Abstract
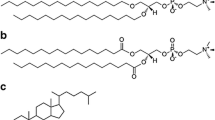
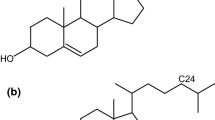
Phospholipid/cholesterol vesicles were solu-bilized by 3-[(3-cholamidopropyl)dimethylammonio]-1-propanesulfonate (CHAPS). Above 30 mol% cholesterol (Ch) in the lipid vesicles several remarkable changes of the solubilization process were observed. (i) Two modes of solubilization: The effective detergent to lipid ratio Rc(M) for the formation of mixed micelles decreased from Rc(M) = 43 ± 3 at low lipid concentrations, [L]≤ 0.15 mm, to Rc(M) = 2.4 ± 0.3 above [L] = 0.5 mm (40 mol% Ch, T = 20 °C). (ii) At subsolubilizing CHAPS concentrations, filamentous and helical microstructures were formed, similar to those which were observed in native and model bile. (iii) The number of observed fibers was about two orders of magnitude higher in the presence of the negatively charged lipids phosphatidylglycerol (PG) and phosphatidic acid (PA) compared to the zwitterionic phosphatidylcholine (PC). Fiber formation began after 16–18 h using PG and PA compared to 3–4 days in the presence of PC. Screening of the charged lipids by NaCl effectively reduced the formation of fibers. Assuming binding of Na+ to the charged lipid aggregates, an intrinsic binding constant Kint = 0.6 M–1 was determined by applying the Gouy-Chapman theory. After the addition of CHAPS to PG/Ch vesicles, a fast initial solubilization of the vesicles (<1 min) to mixed micelles (rh = 2.3 ± 0.2 nm) and small vesicles (rh = 23 ± 1 nm) was observed, followed by an intermediate period of 2 h, after which the formation of fibers occurred (>15 h). The microstructures are visualized by darkfield and electron microscopy. The method of vesicle solubilization is compared to the dilution of concentrated micellar solutions, which is usually applied to model bile systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 28 May 1996 / Accepted: 26 July 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schröder, T., Schürholz, T. Bimodal solubilization of phospholipid-cholesterol vesicles in 3-[(3-cholamidopropyl)dimethylammonio]-1-propanesulfonate (CHAPS) solutions. Formation of filamentous and helical microstructures depends on negatively charged lipids. Eur Biophys J 25, 67–73 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002490050019
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002490050019