Abstract
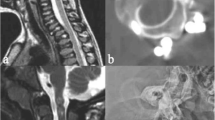
Cranial CT and/or MRI imaging of 8 patients with mucopolysaccharidosis (MPS) was retrospectively evaluated. Two patients had MPS IH, 1 had MPS IS, 1 had MPS IVA and 4 had MPS IV. CT and MRI showed thickening of dura mater at the cranio-cervical junction, causing narrowing of the subarachnoid space, in all the patients examined. Spinal cord compression was detected in 4 patients. Other findings were: white matter alterations, mild to severe hydrocephalus, skull dysplasia and odontoid dysplasia. White matter alterations were evident as large areas and as multiple dispersed spots of prolonged T1 and T2 value. Reduced gray/white matter contrast was demonstrated on T2-weighted MRI images. It is important to examine the cranio-cervical junction carefully for thickening of dura mater in all patients with mucopolysaccharidosis examined by CT or MRI, because of the generally progressive clinical course of MPS. In patients with symptomatic cord compression, surgical intervention should be considered.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
McKusick VA, Neufeld EF, Kelly TE (1983) The mucopolysaccharide storage diseases. In: Stanbury JB, Wyngaarden JB, Frederickson DS, Goldstein JL, Brown MS (eds) The metabolic basis of inherited diseases, 5th edn. McGraw-Hill, New York, p 751
Watts RWE, Spellacy E, Kendall BE, Boulay G du, Gibbs DA (1981) Computed tomography studies on patients with mucopolysaccharidoses. Neuroradiology 21:9
Nelson J, Grebbel FS (1987) The value of computed tomography in patients with mocupolysaccharidosis. Neuroradiology 29:544
Schmidt H, Ulrich K, Lengerke H-J von, Kleine M, Bramswig J (1987) Radiological findings in patients with mucopolysaccharidosis I H/5 (Hurler-Scheie syndrome). Pediatr Radiol 17:409
Yamada H, Ohya M, Higeta T, Kinoshita S (1987) Craniosynostosis and hydrocephalus in I-cell disease (mucolipidosis II). Child Nerv Syst 3:55
Ludwig B, Kishikawa T, Wende S, Rochel M, Gehlher J (1983) Cranial computed tomography in disorders of complex carbohydrate metabolism and related storage diseases. AJNR 4:431
Murata R, Nakajima S, Tanaka A, Miyagi N, Matsuoka O, Kogame S, Inoue Y (1989) MR imaging of the brain in patients with mucopolysaccharidosis. AJNR 10:1165
Rauch RA, Friloux LA III, Lott IT (1989) MR imaging of cavitary lesions in the brain with Hurler/Scheie. AJNR 10:51
Kaufmann HH, Rosenburg HS, Scott CI, Lee YY, Pruessner JL, Butler IJ (1982) Cervical myelopathy due to dural compression in mucopolysaccharidosis. Surg Neurol 17:404
Wald SL, Schmidek HH (1984) Compressive myelopathy associated with type VI mucopolysaccharidosis (Maroteaux-Lamy syndrome). Neurosurgery 14:83
Tamaki N, Kojima N, Tanimoto M, Suyama T, Matsumoto S (1987) Myelopathy due to diffuse thickening of the cervical dura mater in Maroteaux-Lamy syndrome: report of a case. Neurosurgery 21:416
Rampini S, Grauer W, Imhof HG, Gitzelman R (1987) Mucopolysaccharidosis VI A (Maroteaux-Lamy disease, severe form): incipient compressive myelopathy, cerebrospinal fluid fistula and tracheal stenosis in an adult patient. Helv Paediatr Acta 41:515
Brill CB, Rose JS, Godmilow L, Sklower S, Willner J, Hirschhorn K (1978) Spastic quadriparesis due to C1-C2 subluxation in Hurler syndrome. J Pediatr 92:441
Kopits SE (1976) Orthopedic complications of dwarfism. Clin Orthop 114:153
McKusick VA (1972) In: Hereditable disorders of connective tissue, 4th edn. Mosby, St Louis, p. 521
Blaw ME, Langer LO (1969) Spinal cord compression in Morquio-Brailsford disease. J Pediatr 74:593
Pilz H, Figura K von, Goebel HH (1979) Deficiency of arylsulfatase B in 2 brothers aged 40 and 38 years (Maroteaux-Lamy syndrome, type B). Ann Neurol 6:315
Becker LE, Yates AJ (1991) Inherited metabolic diseases. In: Textbook of neuropathology, 2nd edn. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, p 331
Lake BD (1984) Lysosomal enzyme deficiencies. In: Adams JH, Corsellis JAN, Duchen LW (eds) Greenfield's neuropathology, 4th edn. Edward Arnold, London, p 491
Dekaban AS, Constantopoulos G (1977) Mucopolysaccharidosis type I, II, IIIA and V. Pathological and biochemical abnormalities in the neural and mesenchymal elements of the brain. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 39:1
Johnson MA, Desai S, Hughes-Jones K, Starer F (1984) Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain in Hurler syndrome. AJNR 5:816
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taccone, A., Donati, P.T., Marzoli, A. et al. Mucopolysaccharidosis: thickening of dura mater at the craniocervical junction and other CT/MRI findings. Pediatr Radiol 23, 349–352 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02011954
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02011954