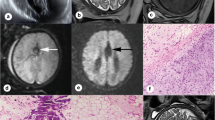
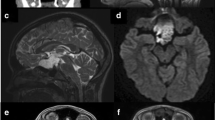
We report a man with a ruptured intracranial dermoid cyst, suffering from headache, nausea, vomiting and a generalised seizure. MRI was performed before and 2 weeks after surgical resection. On T1-weighted images the tumour gave high signal, as did fatty material in the frontal and parietal brain sulci. Identification of this hyperintense material as lipids was possible by chemical-shift-selective 3 D gradient-echo imaging, which provided excellent contrast between the subarachnoid lipids and the adjacent normal brain, with a good spatial resolution. Possible complications of subarachnoid and intraventricular lipid particles after dermoid cyst rupture are discussed and the diagnostic value of 3 D chemical-shift-selective additional to conventional T1-weighted spin-echo images in identification of even small amounts of fat is emphasised.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramson RC, Morawetz RB, Schlitt M (1989) Multiple complications from an intracranial epidermoid cyst: case report and literature review. Neurosurgery 24:574–578
Miller NR, Epstein MH (1975) Giant intracranial dermoid cyst: case report and review of the literature on intracranial dermoids and epidermoids. Can J Neurol Sci 2:127–134
Davidson HD, Ouchi T, Steiner RE (1985) NMR imaging of congenital intracranial germinal layer neoplasms. Neuroradiology 27:301–303
Hahn FJ, Ong E, McComb RD, Mawk JR, Leibrock LG (1986) MR imaging of ruptured intracranial dermoid. J Comput Assist Tomogr 10:888–892
Netzky MG (1988) Epidermoid tumors. Review of the literature. Surg Neurol 29:477–483
Lunardi P, Missori P, Rizzo A, Gagliardi FM (1989) Chemical meningitis in a ruptured intracranial dermoid. Case report and review of the literature. Surg Neurol 32:449–452
Maravilla KR (1977) Intraventricular fat-fluid level secondary to rupture of an intracranial dermoid cyst. AJR 128: 500–501
Mikhael MA (1982) Transient spasm of carotid siphon complicating ruptured dermoid cyst. Radiology 144:824
Cornell SH, Graf CJ, Dolan KD (1977) Fat-fluid level in intracranial epidermoid cyst. AJR 128:502–503
Schwartz JF, Balentine JD (1978) Recurrent meningitis due to an intracranial epidermoid. Neurology 28:124–129
Wilms G, Casselman J, Demaerel P, Plets C, De Haene I, Baert AL (1991) CT and MRI of ruptured intracranial dermoids. Neuroradiology 33:149–151
Smith AS, Benson JE, Blaser SI, Mizushima A, Tarr RW, Bellon EM (1991) Diagnosis of ruptured intracranial dermoid cyst: value of MR over CT. AJNR 12:175–180
Klose U, Grodd W, Kölbel G (1989) Selective chemical imaging with a three-dimensional gradient echo sequence. J Comput Assist Tomogr 13: 724–729
Yasargil MG, Abernathey CD, Sarioglu AC (1989) Microneurosurgical treatment of intracranial epidermoid and dermoid tumors. Neurosurgery 24:561–567
Zülch KJ (1986) Brain tumors: their biology and pathology. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 433–437
Phillips WE, Martinez CR, Cahill DW (1994) Ruptured intracranial dermoid tumor secondary to closed head trauma. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. J Neuroimag 4: 169–170
Larsson EM, Brandt L, Holtas S (1987) Persisting intraventricular fat-fluid levels following surgery on a ruptured dermoid cyst of the posterior fossa. Acta Radiol 28:489–490
Bydder GM, Young IR (1985) MR imaging: clinical use of the inversion recovery sequence. J Comput Assist Tomogr 9:659–675
Schick F, Bongers H, Jung WI, Skaleij M, Lutz O (1991) Localized Larmor frequency-guided fat and water proton MRI of the spine: a method to emphasize pathological findings. Magn Reson Imaging 9:509–515
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nägele, T., Klose, U., Grodd, W. et al. Three-dimensional chemical shift-selective MRI of a ruptured intracranial dermoid cyst. Neuroradiology 38, 572–574 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00626102
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00626102