Summary
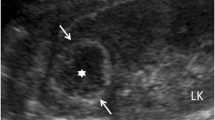
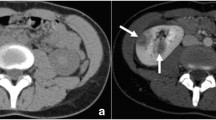
Based on a report of 16 patients, the authors describe and evaluate the sonographic aspects of renal inflammatory diseases (RID) in children. In acute disease, thickening of the renal pelvic wall as evidence of pyelitis was the most common pattern demonstrated. Increased renal volume, nontumoral parenchymal area of hyperechnogenicity, abscess-type mass or calcified solid mass (in the case of xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis) were other aspects encountered. Related findings included evidence of chronic pyelonephritis (cortical thinning) and of renal malformations. In patients with RID, the role of ultrasound is doubly important. While it is being employed increasingly as a screening test, it is most useful as a follow-up technique to detect complications and assess renal growth. Nevertheless, it should be stressed that ultrasound may be totally normal in cases of RID and complementary examinations (IVP, VCUG and nuclear scanning) are still necessary.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Levin R, Burbridge KA, Abramson S, Berdon WE, Hensle TW (1984) The diagnosis and management of renal inflammatory processes in children. Urol 132:718
Piccirillo M, Rigsby CM, Rosenfield AT (1987) Sonography of renal inflammatory disease. Urol Radiol 9:66
Kangarloo H, Gold RH, Fine RN, Diament MJ, Boechat MI (1985) Urinary tract infection in infants and children evaluated by ultrasound. Radiology 154:367
Leonidas JC, McCauley RGK, Klauber GC, Fretzayas AM (1985) Sonography as a substitute for excretory urography in children with urinary tract infection. AJR 144:815
Avni EF, van Gansbeke D, Thoua Y, Matos C, Marconi V, Lemaitre L, Schulman CC (1988) Ultrasonic demonstration of pyelitis and ureteritis in children. Pediatr Radiol (in press)
Poole CA, Ferris AJ, Haukohl RS (1970) Radiolucent folds in the upper urinary tract. Radiology 110:529
Han BK, Babcock DS (1985) Sonographic measurements and appearance of normal kidneys in children. AJR 145:611
Watts FB, Slovis TL, Conway JJ, Traisman ES, Dietrich RB (1987) Update: organ imaging of genitourinary tract. Dialogues in pediatric urology 10:8
Zaontz MR, Pamira JJ, Wolfman M, Gargurevitch AJ, Zeman RK (1985) Acute focal bacterial nephritis: a systematic approach to diagnosis and treatment. J Urol 133:752
Rigsby CM, Rosenfield AT, Glickman GM, Hodson J (1986) Hemorrhagic focal bacterial nephritis: findings on gray-scale sonography and CT. AJR 146:1173
Greenfield SP, Montgomery P (1987) Computerized tomography and acute pyelonephritis in children. Urology 29:137
Van Kirk OC, Go RT, Wedel VJ (1980) Sonographic features of xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis. AJR 134:1035
Kierce F, Carroll R, Guiney EJ (1985) Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis in childhood. Br J Urol 57:261
Blickman JG, Taylor GA, Lebowitz RL (1985) Voiding cystourethrography: the initial radiologic study in children with urinary tract infection. Radiology 156:659
Sotolongo JR, Schiff H, Wulfsohn MA (1982) Radiographic findings in acute segmental pyelonephritis. Urology 19:335
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Avni, E.F., Vandemerckt, C., Braude, P. et al. Sonographic evaluation of renal inflammatory diseases in children. World J Urol 6, 18–21 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00326837
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00326837