Abstract
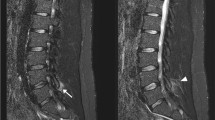
Our purpose was to determine if specific MRI findings in spinal epidural abscess (SEA), at the time of diagnosis, are associated with the clinical outcome. The clinical records and MRI studies of 18 patients with SEA were reviewed and follow-up was obtained from the outpatient medical record, telephone interview, or both. The association between findings on contrast-enhanced MRI and clinical outcome (weakness, neck or back pain, and incomplete functional recovery) was evaluated. With univariate analysis, narrowing of 50 % or more of the central spinal canal (P = 0.03), peripheral contrast-enhancement (P = 0.05), and abnormal spinal cord signal intensity (P = 0.05) were associated with weakness at follow-up. Persistent neck or back pain was associated with spinal canal narrowing (P = 0.02), peripheral contrast-enhancement (P = 0.02), and an abscess longer than 3 cm (P = 0.04) on MRI. Incomplete clinical recovery was associated with both abscess length (P = 0.01) and the severity of canal narrowing (P = 0.01). Abscess length, enhancement pattern, and severity of canal narrowing can be incorporated in a grading system that can be used to predict outcome.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 9 September 1998 Accepted: 6 March 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tung, G., Yim, J., Mermel, L. et al. Spinal epidural abscess: correlation between MRI findings and outcome. Neuroradiology 41, 904–909 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002340050865
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002340050865