Abstract
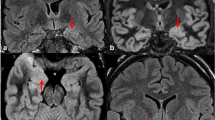
We reviewed the preoperative images of 28 patients with pathologically proven mesial temporal sclerosis, to assess thalamic asymmetry and signal change. A further 25 nonsurgical patients with temporal lobe epilepsy and unequivocal, unilateral changes of mesial temporal sclerosis, and 20 controls, were also reviewed. None of the control group had unequivocal asymmetry of the thalamus. There was an ipsilateral asymmetrically small thalamus in five (18 %) of the surgical group and in three (12 %) of the nonsurgical patients. In four cases there was thalamic signal change. In three patients with thalamic volume loss there was ipsilateral hemiatrophy. All patients with an asymmetrically small thalamus had an asymmetrically small fornix and all but one a small ipsilateral mamillary body.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received 18 October 1998/Accepted: 6 November 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deasy, N., Jarosz, J., Elwes, R. et al. Thalamic changes with mesial temporal sclerosis: MRI. Neuroradiology 42, 346–351 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002340050896
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002340050896