Abstract.
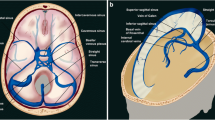
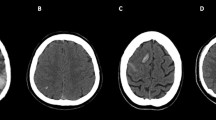
In this paper, the authors present the contribution of CT and MRI to the diagnosis of acute stroke caused by arterial or venous occlusion. The term “early” used in this context means within 6 h of the onset of symptoms. Signs of early ischemic edema are subtle and sometimes difficult to detect by CT or MRI. The purpose of this presentation is to familiarize the clinician and the radiologist with the subtle brain parenchymal changes seen within the first 6 h after onset of symptoms, in order to improve detection of early ischemic infarction and to improve patient care.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received 19 May 1998; Accepted 27 May 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manelfe, C., Cognard, C., Laval, C. et al. Intracranial vascular involvement of brain pathologies and venous occlusions. Eur Radiol 8, 1106–1115 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003300050517
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003300050517