Abstract
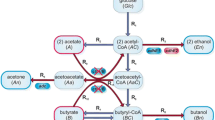
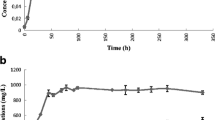
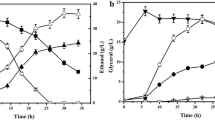
The biochemical mechanisms for growth tolerance to a 100% CO headspace in cultures, and butanol plus ethanol production from CO by Butyribacterium methylotrophicum were assessed in the wild-type and CO-adapted strains. The CO-adapted strain grew on glucose or CO under a 100% CO headspace, whereas, the growth of the wild-type strain was severely inhibited by 100% CO. The CO-adapted strain, unlike the wild-type, also produced butyrate, from either pyruvate or CO. The CO-adapted strain was a metabolic mutant having higher levels of ferredoxin–NAD oxidoreductase activity, which was not inhibited by NADH. Consequently, only the CO-adapted strain can grow on CO because CO oxidation generates reduced ferredoxin which, via the mutated ferredoxin–NAD reductase activity, forms reduced NADH required for catabolism. When the CO-adapted strain was grown at pH 6.0 it produced butanol (0.33 g/l) and ethanol (0.5 g/l) from CO and the cells contained the following NAD-linked enzyme activities (μmol min−1 mg protein−1): butyraldehyde dehydrogenase (227), butanol dehydrogenase (686), acetaldehyde dehydrogenase (82) and ethanol dehydrogenase (129).
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 15 September 1998 / Received revision: 12 February 1999 / Accepted: 19 February 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, GJ., Shieh, JS., Grethlein, A. et al. Biochemical basis for carbon monoxide tolerance and butanol production by Butyribacterium methylotrophicum . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 51, 827–832 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530051469
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530051469