Abstract
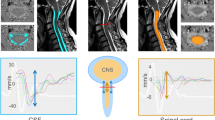
We present MRI findings in three patients with acute spontaneous subdural haematomas of the spine. Acute haematomas (1–3 days) were isointense or gave slightly high signal on T1- and heterogeneous signal on T2-weighted images. MRI precisely defined the level and extent of the haematoma preoperatively. The MRI was prospectively correctly interpreted as acute subdural haematomas in all patients. As a specific, noninvasive modality, MRI is the preferred imaging technique in this rare clinical entity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 13 September 1999 Accepted: 17 January 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kirsch, E., Khangure, M., Holthouse, D. et al. Acute spontaneous spinal subdural haematoma: MRI features. Neuroradiology 42, 586–590 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002340000331
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002340000331